|
German Cruiser Lützow (1940)
''Deutschland'' was the lead ship of her class of heavy cruisers (often termed pocket battleships) which served with the Kriegsmarine of Nazi Germany during World War II. Ordered by the Weimar government for the Reichsmarine, she was laid down at the ''Deutsche Werke'' shipyard in Kiel in February 1929 and completed by April 1933. Originally classified as an armored ship (''Panzerschiff'') by the Reichsmarine, in February 1940 the Germans reclassified the remaining two ships of this class as heavy cruisers. In 1940, she was renamed ''Lützow'', after the unfinished heavy cruiser was sold to the Soviet Union the previous year. The ship saw significant action with the Kriegsmarine, including several non-intervention patrols in the Spanish Civil War, during which she was attacked by Republican bombers. At the outbreak of World War II, she was cruising the North Atlantic, prepared to attack Allied merchant traffic. Bad weather hampered her efforts, and she sank or captured only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany, the head of gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsmarine
The ''Reichsmarine'' ( en, Realm Navy) was the name of the German Navy during the Weimar Republic and first two years of Nazi Germany. It was the naval branch of the ''Reichswehr'', existing from 1919 to 1935. In 1935, it became known as the ''Kriegsmarine'' (War Navy), a branch of the ''Wehrmacht''; a change implemented by Adolf Hitler. Many of the administrative and organizational tenets of the ''Reichsmarine'' were then carried over into the organization of the ''Kriegsmarine''. ''Vorläufige Reichsmarine'' The ''Vorläufige Reichsmarine'' ( en, Provisional Realm Navy) was formed after the end of World War I from the Imperial German Navy. The provisions of the Treaty of Versailles restricted the German Navy to 15,000 men and no submarines, while the fleet was limited to six pre-dreadnought battleships, six light cruisers, twelve destroyers, and twelve torpedo boats. Replacements for the outdated battleships were restricted to a maximum size of 10,000 tons. ''Reichsmarine'' T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The " Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
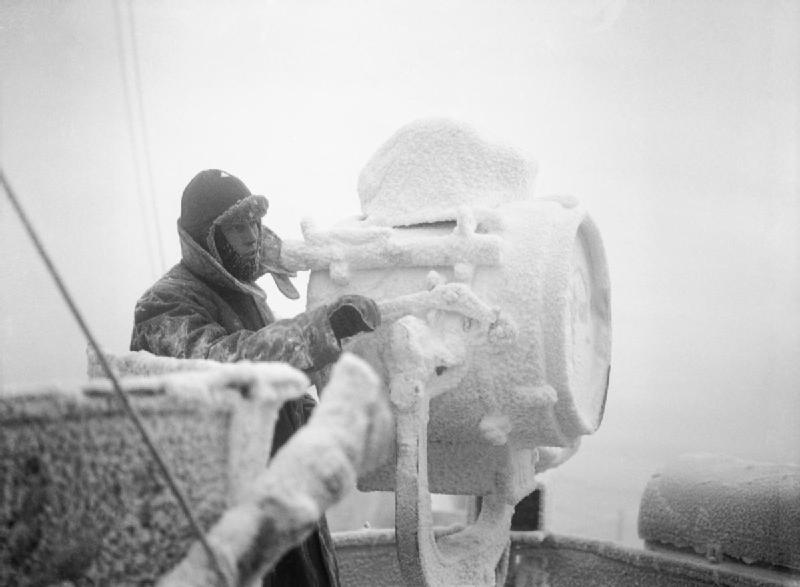
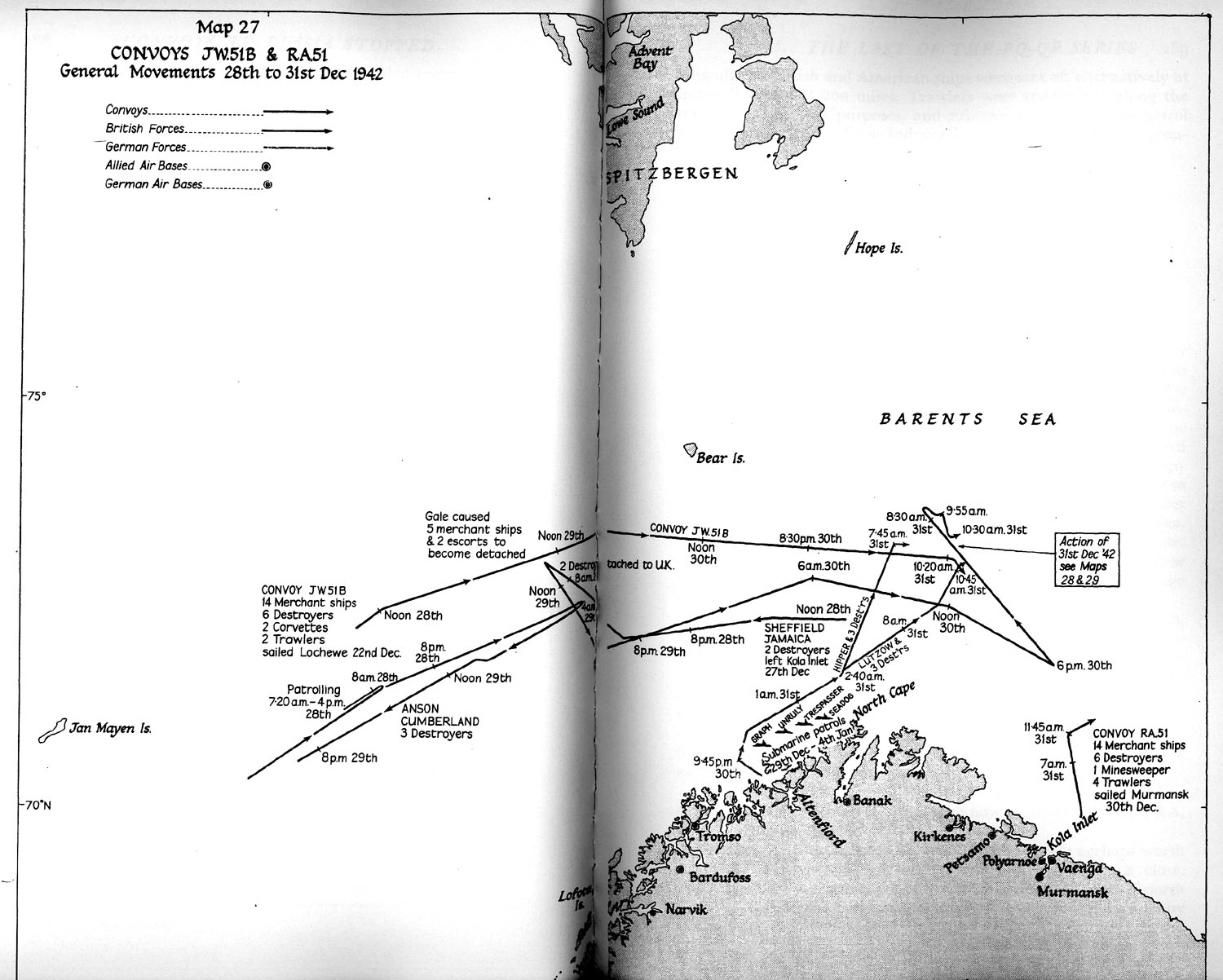
JW 51B
Convoy JW 51B was an Arctic convoy sent from United Kingdom by the Western Allies to aid the Soviet Union during World War II. It sailed in late December 1942, reaching the Soviet northern ports in early January 1943. JW 51B came under attack by German surface units, engaged in Operation Regenbogen, on 31 December. In the clash that ensued, one defending minesweeper and one attacking destroyer were sunk with all hands and a defending destroyer was sunk; no ships were lost from the convoy. This engagement became known as the Battle of the Barents Sea. Forces JW 51A consisted of 15 merchant ships which departed from Loch Ewe on 22 December 1942. Close escort was provided by the minesweeper , two corvettes and two armed trawlers. The close escort was supported by six Home Fleet destroyers led by (Capt Robert Sherbrooke commanding). The convoy sailed with a local escort group from Britain and was joined later by a local escort group from Murmansk. A cruiser cover force comprisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Barents Sea
The Battle of the Barents Sea was a World War II naval engagement on 31 December 1942 between warships of the German Navy (''Kriegsmarine'') and British ships escorting convoy JW 51B to Kola Inlet in the USSR. The action took place in the Barents Sea north of North Cape, Norway. The German raiders' failure to inflict significant losses on the convoy infuriated Hitler, who ordered that German naval strategy would henceforth concentrate on the U-boat fleet rather than surface ships. Background JW 51B Convoy JW 51B comprised fourteen merchant ships carrying war materials to the USSR — some 202 tanks, 2,046 vehicles, 87 fighters, 33 bombers, of fuel, of aviation fuel and just over of other supplies. They were protected by the destroyers , , , , and ; the s and ; the minesweeper ; and trawlers and . The escort commander was Captain Robert Sherbrooke RN (flag in ''Onslow''). The convoy sailed in the dead of winter to preclude attacks by German aircraft, like those that d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PQ 17
PQ 17 was the code name for an Allies of World War II, Allied Arctic convoys, Arctic convoy during the Second World War. On 27 June 1942, the ships sailed from Hvalfjörður, Iceland, for the port of Arkhangelsk in the Soviet Union. The convoy was located by Nazi Germany, German forces on 1 July, after which it was shadowed continuously and attacked. The First Sea Lord Admiral Dudley Pound, acting on information that Kriegsmarine#Surface ships, German surface units, including the German battleship Tirpitz, German battleship ''Tirpitz'', were moving to intercept, ordered the covering force built around the Allied battleships HMS Duke of York (17), HMS ''Duke of York'' and the USS Washington (BB-56), USS ''Washington'' away from the convoy and told the convoy to scatter. Because of vacillation by ''Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW, German armed forces high command), the ''Tirpitz'' raid never materialised. The convoy was the first large joint Anglo-American naval operation under Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Rösselsprung (1942)
Rösselsprung was a plan by the German ''Kriegsmarine'' to intercept an Arctic convoy in mid-1942. It was the German Navy's largest operation of its type and arguably the most successful since it resulted in the near-destruction of Convoy PQ 17. Ironically, that success was entirely indirect, as no ''Rösselsprung'' ship caught sight of the convoy or fired a shot at it. PQ 17's losses were instead caused by U-boat and aircraft attacks. Despite not making contact with the convoy a number of the ''Rösselsprung'' ships were damaged in the course of the operation, notably the heavy cruiser '' Lützow'', which ran aground in thick fog and needed three months of repairs. Background The name ''Rösselsprung'' refers to the Knight’s Move in Chess. It was an attempt to intercept the arctic convoy expected in late June 1942, which would be PQ 17. Two naval forces were assembled and held in readiness: the first, at Trondheim, comprised the battleship , the heavy cruiser and six destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Shipping To The Soviet Union
The Arctic convoys of World War II were oceangoing convoys which sailed from the United Kingdom, Iceland, and North America to northern ports in the Soviet Union – primarily Arkhangelsk (Archangel) and Murmansk in Russia. There were 78 convoys between August 1941 and May 1945, sailing via several seas of the Atlantic and Arctic oceans, with two gaps with no sailings between July and September 1942, and March and November 1943. About 1,400 merchant ships delivered essential supplies to the Soviet Union under the Anglo-Soviet agreement and US Lend-Lease program, escorted by ships of the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy, and the U.S. Navy. Eighty-five merchant vessels and 16 Royal Navy warships (two cruisers, six destroyers, eight other escort ships) were lost. Nazi Germany's ''Kriegsmarine'' lost a number of vessels including one battleship, three destroyers, 30 U-boats, and many aircraft. The convoys demonstrated the Allies' commitment to helping the Soviet Union, prior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Drøbak Sound
The Battle of Drøbak Sound took place in Drøbak Sound, the northernmost part of the outer Oslofjord in southern Norway, on 9 April 1940. It marked the end of the "Phoney War" and the beginning of World War II in Western Europe. A German fleet led by the cruiser '' Blücher'' was dispatched up the Oslofjord to begin the German invasion of Norway, with the objective of seizing the Norwegian capital of Oslo and capturing King Haakon VII and his government. The fleet was engaged in the fjord by Oscarsborg Fortress, an aging coastal installation near Drøbak, that had been relegated to training coastal artillery servicemen, leading the Germans to disregard its defensive value. However, unbeknownst to German military intelligence, the fortress' most powerful weapon was a torpedo battery, which would be used to great effect against the German invaders. The fortress' armaments worked flawlessly despite their age, sinking the ''Blücher'' in the sound and forcing the German fleet to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Weserübung
Operation Weserübung (german: Unternehmen Weserübung , , 9 April – 10 June 1940) was Germany's assault on Denmark and Norway during the Second World War and the opening operation of the Norwegian Campaign. In the early morning of 9 April 1940 (''Wesertag'', "Weser Day"), Germany occupied Denmark and invaded Norway, ostensibly as a preventive manoeuvre against a planned, and openly discussed, French-British occupation of Norway known as Plan R 4 (actually developed as a response to any German aggression against Norway). After the occupation of Denmark (the Danish military was ordered to stand down as Denmark did not declare war with Germany), envoys of the Germans informed the governments of Denmark and Norway that the ''Wehrmacht'' had come to protect the countries' neutrality against Franco-British aggression. Significant differences in geography, location and climate between the two nations made the actual military operations very dissimilar. The invasion fleet's no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |