|
Genomic DNA
Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated as gDNA) is chromosomal DNA, in contrast to extra-chromosomal DNAs like plasmids. Most organisms have the same genomic DNA in every cell; however, only certain genes are active in each cell to allow for cell function and differentiation within the body. The genome of an organism (encoded by the genomic DNA) is the (biological) information of heredity which is passed from one generation of organism to the next. That genome is transcribed to produce various RNAs, which are necessary for the function of the organism. Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is transcribed by RNA polymerase II in the nucleus. pre-mRNA is then processed by splicing to remove introns, leaving the exons in the mature messenger RNA (mRNA). Additional processing includes the addition of a 5' cap and a poly(A) tail to the pre-mRNA. The mature mRNA may then be transported to the cytosol and translated by the ribosome into a protein. Other types of RNA include ribosomal RNA (rR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of Transcription (biology), transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as Translation (biology), translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA (mRNA); or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. tRNAs genes from Bacteria are typically shorter (mean = 77.6 bp) than tRNAs from Archaea (mean = 83.1 bp) and eukaryotes (mean = 84.7 bp). The mature tRNA follows an opposite pattern with tRNAs from Bacteria being usually longer (median = 77.6 nt) than tRNAs from Archaea (median = 76.8 nt), with eukaryotes exhibiting the shortest mature tRNAs (median = 74.5 nt). Transfer RNA (tRNA) does this by carrying an amino acid to the protein synthesizing machinery of a cell called the ribosome. Complementation of a 3-nucleotide codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) by a 3-nucleotide anticodon of the tRNA results in protein synthesis based on the mRNA code. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequences commonly forms stem-loop configurations. The length and position of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells (intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
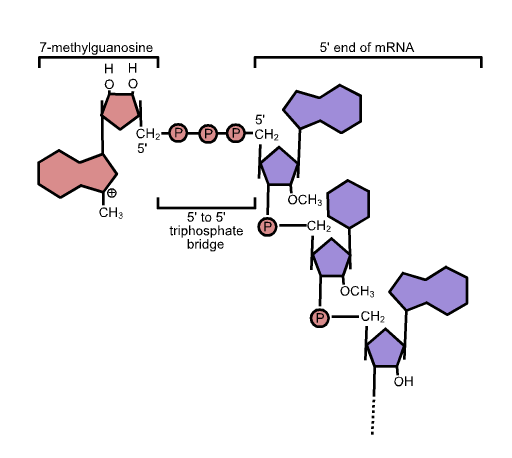
Five-prime Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exons
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' derives from the expressed region and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron… must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before being translated. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Activation
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network. Gene regulation is essential for viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes as it increases the versatility and adaptability of an organism by allowing the cell to express protein when needed. Although as early as 1951, Barbara McClintock showed interaction between two genetic loci, Activator (''Ac'') and Dissociator (''Ds''), in the color formation of maize seeds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |