|
Generalized Linear Array Model
In statistics, the generalized linear array model (GLAM) is used for analyzing data sets with array structures. It based on the generalized linear model with the design matrix written as a Kronecker product. Overview The generalized linear array model or GLAM was introduced in 2006. Such models provide a structure and a computational procedure for fitting generalized linear models or GLMs whose model matrix can be written as a Kronecker product and whose data can be written as an array. In a large GLM, the GLAM approach gives very substantial savings in both storage and computational time over the usual GLM algorithm. Suppose that the data \mathbf Y is arranged in a d-dimensional array with size n_1\times n_2\times\dots\times n_d; thus, the corresponding data vector \mathbf y = \operatorname(\mathbf Y) has size n_1n_2n_3\cdots n_d. Suppose also that the design matrix In statistics and in particular in regression analysis, a design matrix, also known as model matrix or regress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Generalized Linear Model
In statistics, a generalized linear model (GLM) is a flexible generalization of ordinary linear regression. The GLM generalizes linear regression by allowing the linear model to be related to the response variable via a ''link function'' and by allowing the magnitude of the variance of each measurement to be a function of its predicted value. Generalized linear models were formulated by John Nelder and Robert Wedderburn as a way of unifying various other statistical models, including linear regression, logistic regression and Poisson regression. They proposed an iteratively reweighted least squares method for maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) of the model parameters. MLE remains popular and is the default method on many statistical computing packages. Other approaches, including Bayesian regression and least squares fitting to variance stabilized responses, have been developed. Intuition Ordinary linear regression predicts the expected value of a given unknown quanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Design Matrix
In statistics and in particular in regression analysis, a design matrix, also known as model matrix or regressor matrix and often denoted by X, is a matrix of values of explanatory variables of a set of objects. Each row represents an individual object, with the successive columns corresponding to the variables and their specific values for that object. The design matrix is used in certain statistical models, e.g., the general linear model. It can contain indicator variables (ones and zeros) that indicate group membership in an ANOVA, or it can contain values of continuous variables. The design matrix contains data on the independent variables (also called explanatory variables), in a statistical model that is intended to explain observed data on a response variable (often called a dependent variable). The theory relating to such models uses the design matrix as input to some linear algebra : see for example linear regression. A notable feature of the concept of a design matrix i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kronecker Product
In mathematics, the Kronecker product, sometimes denoted by ⊗, is an operation on two matrices of arbitrary size resulting in a block matrix. It is a specialization of the tensor product (which is denoted by the same symbol) from vectors to matrices and gives the matrix of the tensor product linear map with respect to a standard choice of basis. The Kronecker product is to be distinguished from the usual matrix multiplication, which is an entirely different operation. The Kronecker product is also sometimes called matrix direct product. The Kronecker product is named after the German mathematician Leopold Kronecker (1823–1891), even though there is little evidence that he was the first to define and use it. The Kronecker product has also been called the ''Zehfuss matrix'', and the ''Zehfuss product'', after , who in 1858 described this matrix operation, but Kronecker product is currently the most widely used term. The misattribution to Kronecker rather than Zehfuss wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journal Of The Royal Statistical Society
The ''Journal of the Royal Statistical Society'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of statistics. It comprises three series and is published by Oxford University Press for the Royal Statistical Society. History The Statistical Society of London was founded in 1834, but would not begin producing a journal for four years. From 1834 to 1837, members of the society would read the results of their studies to the other members, and some details were recorded in the proceedings. The first study reported to the society in 1834 was a simple survey of the occupations of people in Manchester, England. Conducted by going door-to-door and inquiring, the study revealed that the most common profession was mill-hands, followed closely by weavers. When founded, the membership of the Statistical Society of London overlapped almost completely with the statistical section of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. In 1837 a volume of ''Transactions of the Statistical Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Khatri–Rao Product
In mathematics, the Khatri–Rao product or block Kronecker product of two partitioned matrix, partitioned matrices \mathbf and \mathbf is defined as : \mathbf \ast \mathbf = \left(\mathbf_ \otimes \mathbf_\right)_ in which the ''ij''-th block is the sized Kronecker product of the corresponding blocks of A and B, assuming the number of row and column partitions of both Matrix (mathematics), matrices is equal. The size of the product is then . For example, if A and B both are partitioned matrices e.g.: : \mathbf = \left[ \begin \mathbf_ & \mathbf_ \\ \hline \mathbf_ & \mathbf_ \end \right] = \left[ \begin 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 & 6 \\ \hline 7 & 8 & 9 \end \right] ,\quad \mathbf = \left[ \begin \mathbf_ & \mathbf_ \\ \hline \mathbf_ & \mathbf_ \end \right] = \left[ \begin 1 & 4 & 7 \\ \hline 2 & 5 & 8 \\ 3 & 6 & 9 \end \right] , we obtain: : \mathbf \ast \mathbf = \left[ \begin \mathbf_ \otimes \mathbf_ & \mathbf_ \otimes \mathbf_ \\ \hline \mathbf_ \otimes \mathbf_ & \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vadym Slyusar
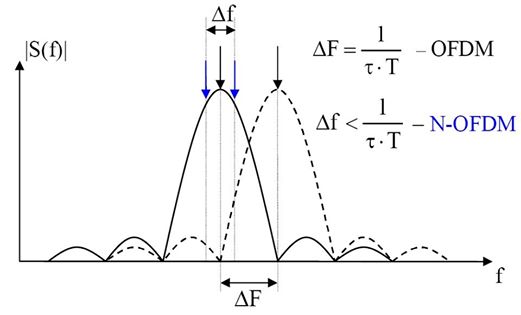
Vadym Slyusar (born 15 October 1964, vil. Kolotii, Reshetylivka Raion, Poltava region, Ukraine) is a Soviet and Ukrainian scientist, Professor, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Honored Scientist and Technician of Ukraine, founder of tensor-matrix theory of digital antenna arrays (DAAs), N-OFDM and other theories in fields of radar systems, smart antennas for wireless communications and digital beamforming. Scientific results N-OFDM theory In 1992 Vadym Slyusar patented the 1st optimal demodulation method for N-OFDM signals after Fast Fourier transform (FFT).RU2054684 (C1) G01R 23/16. Amplitude-frequency response measurement technique// Slyusar V. – Appl. Number SU 19925055759, Priority Data: 19920722. – Official Publication Data: 1996-02-2/ref> From this patent was started the history of N-OFDM signals theory. In this regard, W. Kozek and A. F. Molisch wrote in 1998 about N-OFDM signals with the sub-carrier spacing \alpha before the conference paper of I. Darwazeh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Regression Models
Regression or regressions may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Regression'' (film), a 2015 horror film by Alejandro Amenábar, starring Ethan Hawke and Emma Watson * ''Regression'' (magazine), an Australian punk rock fanzine (1982–1984) * ''Regressions'' (album), 2010 album by Cleric Computing * Software regression, the appearance of a bug in functionality that was working correctly in a previous revision ** Regression testing, a software testing method which seeks to uncover regression bugs Hypnosis * Age regression in therapy, a process claiming to retrieve memories * Past life regression, a process claiming to retrieve memories of previous lives Science * Marine regression, coastal advance due to falling sea level, the opposite of marine transgression * Regression (medicine), a characteristic of diseases to express lighter symptoms or less extent (mainly for tumors), without disappearing totally * Regression (psychology), a defensive reaction to some unaccepted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |