|
Gerald Edward Brown
Gerald Edward Brown (born July 22, 1926 in Brookings, South Dakota; † May 31, 2013 in New York City) was an American theoretical physicist who worked on nuclear physics and astrophysics. Since 1968 he had been a professor at the Stony Brook University. He was a distinguished professor emeritus of the C. N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics at Stony Brook University. Life and work Brown received his bachelor's degree in physics in 1946 from the University of Wisconsin and in 1948 his master's degree from Yale University, where in 1950 he earned his PhD. In 1957 he earned his D.Sc. from the University of Birmingham in England (under Rudolf Peierls), where he was from 1955 docent and in 1959/60 was professor for theoretical physics. From 1960 to 1985 he was a professor at NORDITA in Copenhagen and concurrently from 1964 to 1968 Professor at Princeton and since 1968 he was a professor at the State University of New York at Stony Brook, where he became Distinguished Professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brookings, South Dakota
Brookings is a city in Brookings County, South Dakota, Brookings County, South Dakota, United States. Brookings is South Dakota's List of cities in South Dakota, fourth largest city, with a population of 23,377 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the county seat of Brookings County, and home to South Dakota State University, the state's largest institution of higher education. Also in Brookings are the South Dakota Art Museum, the Children's Museum of South Dakota, the annual Brookings Summer Arts Festival, and the headquarters of several manufacturing companies and agricultural operations. History Pioneer The county and city were both named after one of South Dakota's pioneer promoters, Wilmot Brookings. Brookings set out for the Dakota Territory in June 1857. He arrived at Sioux Falls on August 27, 1857, and became one of the first settlers there. He and his group represented the Western Town Company. After a time in Sioux Falls, Wilmot Brookings, Brookings and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State University Of New York At Stony Brook
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system's two flagship institutions. Its campus consists of 213 buildings on over of land in Suffolk County and it is the largest public university (by area) in the state of New York. Opened in 1957 in Oyster Bay as the State University College on Long Island, the institution moved to Stony Brook in 1962. In 2001, Stony Brook was elected to the Association of American Universities, a selective group of major research universities in North America. It is also a member of the larger Universities Research Association. It is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Stony Brook University, in partnership with Battelle, manages Brookhaven National Laboratory, a national laboratory of the United States Departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin language, Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Collapse
Gravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe. Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter will collapse to form pockets of higher density, typically creating a hierarchy of condensed structures such as clusters of galaxies, stellar groups, stars and planets. A star is born through the gradual gravitational collapse of a cloud of interstellar matter. The compression caused by the collapse raises the temperature until thermonuclear fusion occurs at the center of the star, at which point the collapse gradually comes to a halt as the outward thermal pressure balances the gravitational forces. The star then exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Once all its energy sources are exhausted, a star will again collapse until it reaches a new equilibrium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Stars
In astronomy, the term compact star (or compact object) refers collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It would grow to include exotic stars if such hypothetical, dense bodies are confirmed to exist. All compact objects have a high mass relative to their radius, giving them a very high density, compared to ordinary atomic matter. Compact stars are often the endpoints of stellar evolution and, in this respect, are also called stellar remnants. The state and type of a stellar remnant depends primarily on the mass of the star that it formed from. The ambiguous term ''compact star'' is often used when the exact nature of the star is not known, but evidence suggests that it has a very small radius compared to ordinary stars. A compact star that is not a black hole may be called a degenerate star. In June 2020, astronomers reported narrowing down the source of Fast radio burst, Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs), which may now plausibly include "compact-object mergers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Bethe
Hans Albrecht Bethe (; July 2, 1906 – March 6, 2005) was a German-American theoretical physicist who made major contributions to nuclear physics, astrophysics, quantum electrodynamics, and solid-state physics, and who won the 1967 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis. For most of his career, Bethe was a professor at Cornell University.Available at www.JamesKeckCollectedWorks.or are the class notes taken by one of his students at Cornell from the graduate courses on Nuclear Physics and on Applications of Quantum Mechanics he taught in the spring of 1947. During World War II, he was head of the Theoretical Division at the secret Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos laboratory that developed the first atomic bombs. There he played a key role in calculating the critical mass of the weapons and developing the theory behind the implosion method used in both the Trinity test and the "Fat Man" weapon dropped on Nagasaki in August 1945. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meson
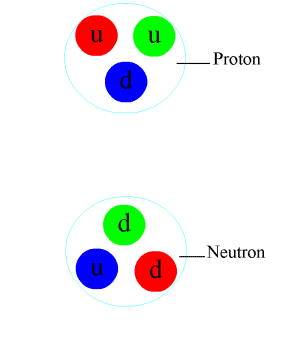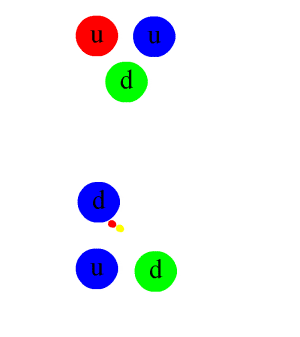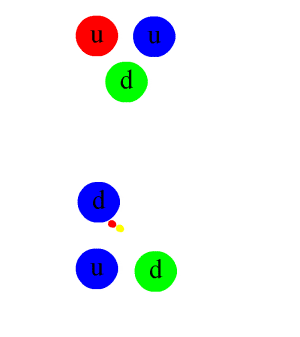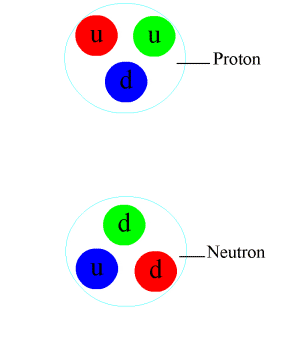
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons. Outside the nucleus, mesons appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy collisions between particles made of quarks, such as cosmic rays (high-energy protons and neutrons) and baryonic matter. Mesons are routinely produced artificially in cyclotrons or other particle accelerators in the collisions of protons, antiprotons, or other particles. Higher-energy (more massive) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannque Rho
Mannque Rho (born December 14, 1936) is a South Korean-frenchtheoretical physicist. He has contributed to theoretical nuclear/hadron physics and suggested Brown-Rho Scaling with Gerald E. Brown which predicts how the masses of the hadrons disappear in hot and dense environments. Birth and education Mannque Rho was born in Hamyang, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea in 1936. He graduated from Kyunggi High School and started his college study at the political science department of Seoul National University. After that he moved to the United States and entered Clark University. At first he registered for the pre-med study but later changed his major to chemistry and received his bachelor's degree in 1960. During his college studies, he attended some lectures about the structure of nuclei by Ben Roy Mottelson and Niels Bohr who were visiting the university at that time. He was affected by them and this led him to study hadron physics. He received his Ph.D in nuclear physics from University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |