|
Gilbert Nicholetts
Air Marshal Sir Gilbert Edward Nicholetts, (9 November 1902 – 7 September 1983) was a senior commander in the Royal Air Force during the 1950s. RAF career Educated at Royal Naval College, Dartmouth, Nicholetts joined the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1921. He developed a career in flying boat units and with the Fleet Air Arm, then under RAF control. In the late 1920s he was based in the Far East, flying the Short Singapore. In 1933 Nicholetts established a long-distance flight record from Cranwell, England to Walvis Bay, South West Africa as navigator on the Fairey Long-range Monoplane, continuing on to Cape Town. He was awarded the Air Force Cross. Nicholetts was appointed Officer Commanding No. 228 Squadron, just after the outbreak of the Second World War. Based at Alexandria, Egypt, flying a Short Sunderland, Nicholetts personally commanded the RAF reconnaissance flight preceding the November 1940 Fleet Air Arm Taranto raid. He went on to be Station Commander at RAF Haifa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Commander Of The Order Of The British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order. Recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire were originally made on the nomination of the United Kingdom, the self-governing Dominions of the Empire (later Commonwealth) and the Viceroy of India. Nominations continue today from Commonwealth countries that participate in recommending British honours. Most Commonwealth countries ceased recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire when they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companions Of The Order Of The Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved bathing (as a symbol of purification) as one of its elements. The knights so created were known as "Knights of the Bath". George I "erected the Knights of the Bath into a regular Military Order". He did not (as is commonly believed) revive the Order of the Bath, since it had never previously existed as an Order, in the sense of a body of knights who were governed by a set of statutes and whose numbers were replenished when vacancies occurred. The Order consists of the Sovereign (currently King Charles III), the Great Master (currently vacant) and three Classes of members: *Knight Grand Cross ( GCB) ''or'' Dame Grand Cross ( GCB) *Knight Commander ( KCB) ''or'' Dame Commander ( DCB) *Companion ( CB) Members belong to either the Civil or the Military Division.''Statutes'' 1925, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983 Deaths
The year 1983 saw both the official beginning of the Internet and the first mobile cellular telephone call. Events January * January 1 – The migration of the ARPANET to TCP/IP is officially completed (this is considered to be the beginning of the true Internet). * January 24 – Twenty-five members of the Red Brigades are sentenced to life imprisonment for the 1978 murder of Italian politician Aldo Moro. * January 25 ** High-ranking Nazi war criminal Klaus Barbie is arrested in Bolivia. ** IRAS is launched from Vandenberg AFB, to conduct the world's first all-sky infrared survey from space. February * February 2 – Giovanni Vigliotto goes on trial on charges of polygamy involving 105 women. * February 3 – Prime Minister of Australia Malcolm Fraser is granted a double dissolution of both houses of parliament, for elections on March 5, 1983. As Fraser is being granted the dissolution, Bill Hayden resigns as leader of the Australian Labor Party, and in the subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1902 Births
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Whitley (RAF Officer)
Air Marshal Sir John Rene Whitley, (7 September 1905 – 26 December 1997) was a senior commander in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War and also in the post-war years. RAF career Whitley joined the Royal Air Force in 1926. While serving in India, he was awarded the Air Force Cross for relief flights after the 1935 Quetta earthquake. He served in the Second World War as Officer Commanding No. 149 Squadron and then as Station Commander at RAF Linton-on-Ouse. In April 1943, he was shot down in a Halifax bomber over Belgium. Landing by parachute in Northern France, with the help of the French Resistance he escaped through the Basque country to Spain. Returning to England, he continued his war service as Station Commander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Dawson (RAF Officer)
Air chief marshal Sir Walter Lloyd Dawson, (6 May 1902 – 10 June 1994) was a senior commander in the Royal Air Force in the 1950s. He was the last RAF commander in Palestine, before the creation of the State of Israel. RAF career Dawson joined the Royal Air Force as a boy mechanic in 1919. He served in the Second World War on the air staff at RAF Middle East and then in the Directorate of Plans at the Air Ministry. He continued his war service as Station Commander at RAF St Eval from 1942, Director of Operations (Naval Co-operation) from 1943 and Director of Plans from 1944. After the war he was made Air Officer Commanding AHQ Levant at a difficult time when the State of Israel was being established. He was appointed Commandant of the School of Land/Air Warfare in 1948 and then served as Senior RAF Instructor at the Imperial Defence College from 1950 before becoming Assistant Chief of the Air Staff (Policy) in 1952. He went on to be Deputy Chief of Staff for Plans & Policy at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inspector-General Of The RAF
The Inspector-General of the RAF was a senior appointment in the Royal Air Force, responsible for the inspection of airfields. The post existed from 1918 to 1920 and from 1935 until the late 1960s. For much of World War II, a second inspector-general post existed. The first creation of the post began on 22 August 1918 as a member of the Air Council. However, in February or March of the following year, the Inspector-General ceased to sit on the Air Council. Inspectors-general The following people served as Inspector-General of the RAF: *22 August 1918 Major General Sir Godfrey Paine (Air Vice-Marshal from 1 August 1919) *''1920 to 1935 - Post Abolished'' *1 August 1935 Air Chief Marshal Sir Robert Brooke-Popham *1 September 1937 Marshal of the Royal Air Force Sir Edward Ellington *1 July 1939 Air Chief Marshal Sir Charles Burnett *15 January 1940 Air Marshal Sir Leslie Gossage *14 April 1940 Air Chief Marshal Sir Edgar Ludlow-Hewitt From May 1940 to November 1943, a second in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Coastal Command
RAF Coastal Command was a formation within the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was founded in 1936, when the RAF was restructured into Fighter, Bomber and Coastal Commands and played an important role during the Second World War. Maritime Aviation had been neglected in the inter-war period, due to disagreements between the Royal Navy (RN) and RAF over the ownership, roles and investment in maritime air power. The Admiralty's main concern until 1937 was the return of the Fleet Air Arm to the Royal Navy while the RAF prioritised the development of a bombing force to provide a deterrent. Coastal Command was referred to as the "Cinderella Service" by A V Alexander, the First Lord of the Admiralty in November 1940. Soon after RAF Coastal Area was elevated to Coastal Command, its headquarters moved from Lee-on-Solent to Northwood in northwest London. During the Second World War, Coastal Command's most important contribution was the protection of Allied convoys from attacks by the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State for Air. Organisations before the Air Ministry The Air Committee On 13 April 1912, less than two weeks after the creation of the Royal Flying Corps (which initially consisted of both a naval and a military wing), an Air Committee was established to act as an intermediary between the Admiralty and the War Office in matters relating to aviation. The new Air Committee was composed of representatives of the two war ministries, and although it could make recommendations, it lacked executive authority. The recommendations of the Air Committee had to be ratified by the Admiralty Board and the Imperial General Staff and, in consequence, the Committee was not particularly effective. The increasing separation of army and naval aviation from 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
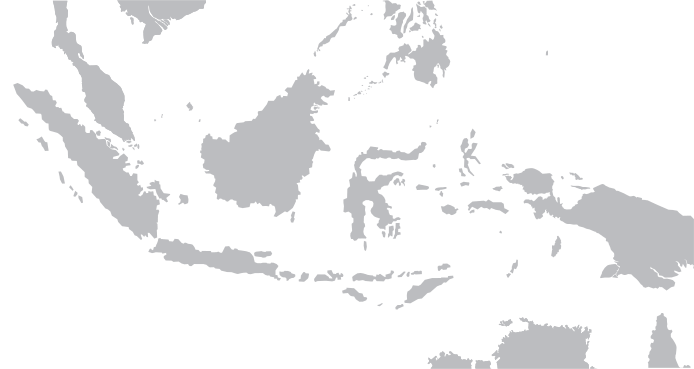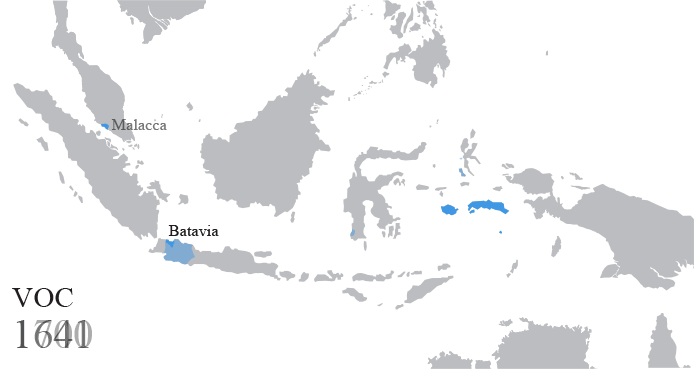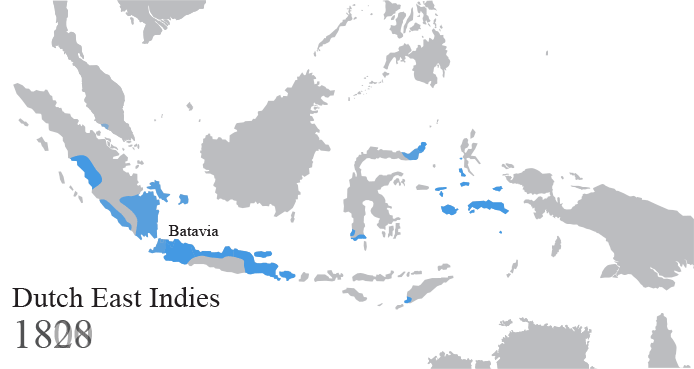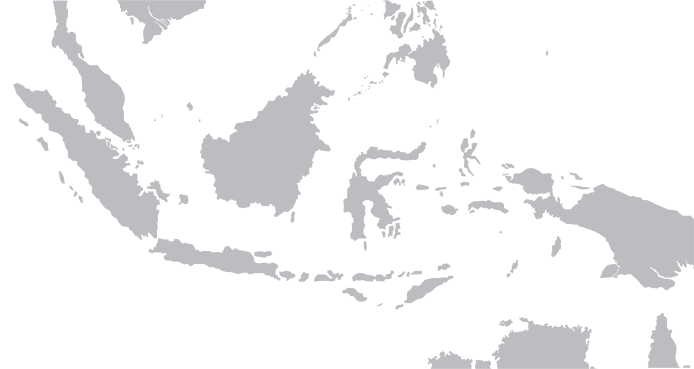
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |