|
Genital Regeneration
Genital regeneration encompasses various forms of treatment for genital anomalies. The goal of these treatments is to restore form and function to male and female genitalia by taking advantage of innate responses in the body. In order to do this, doctors have experimented with stem cells and extracellular matrix to provide a framework for regenerating missing structures. More research is needed to successfully move the science from laboratory trials to routine procedures."Bioengineered corporal tissue for structural and functional restoration of the penis" 2009 Chen, K. Eberli, D. Yoo, J. and Atala, A. 2009 ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'' 107 No 8, pp. 3346-3350. Patients who can benefit most from this field are those who have congenital defect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs. Regenerative medicine also includes the possibility of growing tissues and organs in the laboratory and implanting them when the body cannot heal itself. When the cell source for a regenerated organ is derived from the patient's own tissue or cells, the challenge of organ transplant rejection via immunological mismatch is circumvented. This approach could alleviate the problem of the shortage of organs available for donation. Some of the biomedical approaches within the field of regenerative medicine may involve the use of stem cells. Examples include the injection of stem cells or progenitor cells obtained through directed differenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
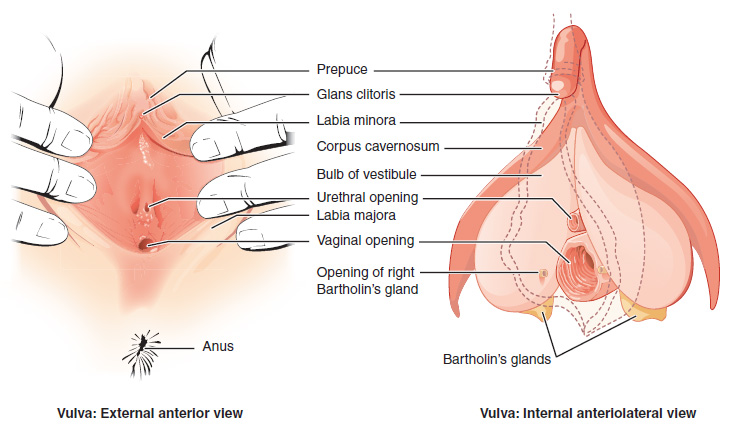
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimented
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, are called the ''primary sex organs''. All others are called ''secondary sex organs'', divided between the external sex organs—the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes—and the internal sex organs. Mosses, ferns, and some similar plants have gametangia for reproductive organs, which are part of the gametophyte. The flowers of flowering plants produce pollen and egg cells, but the sex organs themselves are inside the gametophytes within the pollen and the ovule. Coniferous plants likewise produce their sexually reproductive structures within the gametophytes contained within the cones and pollen. The cones and pollen are not themselves sexual organs. Terminology The ''primary sex organs'' are the gonads, a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
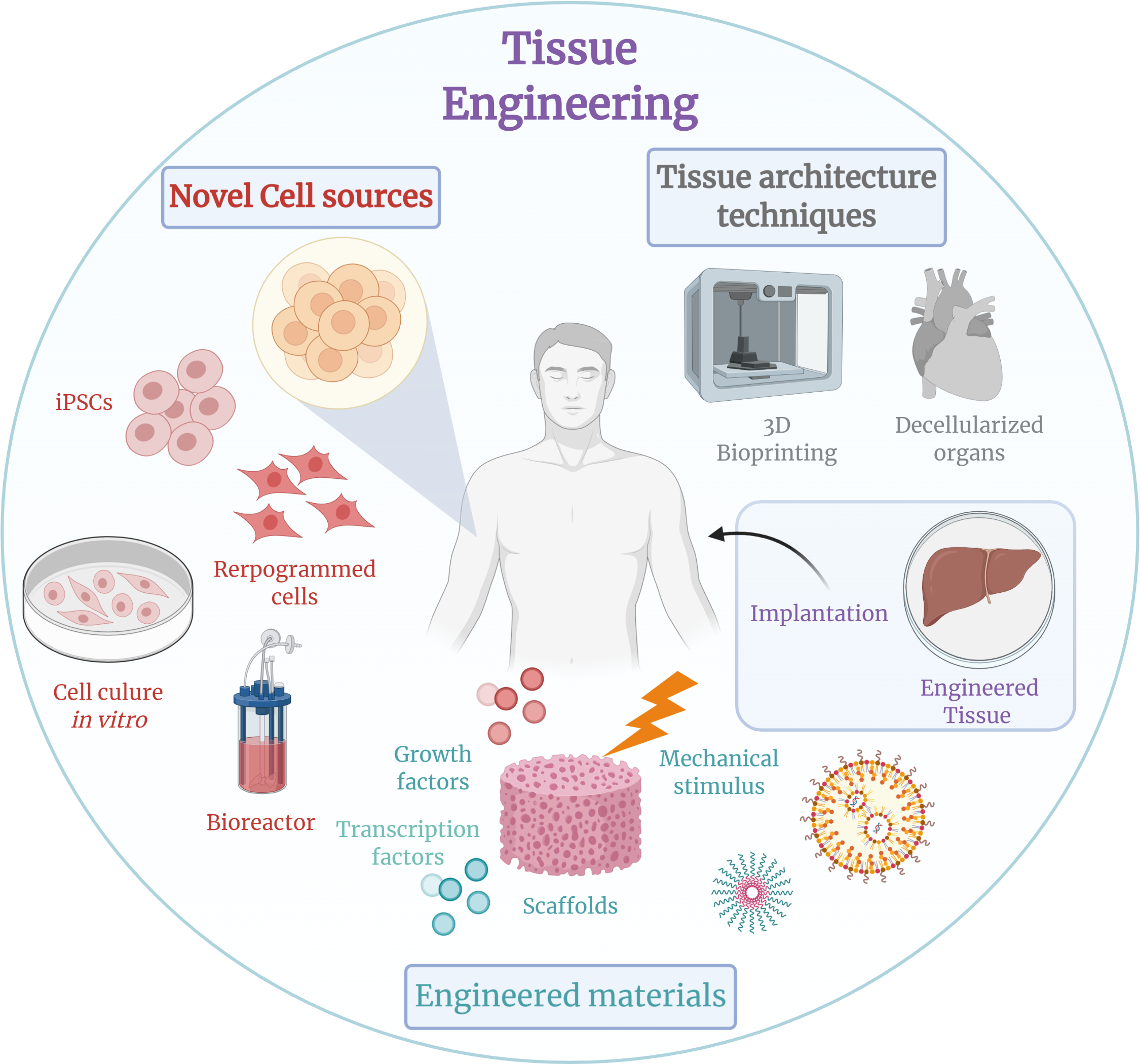
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biology, biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, Autologous chondrocyte implantation, cartilage, blood vessels, Urinary bladder, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Genital Mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found in some countries of Africa, Asia and the Middle East, and within communities abroad from countries in which FGM is common. UNICEF estimated, in 2016, that 200 million women in 30 countries—Indonesia, Iraq, Yemen, and 27 African countries including Egypt—had been subjected to one or more types of FGM. Typically carried out by a traditional circumciser using a blade, FGM is conducted from days after birth to puberty and beyond. In half of the countries for which national statistics are available, most girls are cut before the age of five. Procedures differ according to the country or ethnic group. They include removal of the clitoral hood (type 1-a) and clitoral glans (1-b); removal of the inner labia; and removal of the inner and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Foldès
The French surgeon, of Hungarian origin, Pierre Foldès (6 May 1951, Paris) is the inventor, in collaboration with the urologist Jean-Antoine Robein, of a clitoral restoration surgery technique to repair the damage caused by female genital mutilation. This technique repairs some of the urologic and obstetric problems related to FGC, and also may allow the women to experience more pleasure during sexual stimulation. For the past 25 years, Foldès has worked to treat women who have experienced genital mutilation. He currently operates on approximately 200 women per year. His procedure consists of the removal of any scar tissue from the vulva, and of the lowering of the clitoris by cutting ligaments that support it while preserving nerves and blood vessels. Wedge plasty is used to reconstruct a clitoral glans. Months of healing are required for the women to gain sensation in their newly exposed tissue. Pierre Foldès continues his work despite repeated death threats. In 2006 the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wake Forest Institute For Regenerative Medicine
The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine (WFIRM) is a research institute affiliated with Wake Forest School of Medicine and located in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, United States WFIRM's goal is to apply the principles of regenerative medicine to repair or replace diseased tissues and organs. Among other goals, WFIRM scientists are looking for ways to create insulin-producing cells in the laboratory, engineered blood vessels for heart bypass surgery and treat knee injuries through regenerated meniscus tissues. WFIRM has also led two federal initiatives to regenerate tissues from battlefield injuries (AFIRM I and AFIRM II), with a combined funding of $160 million from the U.S. Department of Defense. WFIRM is working to develop more than 40 different organs and tissues in the laboratory. Anthony Atala, M.D., is the director of the institute, which is located in Wake Forest Innovation Quarter in downtown Winston-Salem. Atala was recruited by Wake Forest Baptist Medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security and the United States Armed Forces. The DoD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.34 million active-duty service members (soldiers, marines, sailors, airmen, and guardians) as of June 2022. The DoD also maintains over 778,000 National Guard and reservists, and over 747,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.87 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security". The Department of Defense is headed by the secretary of defense, a cabinet-level head who reports directly to the president of the United States. Beneath the Department of Defense are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Institute For Regenerative Medicine
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) was created in 2004 after 59% of California voters approved California Proposition 71: the Research and Cures Initiative, which allocated $3 billion to fund stem cell research in California. Institutes dedicated to stem cell research and training exist at Sanford Consortium, University of California, Santa Cruz, Stanford University, University of California Davis, University of California Irvine, University of California San Francisco, University of California Los Angeles and University of Southern California. Five “Alpha Stem Cell Clinics have also been established to lead clinical trials for stem cell therapies at City of Hope, University of California San Diego, University of California San Francisco, University of California Davis and a joint clinic at University of California Los Angeles and University of California Irvine. History CIRM was established via California Proposition 71 (2004). However, its implementation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_2.jpg)
