|
Geophone
A geophone is a device that converts ground movement (velocity) into voltage, which may be recorded at a recording station. The deviation of this measured voltage from the base line is called the seismic response and is analyzed for structure of the earth. Etymology The term geophone derives from the Greek word "γῆ (ge) " meaning "earth" and "phone" meaning "sound". Construction Geophones have historically been passive analog devices and typically comprise a spring-mounted wire coil moving within the field of a case-mounted permanent magnet to generate an electrical signal. Recent designs have been based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology which generates an electrical response to ground motion through an active feedback circuit to maintain the position of a small piece of silicon. The response of a coil/magnet geophone is proportional to ground velocity, while MEMS devices usually respond proportional to acceleration. MEMS have a much higher noise level (5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophone SM-24
A geophone is a device that converts ground movement (velocity) into voltage, which may be recorded at a recording station. The deviation of this measured voltage from the base line is called the seismic response and is analyzed for structure of the earth. Etymology The term geophone derives from the Greek word "γῆ (ge) " meaning "earth" and "phone" meaning "sound". Construction Geophones have historically been passive analog devices and typically comprise a spring-mounted wire coil moving within the field of a case-mounted permanent magnet to generate an electrical signal. Recent designs have been based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology which generates an electrical response to ground motion through an active feedback circuit to maintain the position of a small piece of silicon. The response of a coil/magnet geophone is proportional to ground velocity, while MEMS devices usually respond proportional to acceleration. MEMS have a much higher noise level (50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GeoPhone
A geophone is a device that converts ground movement (velocity) into voltage, which may be recorded at a recording station. The deviation of this measured voltage from the base line is called the seismic response and is analyzed for structure of the earth. Etymology The term geophone derives from the Greek word "γῆ (ge) " meaning "earth" and "phone" meaning "sound". Construction Geophones have historically been passive analog devices and typically comprise a spring-mounted wire coil moving within the field of a case-mounted permanent magnet to generate an electrical signal. Recent designs have been based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology which generates an electrical response to ground motion through an active feedback circuit to maintain the position of a small piece of silicon. The response of a coil/magnet geophone is proportional to ground velocity, while MEMS devices usually respond proportional to acceleration. MEMS have a much higher noise level (5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophone
A hydrophone ( grc, ὕδωρ + φωνή, , water + sound) is a microphone designed to be used underwater for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones are based on a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a sound wave. Some piezoelectric transducers can also serve as a sound projector, but not all have this capability, and some may be destroyed if used in such a manner. A hydrophone can detect airborne sounds, but will be insensitive because it is designed to match the acoustic impedance of water, a denser fluid than air. Sound travels 4.3 times faster in water than in air, and a sound wave in water exerts a pressure 60 times that exerted by a wave of the same amplitude in air. Similarly, a standard microphone can be buried in the ground, or immersed in water if it is put in a waterproof container, but will give poor performance due to the similarly bad acoustic impedance match. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
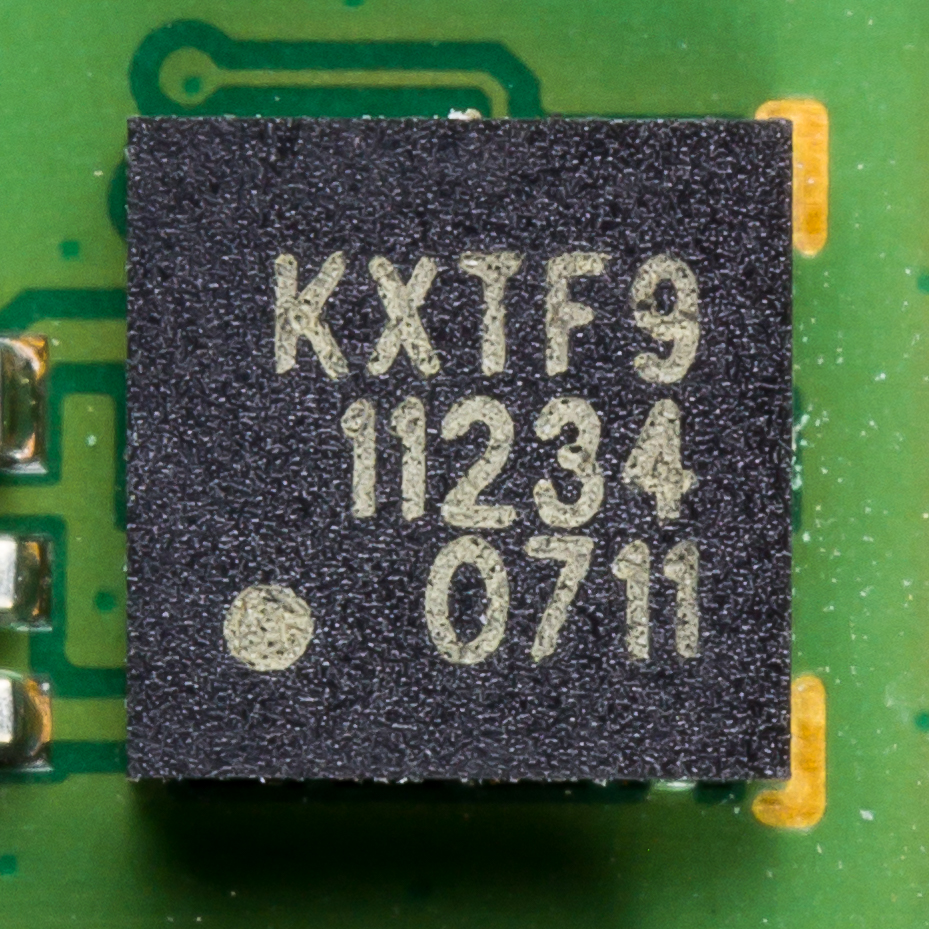
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
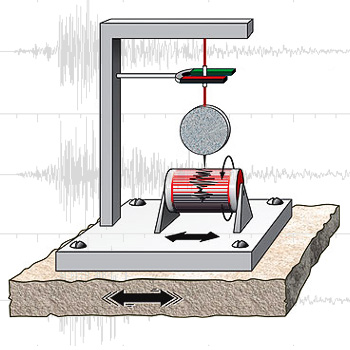
Seismometers
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends not to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends not to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Circuit
Analogue electronics ( en-US, analog electronics) are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal. The word analogue is derived from the el, word ανάλογος (analogos) meaning "proportional". Analogue signals An analogue signal uses some attribute of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses the angular position of a needle as the signal to convey the information of changes in atmospheric pressure. Electrical signals may represent information by changing their voltage, current, frequency, or total charge. Information is converted from some other physical form (such as sound, light, temperature, pressure, position) to an electrical signal by a transducer which converts one type of energy into another (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Receivers Single Fold-3 Fold
Source may refer to: Research * Historical document * Historical source * Source (intelligence) or sub source, typically a confidential provider of non open-source intelligence * Source (journalism), a person, publication, publishing institute or other record or document that gives information * Source document, a document in which data collected for a clinical trial is first recorded * Source text, in research (especially in the humanities), a source of information referred to by citation ** Primary source, a first-hand written evidence of history made at the time of the event by someone who was present ** Secondary source, a written account of history based upon the evidence from primary sources ** Tertiary source, a compilation based upon primary and secondary sources * Sources (website), a directory of expert contacts and media spokespersons * Open source, a philosophy of dissemination of intellectual products Law * Sources of international law, the materials and processes ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
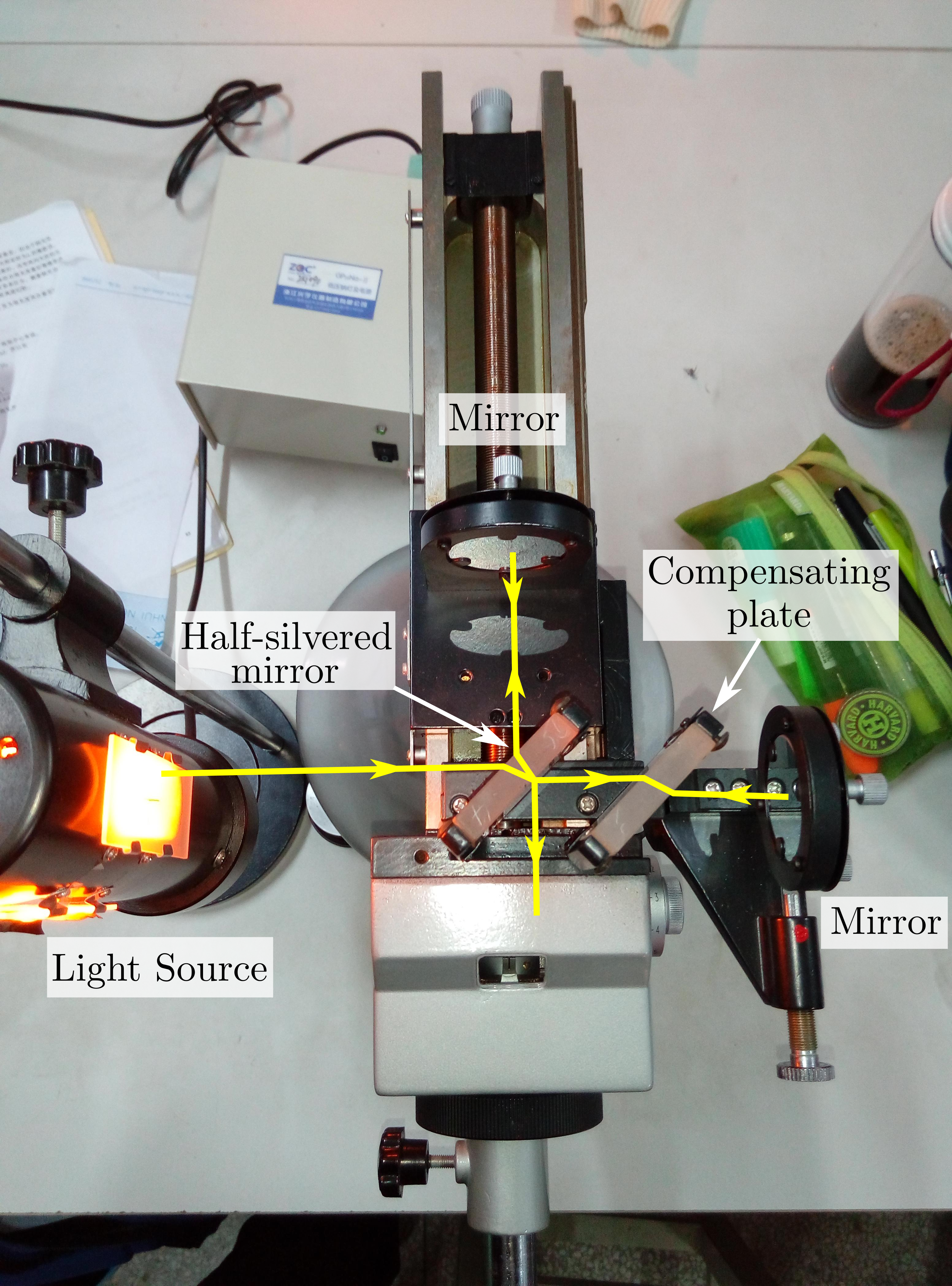
Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the 19/20th-century American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test. The Michelson interferometer (among other interferometer configurations) is employed in many scientific experiments and became well known for its use by Michelson and Edward Morley in the famous Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) in a configuration which would have detected the Earth's motion through the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation of a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
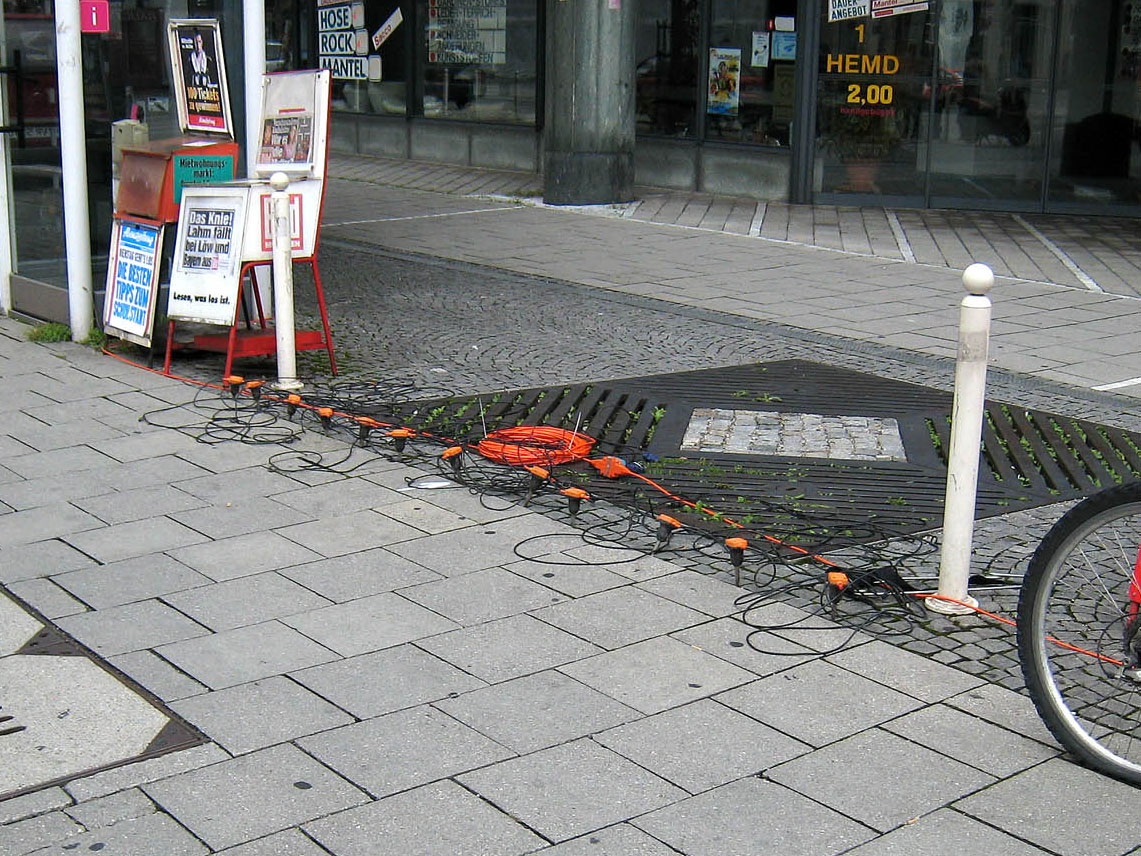
Unattended Ground Sensors
The unattended ground sensor (UGS) is under development as part of the United States Army's Future Combat Systems Program. For information on currently fielded UGS systems, refer to the Current Force UGS Program or CF UGS. The CF UGS systems employ various sensor modalities including seismic, acoustic, magnetic, and pyroelectric transducers, daylight imagers and passive infrared imagers to automatically detect the presence of persons or vehicles, and transmit activity reports or imagery via radio-frequency (RF) or satellite communications (SATCOM) links to a remote processing, exploitation, and dissemination (PED) station. The systems are packaged for concealed emplacement in the field and for long-duration unattended operation. The Army Research Laboratory developed unattended ground-sensor technologies for detection and tracking of personnel and vehicles for perimeter defense and border-monitoring applications. In 2005, the OmniSense system was commercialized and fielded. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |