|
Geschwind–Galaburda Hypothesis
The Geschwind–Galaburda hypothesis is a neurological theory proposed by Norman Geschwind and Albert Galaburda in 1987. The hypothesis posits there are sex differences in cognitive abilities by relating them to lateralisation of brain function. The maturation rates of cerebral hemispheres differ and are mediated by circuiting testosterone levels, which are substantially influenced during the foetal and post-puberty development stages. According to the hypothesis, testosterone delays the maturation of the brain, particularly the left hemisphere, resulting in corresponding regions of the right hemisphere and unaffected areas of the left hemisphere developing more rapidly. This leads to reduced verbal skills and an increased risk of developing language disorders, e.g dyslexia, while a rapid development of the right hemisphere and the skills corresponding to it, such as attention and problem-solving. Focusing on foetal testosterone, the rise in levels hinders the development of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethylstilbestrol
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency, treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer, and other uses. By 2007, it was only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. In 2011, Hoover and colleagues reported on adverse health outcomes linked to DES including infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preeclampsia, preterm birth, stillbirth, infant death, menopause prior to age 45, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and vaginal cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance, vaginal, topical, and by injection. DES is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors, the biological target ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
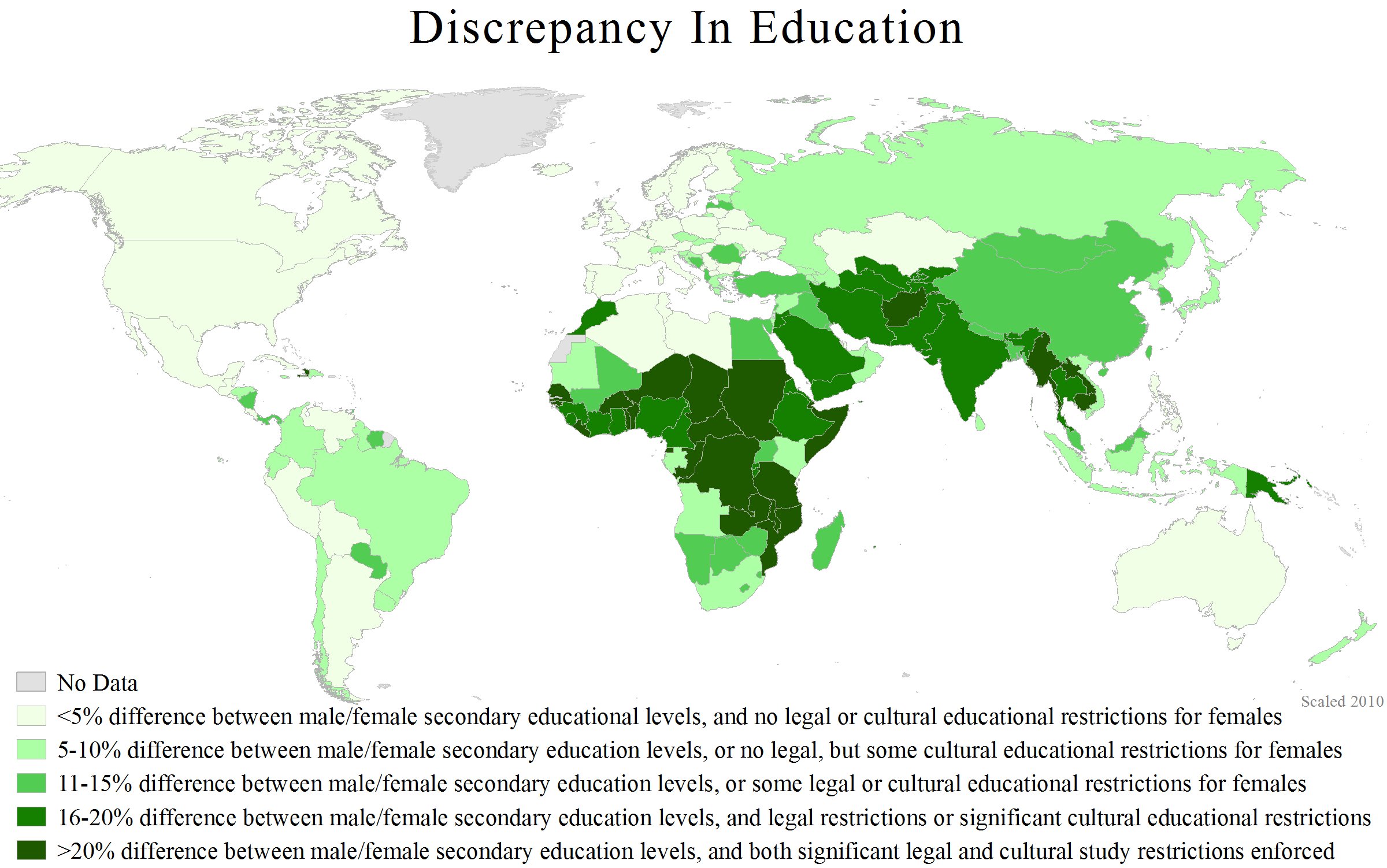
Sex Differences In Humans
Sex differences in humans have been studied in a variety of fields. Sex determination occurs by the presence or absence of a Y in the 23rd pair of chromosomes in the human genome. Phenotypic sex refers to an individual's sex as determined by their internal and external genitalia and expression of secondary sex characteristics. Sex differences generally refer to traits that are sexually dimorphic. A subset of such differences is hypothesized to be the product of the evolutionary process of sexual selection.Mealey, L. (2000). ''Sex differences''. NY: Academic Press. Medicine Sex differences in medicine include sex-specific diseases, which are diseases that occur ''only'' in people of one sex; and sex-related diseases, which are diseases that are more usual to one sex, or which manifest differently in each sex. For example, certain autoimmune diseases may occur predominantly in one sex, for unknown reasons. 90% of primary biliary cirrhosis cases are women, whereas primary scle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |