|
Geopotential
Geopotential is the potential of the Earth's gravity field. For convenience it is often defined as the ''negative'' of the potential energy per unit mass, so that the gravity vector is obtained as the gradient of this potential, without the negation. In addition to the actual potential (the geopotential), a hypothetical normal potential and their difference, the disturbing potential, can also be defined. Concept For geophysical applications, gravity is distinguished from gravitation. Gravity is defined as the resultant force of gravitation and the centrifugal force caused by the Earth's rotation. Likewise, the respective scalar potentials can be added to form an effective potential called the geopotential, W. Global mean sea surface is close to one of the isosurfaces of the geopotential. This ''equipotential surface'', or surface of constant geopotential, is called the ''geoid''. How the gravitational force and the centrifugal force add up to a force orthogonal to the geoid is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Potential
Geopotential is the potential of the Earth's gravity field. For convenience it is often defined as the ''negative'' of the potential energy per unit mass, so that the gravity vector is obtained as the gradient of this potential, without the negation. In addition to the actual potential (the geopotential), a hypothetical normal potential and their difference, the disturbing potential, can also be defined. Concept For geophysical applications, gravity is distinguished from gravitation. Gravity is defined as the resultant force of gravitation and the centrifugal force caused by the Earth's rotation. Likewise, the respective scalar potentials can be added to form an effective potential called the geopotential, W. Global mean sea surface is close to one of the isosurfaces of the geopotential. This ''equipotential surface'', or surface of constant geopotential, is called the ''geoid''. How the gravitational force and the centrifugal force add up to a force orthogonal to the geoid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
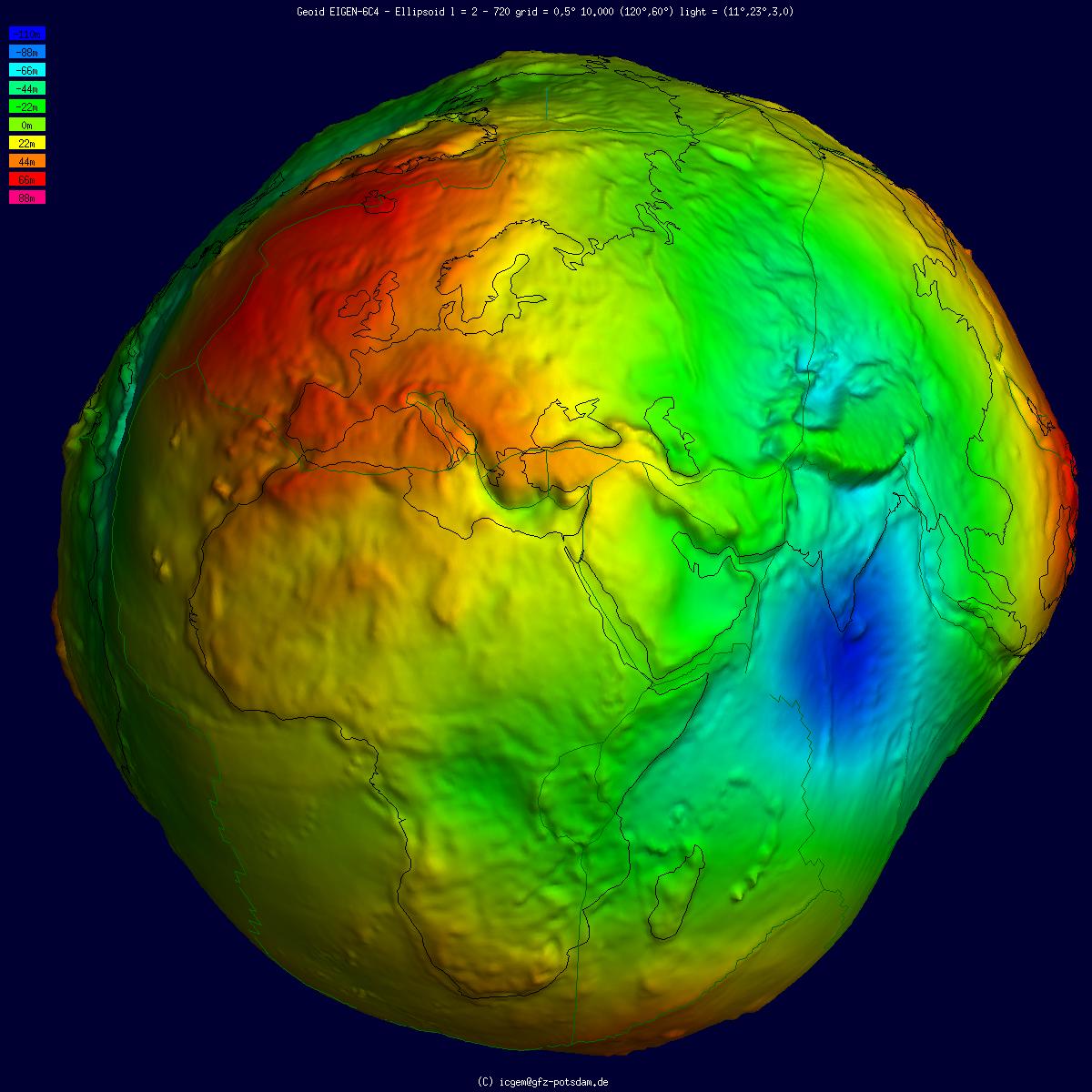
Geoid
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents (such as with very narrow hypothetical canals). According to Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century. All points on a geoid surface have the same geopotential (the sum of gravitational potential energy and centrifugal potential energy). The force of gravity acts everywhere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
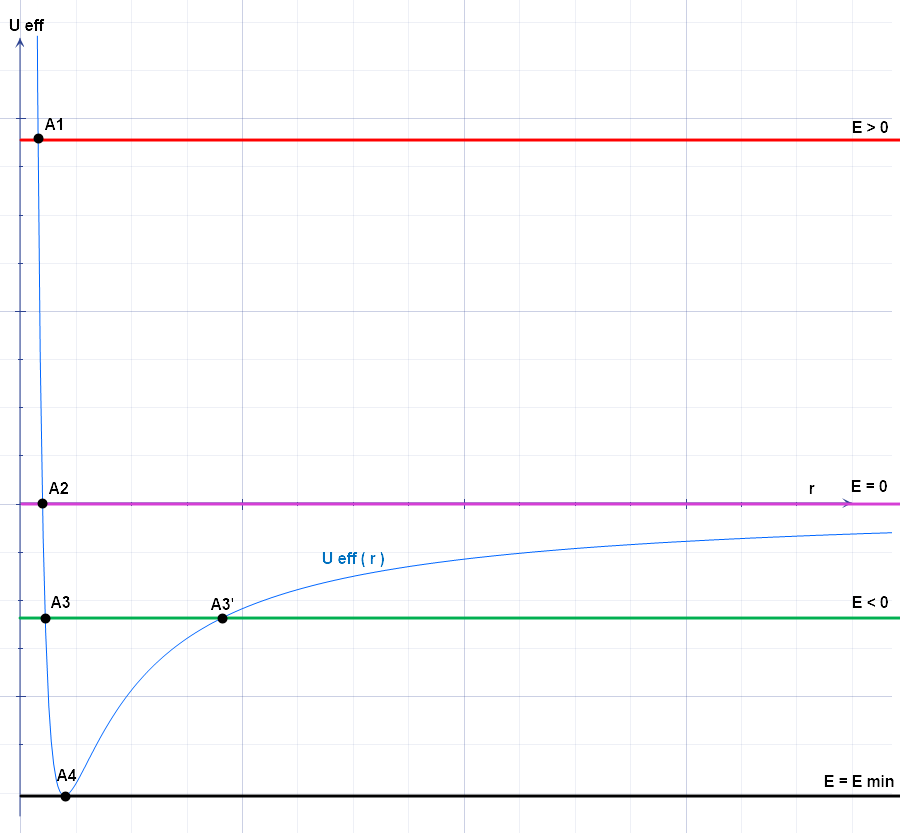
Effective Potential
The effective potential (also known as effective potential energy) combines multiple, perhaps opposing, effects into a single potential. In its basic form, it is the sum of the 'opposing' centrifugal potential energy with the potential energy of a dynamical system. It may be used to determine the orbits of planets (both Newtonian and relativistic) and to perform semi-classical atomic calculations, and often allows problems to be reduced to fewer dimensions. Definition The basic form of potential U_\text is defined as: U_\text(\mathbf) = \frac + U(\mathbf), where *''L'' is the angular momentum *''r'' is the distance between the two masses *''μ'' is the reduced mass of the two bodies (approximately equal to the mass of the orbiting body if one mass is much larger than the other); and *''U''(''r'') is the general form of the potential. The effective force, then, is the negative gradient of the effective potential: \begin \mathbf_\text &= -\nabla U_\text(\mathbf) \\ &= \frac \ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocentric Coordinates
The Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system (acronym ECEF), also known as the geocentric coordinate system, is a cartesian spatial reference system that represents locations in the vicinity of the Earth (including its surface, interior, atmosphere, and surrounding outer space) as ''X'', ''Y'', and ''Z'' measurements from its center of mass. Its most common use is in tracking the orbits of satellites and in satellite navigation systems for measuring locations on the surface of the Earth, but it is also used in applications such as tracking crustal motion. The distance from a given point of interest to the center of Earth is called the geocentric distance, , which is a generalization of the '' geocentric radius'', , not restricted to points on the reference ellipsoid surface. The geocentric altitude is a type of altitude defined as the difference between the two aforementioned quantities: ; it is not to be confused for the ''geodetic altitude''. Conversions between ECE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple release of energy by objects to the realization of abilities in people. The philosopher Aristotle incorporated this concept into his theory of potentiality and actuality, a pair of closely connected principles which he used to analyze motion, causality, ethics, and physiology in his ''Physics'', ''Metaphysics'', ''Nicomachean Ethics'', and '' De Anima'', which is about the human psyche. That which is potential can theoretically be made actual by taking the right action; for example, a boulder on the edge of a cliff has potential to fall that could be actualized by pushing it over the edge. Several languages have a potential mood, a grammatical construction that indicates that something is potential. These include Finnish, Japanese, and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is parallel to the axis of rotation and passing through the coordinate system's origin. If the axis of rotation passes through the coordinate system's origin, the centrifugal force is directed radially outwards from that axis. The magnitude of centrifugal force ''F'' on an object of mass ''m'' at the distance ''r'' from the origin of a frame of reference rotating with angular velocity is: F = m\omega^2 r The concept of centrifugal force can be applied in rotating devices, such as centrifuges, centrifugal pumps, centrifugal governors, and centrifugal clutches, and in centrifugal railways, planetary orbits and banked curves, when they are analyzed in a rotating coordinate system. Confusingly, the term has sometimes also been used for the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Ellipsoid
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations. It is a spheroid (an ellipsoid of revolution) whose minor axis (shorter diameter), which connects the geographical North Pole and South Pole, is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation. The ellipsoid is defined by the ''equatorial axis'' (''a'') and the ''polar axis'' (''b''); their radial difference is slightly more than 21 km, or 0.335% of ''a'' (which is not quite 6,400 km). Many methods exist for determination of the axes of an Earth ellipsoid, ranging from meridian arcs up to modern satellite geodesy or the analysis and interconnection of continental geodetic networks. Amongst the different set of data used in national surveys are several of special importance: the Bessel ellipsoid of 1841, the internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial elli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Gravity
In geodesy and geophysics, theoretical gravity or normal gravity is an approximation of the true gravity on Earth's surface by means of a mathematical model representing Earth. The most common model of a smoothed Earth is a rotating Earth ellipsoid of revolution (i.e., a spheroid). Principles The type of gravity model used for the Earth depends upon the degree of fidelity required for a given problem. For many problems such as aircraft simulation, it may be sufficient to consider gravity to be a constant, defined as: :g=g_= based upon data from ''World Geodetic System 1984'' ( WGS-84), where g is understood to be pointing 'down' in the local frame of reference. If it is desirable to model an object's weight on Earth as a function of latitude, one could use the following: :g=g_ - \tfrac(g_-g_) \cos\left(2\, \varphi \cdot \frac\right) where * g_ = * g_ = * g_ = * \varphi = latitude, between −90° and +90° Neither of these accounts for changes in gravity with changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |