|
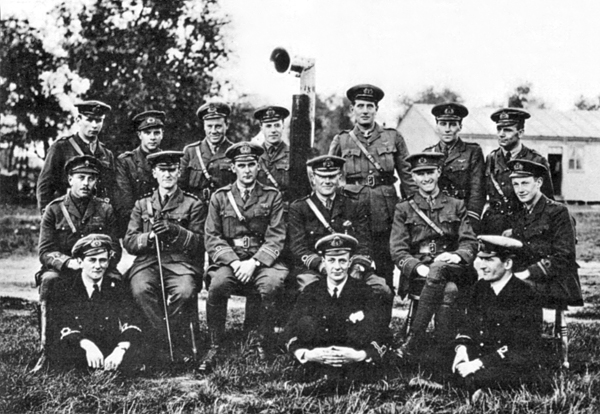
George McElroy
Captain (British Army and Royal Marines), Captain George Edward Henry McElroy Military Cross, MC & Medal bar, Two Bars, Distinguished Flying Cross (United Kingdom), DFC & Bar (14 May 1893 – 31 July 1918) was a leading Irish fighter pilot of the Royal Flying Corps and Royal Air Force during World War I. He was credited with 47 aerial victories. Military career McElroy was born at Donnybrook, Dublin, Donnybrook, County Dublin, Ireland,Franks (2000), p. 26. to Samuel and Ellen McElroy. He enlisted promptly at the start of World War I in August 1914, and was shipped out to France two months later. He was serving as a corporal in the Motor Cyclist Section of the Royal Engineers when he was first commissioned as a second lieutenant on 9 May 1915. While serving in the Royal Irish Regiment (1684-1922), Royal Irish Regiment he was severely affected by mustard gas and was sent home to recuperate. He was in Dublin in April 1916, during the Easter Rising, and was ordered to help quell the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Naval Air Service
The Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) was the air arm of the Royal Navy, under the direction of the Admiralty's Air Department, and existed formally from 1 July 1914 to 1 April 1918, when it was merged with the British Army's Royal Flying Corps to form the Royal Air Force (RAF), the world's first independent air force. It was replaced by the Fleet Air Arm, initially consisting of those RAF units that normally operated from ships, but emerging as a separate unit similar to the original RNAS by the time of World War 2. Background In 1908, the British Government recognised the military potential of aircraft. The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister, H. H. Asquith, approved the formation of an "Advisory Committee for Aeronautics" and an "Aerial Sub-Committee of the Committee of Imperial Defence". Both committees were composed of politicians, British Army, army officers and Royal Navy officers. On 21 July 1908 Captain Reginald Bacon, who was a member of the Aerial Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Aircraft Factory S
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), a 2021 reggae album * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * ''The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * ''Royal'' (Indian magazine), a men's lifestyle bimonthly * Royal T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport 17
The Nieuport 17 C.1 (or Nieuport XVII C.1 in contemporary sources) was a French sesquiplane fighter designed and manufactured by the Nieuport company during World War I. An improvement over the Nieuport 11, it was a little larger than earlier Nieuports and better adapted to the more powerful engine than the interim Nieuport 16. Aside from early examples, it had the new Alkan-Hamy synchronization gear, permitting the use of a fuselage-mounted synchronised Vickers gun firing through the propeller disc. At the time of its introduction in March 1916, the type's outstanding manoeuvrability and excellent rate of climb gave it a significant advantage over fighters on both sides and was described as "the best pursuit plane of the day". It was used by many operators and entered service with every Allied power and copies were also operated by the (German Air Service). Mass-produced by several French firms, the Nieuport 17 and its derivatives were built under licence in Italy by Nieupo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Mannock
Edward Corringham "Mick" Mannock (24 May 1887 – 26 July 1918) was a British flying ace in the Royal Flying Corps and Royal Air Force during the First World War. Mannock was a pioneer of fighter aircraft tactics in aerial warfare. At the time of his death he had amassed 61 aerial victories, making him the List of World War I aces credited with 20 or more victories, fifth highest scoring pilot of the war. Mannock was among the most decorated men in the British Armed Forces. He was honoured with the Military Cross twice, was one of the rare three-time recipients of the Distinguished Service Order, and was Posthumous recognition, posthumously awarded the Victoria Cross. Mannock was born in 1887 to an English father, Edward Mannock, and an Irish mother. Mannock's father served in the British Army and the family moved to India when Mannock was a child. Young Mannock was sickly and developed several ailments in his formative years. Upon his return to England he became a fervent suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's oldest continuously published aviation news magazine. ''Flight International'' is published by DVV Media Group. Competitors include Jane's Information Group and ''Aviation Week''. Former editors of, and contributors include H. F. King, Bill Gunston, John W. R. Taylor and David Learmount. History The founder and first editor of ''Flight'' was Stanley Spooner. He was also the creator and editor of ''The Automotor Journal'', originally titled ''The Automotor Journal and Horseless Vehicle''.Guide To British Industrial History: Biographies: ''Stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upavon
Upavon is a rural village and civil parish in the county of Wiltshire, England. As its name suggests, it is on the upper portion of the River Avon which runs from north to south through the village. It is on the north edge of Salisbury Plain about south of Pewsey, southeast of the market town of Devizes, and north of the cathedral city of Salisbury. The A345 and A342 roads run through the village. History Occupation of the area dates back to the Iron Age and Romano-British settlement at Casterley Camp, approximately southwest of the current village, and to the southeast was the small Iron Age settlement of Chisenbury Camp. The first mention of Upavon is in the 1086 Domesday Book as ''Oppavrene''; although no population was recorded, it can be estimated that the village supported some 200 to 250 people. The village prospered during the 12th and 13th centuries and started to develop features that are recognisable today. A large Norman church replaced the previous Saxon o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Flying School
The Central Flying School (CFS) is the Royal Air Force's primary institution for the training of military flying instructors. Established in 1912 at the Upavon Aerodrome, it is the longest existing flying training school. The school was based at RAF Little Rissington from 1946 to 1976. Its motto is ''Imprimis Praecepta'', Latin for "The Teaching is Everlasting". The school currently manages a series of training squadrons and the RAF Display Team. History The Central Flying School was established by the Royal Navy at Upavon Aerodrome, near Upavon, Wiltshire, on 12 May 1912. The school's strength at the outset was ten Staff Officers and eighty flying students, whose course lasted for sixteen weeks.Hugh Soar, ''Straight & True'' (2012), p. 87 Its first commandant was Captain Godfrey Paine RN, and it also trained pilots for the Royal Flying Corps, created in 1912, and the Royal Naval Air Service, 1914–1918. The school was transferred from the Southern Training Bridge to HQ Train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
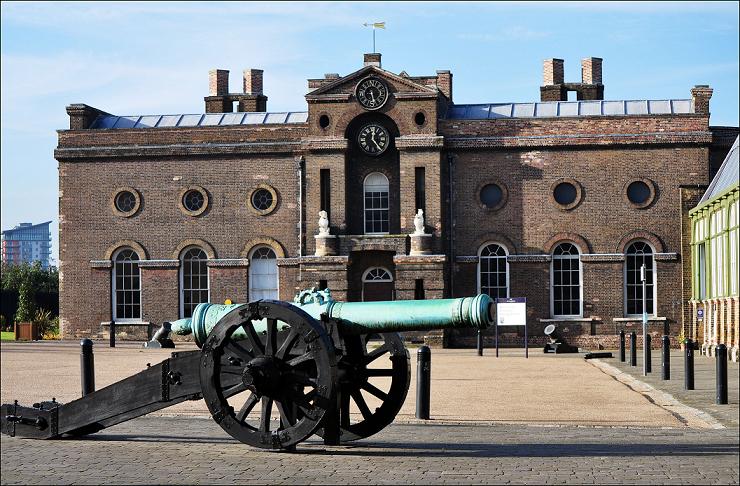
Royal Military Academy, Woolwich
The Royal Military Academy (RMA) at Woolwich, in south-east London, was a British Army military academy for the training of commissioned officers of the Royal Artillery and Royal Engineers. It later also trained officers of the Royal Corps of Signals and other technical corps. RMA Woolwich was commonly known as "The Shop" because its first building was a converted workshop of the Woolwich Arsenal. History Origins in the Royal Arsenal An attempt had been made by the Board of Ordnance in 1720 to set up an academy within its Arsenal (then known as the Warren) to provide training and education for prospective officers of its new Regiment of Artillery and Corps of Engineers (both of which had been established there in 1716). A new building was being constructed in readiness for the Academy and funds had been secured, seemingly, through investment in the South Sea Company; but the latter's collapse led to plans for the Academy being placed on hold. After this false start, the acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |