|
George Adolphus Schott
George Adolphus Schott (also referenced as George Augustus Schott) FRS (25 January 1868 – 15 July 1937) was a British mathematician. He is best known for developing the full theory of radiation from electrons travelling at close to the speed of light. Born in Bradford to German parents, he was educated at Bradford Grammar School and later studied at Trinity College, Cambridge, receiving his Bachelor of Arts in 1890. After obtaining his Doctor of Science he became assistant lecturer to D.M. Lewis in the Department of Physics. After a years leave, in which he travelled to Germany, he became lecturer of Applied Mathematics at Aberystwyth University, where he would spend the rest of his career. In 1910 he became Chair of the Applied Mathematics department and finally vice-president of the college. During Schott's early years at Aberystwyth he published his classical work on electromagnetic radiation, which follows the work laid down by Alfred-Marie Liénard. It was not until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford, England
Bradford is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 census; the second-largest population centre in the county after Leeds, which is to the east of the city. It shares a continuous built-up area with the towns of Shipley, Silsden, Bingley and Keighley in the district as well as with the metropolitan county's other districts. Its name is also given to Bradford Beck. It became a West Riding of Yorkshire municipal borough in 1847 and received its city charter in 1897. Since local government reform in 1974, the city is the administrative centre of a wider metropolitan district, city hall is the meeting place of Bradford City Council. The district has civil parishes and unparished areas and had a population of , making it the most populous district in England. In the century leading up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred-Marie Liénard
Alfred-Marie Liénard (2 April 1869 in Amiens – 29 April 1958 in Paris), was a French physicist and engineer. He is most well known for his derivation of the Liénard–Wiechert potentials. From 1887 to 1889 Liénard was a student at the École Polytechnique and from 1889 to 1892 at the École des mines de Paris. From 1892 to 1895 he was a mining engineer in Valencia, Marseille, and Angers. From 1895 to 1908 he was professor at the École des Mines de Saint-Étienne and from 1908 to 1911 he was professor of electrical engineering at the École des Mines de Paris. In World War I he served in the French Army. Liénard worked in the fields of electricity, magnetism, and mechanics. In 1898 (and two years after him Emil Wiechert), he derived what is now called the Liénard–Wiechert potentials. He also investigated problems related to the elasticity and strength of materials, and wrote papers on thermodynamics and hydrodynamics. Along with M. H. Chipart, Liénard developed the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Physicists
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Mathematicians
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1937 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – Anastasio Somoza García becomes President of Nicaragua. * January 5 – Water levels begin to rise in the Ohio River in the United States, leading to the Ohio River flood of 1937, which continues into February, leaving 1 million people homeless and 385 people dead. * January 15 – Spanish Civil War: Second Battle of the Corunna Road ends inconclusively. * January 20 – Second inauguration of Franklin D. Roosevelt: Franklin D. Roosevelt is sworn in for a second term as President of the United States. This is the first time that the United States presidential inauguration occurs on this date; the change is due to the ratification in 1933 of the Twentieth Amendment to the United States Constitution. * January 23 – Moscow Trials: Trial of the Anti-Soviet Trotskyist Center – In the Soviet Union 17 leading Communists go on trial, accused of participating in a plot led by Leon Trotsky to overthrow Joseph Stalin's regime, and assa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Births
Events January–March * January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries. * January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Japan, declares the ''Meiji Restoration'', his own restoration to full power, under the influence of supporters from the Chōshū and Satsuma Domains, and against the supporters of the Tokugawa shogunate, triggering the Boshin War. * January 5 – Paraguayan War: Brazilian Army commander Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, Duke of Caxias enters Asunción, Paraguay's capital. Some days later he declares the war is over. Nevertheless, Francisco Solano López, Paraguay's president, prepares guerrillas to fight in the countryside. * January 7 – The Arkansas constitutional convention meets in Little Rock. * January 9 – Penal transportation from Britain to Australia ends, with arrival of the convict ship ''Hougoumont'' in Western Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonradiation Condition
Classical nonradiation conditions define the conditions according to classical electromagnetism under which a distribution of accelerating charges will not emit electromagnetic radiation. According to the Larmor formula in classical electromagnetism, a single point charge under acceleration will emit electromagnetic radiation, i.e. light. In some classical electron models a distribution of charges can however be accelerated so that no radiation is emitted. The modern derivation of these nonradiation conditions by Hermann A. Haus is based on the Fourier components of the current produced by a moving point charge. It states that a distribution of accelerated charges will radiate if and only if it has Fourier components synchronous with waves traveling at the speed of light. History Finding a nonradiating model for the electron on an atom dominated the early work on atomic models. In a planetary model of the atom, the orbiting point electron would constantly accelerate towards the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy. Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Cope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Quantum Theory
The old quantum theory is a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent, but was rather a set of heuristic corrections to classical mechanics. The theory is now understood as the semi-classical approximation to modern quantum mechanics. The main and final accomplishments of the old quantum theory were the determination of the modern form of the periodic table by Edmund Stoner and the Pauli Exclusion Principle which were both premised on the Arnold Sommerfeld enhancements to the Bohr model of the atom. The main tool of the old quantum theory was the Bohr–Sommerfeld quantization condition, a procedure for selecting out certain states of a classical system as allowed states: the system can then only exist in one of the allowed states and not in any other state. History The old quantum theory was instigated by the 1900 work of Max Planck on the emission and absorption of light in a bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams Prize
The Adams Prize is one of the most prestigious prizes awarded by the University of Cambridge. It is awarded each year by the Faculty of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge and St John's College to a UK-based mathematician for distinguished research in the Mathematical Sciences. The prize is named after the mathematician John Couch Adams. It was endowed by members of St John's College and was approved by the senate of the university in 1848 to commemorate Adams' controversial role in the discovery of the planet Neptune. Originally open only to Cambridge graduates, the current stipulation is that the mathematician must reside in the UK and must be under forty years of age. Each year applications are invited from mathematicians who have worked in a specific area of mathematics. the Adams Prize is worth approximately £14,000. The prize is awarded in three parts. The first third is paid directly to the candidate; another third is paid to the candidate's institution to fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
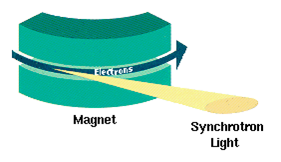
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |