|
Gerrish's Regiment
Gerrish's Regiment was one of the 27 infantry regiments of the Massachusetts line created by the Continental Congress in 1775. Commanded by Colonel Samuel Gerrish, the unit saw action in the Boston and Cambridge campaigns and fought at Bunker Hill June 17, 1775. Formation The unit was one of many established on June 14, 1775, when the Continental Congress assumed responsibility for militia regiments that had been raised by the colonies of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. Most of these units, including Gerrish's Regiment, were stationed outside Boston, Massachusetts, where they besieged the city occupied by British troops under the command of General Thomas Gage. Reorganization As 1775 came to a close, with no end in sight to the siege of Boston and troops in Quebec preparing to attack Quebec City, Congress authorized a second establishment of the army, with a new regimental structure. List of Continental Army units (1775) Gerrish's Regiment then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislative bodies, with some executive function, for thirteen of Britain's colonies in North America, and the newly declared United States just before, during, and after the American Revolutionary War. The term "Continental Congress" most specifically refers to the First and Second Congresses of 1774–1781 and, at the time, was also used to refer to the Congress of the Confederation of 1781–1789, which operated as the first national government of the United States until being replaced under the Constitution of the United States. Thus, the term covers the three congressional bodies of the Thirteen Colonies and the new United States that met between 1774 and 1789. The First Continental Congress was called in 1774 in response to growing tensions between the colonies culminating in the passage of the Intolerable Acts by the British Parliament. It met for about six weeks and sought to repair the fraying relationship between Britain and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Line
The Massachusetts Line was those units within the Continental Army that were assigned to Massachusetts at various times by the Continental Congress during the American Revolutionary War. These, together with similar contingents from the other twelve states, formed the Continental Line. Line regiments were assigned to a particular state, which was then financially responsible for the maintenance (staffing and supplying) of the regiment. The concept of the line was also particularly important in relation to the promotion of commissioned officers. Officers of the Continental Army below the rank of brigadier general were ordinarily ineligible for promotion except in the line of their own state. The size of the Massachusetts Line varied from as many as 27 active regiments (at the outset of the war) to four (at its end). For most of the war after the siege of Boston (April 1775 to March 1776) almost all of these units were deployed outside Massachusetts, serving as far north as Quebec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
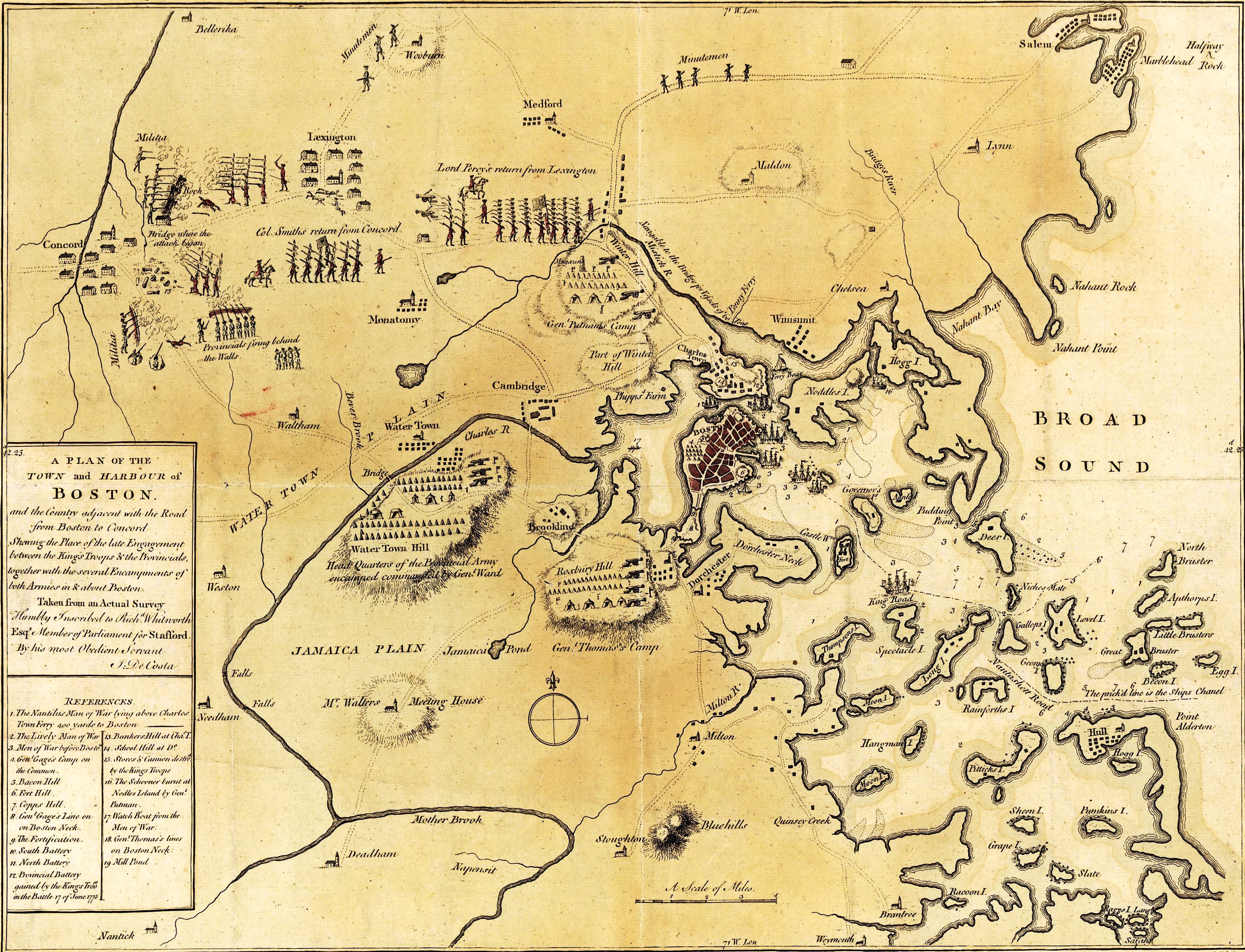
Siege Of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town of Boston, Massachusetts Bay. Both sides had to deal with resource, supply, and personnel issues over the course of the siege. British resupply and reinforcement was limited to sea access, which was impeded by American vessels. The British abandoned Boston after eleven months and transferred their troops and equipment to Nova Scotia. The siege began on April 19 after the Battles of Lexington and Concord, when Massachusetts militias blocked land access to Boston. The Continental Congress formed the Continental Army from the militias involved in the fighting and appointed George Washington as Commander in Chief. In June 1775, the British seized Bunker and Breed's Hills, from which the Continentals were preparing to bombard the city, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston Campaign
The Boston campaign was the opening campaign of the American Revolutionary War, taking place primarily in the Province of Massachusetts Bay. The campaign began with the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775, in which the local colonial militias interdicted a British government attempt to seize military stores and leaders in Concord, Massachusetts. The entire British expedition suffered significant casualties during a running battle back to Charlestown against an ever-growing number of militia. Subsequently, accumulated militia forces surrounded the city of Boston, beginning the siege of Boston. The main action during the siege, the Battle of Bunker Hill on June 17, 1775, was one of the bloodiest encounters of the war, and resulted in a Pyrrhic British victory. Brooks (1999), p. 237 There were also numerous skirmishes near Boston and the coastal areas of Boston, resulting in loss of life, military supplies, or both. In July 1775, George Washington took command of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in the battle. It was the original objective of both the colonial and British troops, though the majority of combat took place on the adjacent hill which later became known as Breed's Hill. On June 13, 1775, the leaders of the colonial forces besieging Boston learned that the British were planning to send troops out from the city to fortify the unoccupied hills surrounding the city, which would give them control of Boston Harbor. In response, 1,200 colonial troops under the command of William Prescott stealthily occupied Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill. During the night, the colonists constructed a strong redoubt on Breed's Hill, as well as smaller fortified lines across the Charlestown Peninsula. By daybreak of June 17, the British became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortification Of Dorchester Heights
The Fortification of Dorchester Heights was a decisive action early in the American Revolutionary War that precipitated the end of the siege of Boston and the withdrawal of British troops from that city. On March 4, 1776, troops from the Continental Army under George Washington's command occupied Dorchester Heights, a series of low hills with a commanding view of Boston and its harbor, and mounted powerful cannons there threatening the city and the Navy ships in the harbor. General William Howe, commander of the British forces occupying Boston, planned an attack to dislodge them. However, after a snowstorm prevented its execution, Howe withdrew instead. British forces, accompanied by Loyalists who had fled to the city during the siege, evacuated the city on March 17 and sailed to Halifax, Nova Scotia. Background The siege of Boston began on April 19, 1775, when, in the aftermath of the Battles of Lexington and Concord, Colonial militia surrounded the city of Boston. Frothin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Thomas Gage
General (United Kingdom), General Thomas Gage (10 March 1718/192 April 1787) was a British Army general officer and Colonialism, colonial official best known for his many years of service in North America, including his role as British Commander-in-Chief, North America, commander-in-chief in the early days of the American Revolution. Being born to an aristocratic family in England, he entered military service, seeing action in the French and Indian War, where he served alongside his future opponent George Washington in the 1755 Battle of the Monongahela. After the Conquest of 1760, fall of Montreal in 1760, he was named its military governor. During this time he did not distinguish himself militarily, but proved himself to be a competent administrator. From 1763 to 1775 he served as commander-in-chief of the British forces in North America, overseeing the British response to the 1763 Pontiac's War, Pontiac's Rebellion. In 1774 he was also appointed the military governor of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Continental Army Units (1775)
The Continental Army was the army raised by the Second Continental Congress to oppose the British Army during the American Revolutionary War. The army went through three major establishments: the first in 1775, the second in 1776, and the third from 1777 until after the end of the war. Creation of the army The Continental Army was established by the Continental Congress on June 14, 1775 which is also recognized as the founding date of its successor, the United States Army. On that day, the Continental Congress assumed responsibility for militia regiments that had been raised by the colonies of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. Most of these troops were stationed outside Boston, Massachusetts, where they besieged the city occupied by British troops under the command of General Thomas Gage. The forces adopted by the Continental Congress amounted to 39 regiments of infantry, and 1 regiment and 1 separate company of artillery. The period of service for ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
26th Continental Regiment
The 26th Continental Regiment (previously known as Gerrish's Regiment and later known as the 9th Massachusetts Regiment) was an infantry unit of the Massachusetts Line during the American Revolutionary War. Gerrish's Regiment was raised in the early days of the war, and the regiment underwent name changes as the Continental Army was reorganized in 1776 and 1777. From 1777 onward, the unit was known as the 9th Massachusetts Regiment. 1775 history In January 1776 the 26th Continental Regiment was organized from the remnant of Gerrish's Regiment, also known in the 1775 army establishment as the 25th Massachusetts. It was at first commanded by Colonel Samuel Gerrish, of Newbury, who was dismissed from the service for cowardice, after he hid in his tent during the battle. On 17 August 1775, the Continental Army court-martialed Gerrish on the charge “That he behaved unworthy an Officer.” With Gen. Nathanael Greene presiding, a panel of officers found him guilty and ordered him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |