|
Gavialids
Gavialidae is a family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Many extinct members are known from a broader range, including the recently extinct ''Hanyusuchus''. Gavialids are generally regarded as lacking the jaw strength to capture the large mammalian prey favoured by crocodiles and alligators of similar size so their thin snout is best used to catch fish, however the false gharial has been found to have a generalist diet with mature adults preying upon larger vertebrates, such as ungulates. Taxonomy The family Gavialidae was proposed by Arthur Adams in 1854 for reptiles with a very long and slender muzzle, webbed feet and nearly equal teeth. It is currently recognized as a crown group, meaning that it only includes the last common ancestor of all extant (living) gavialids (the gharial and false gha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gharial
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males have a distinct boss at the end of the snout, which resembles an earthenware pot known as a ''ghara'', hence the name "gharial". The gharial is well adapted to catching fish because of its long, narrow snout and 110 sharp, interlocking teeth. The gharial probably evolved in the northern Indian subcontinent. Fossil gharial remains were excavated in Pliocene deposits in the Sivalik Hills and the Narmada River valley. It currently inhabits rivers in the plains of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is the most thoroughly aquatic crocodilian, and leaves the water only for basking and building nests on moist sandbanks. Adults mate at the end of the cold season. Females congregate in spring to dig nests, in which they lay 20–95 eggs. They guard t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogenomics
Paleogenomics is a field of science based on the reconstruction and analysis of genomic information in extinct species. Improved methods for the extraction of ancient DNA (aDNA) from museum artifacts, ice cores, archeological or paleontological sites, and next-generation sequencing technologies have spurred this field. It is now possible to detect genetic drift, ancient population migration and interrelationships, the evolutionary history of extinct plant, animal and ''Homo'' species, and identification of phenotypic features across geographic regions. Scientists can also use paleogenomics to compare ancient ancestors against modern-day humans. The rising importance of paleogenomics is evident from the fact that the 2022 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine was awarded to a Swedish geneticist Svante Pääbo 955- who worked on paleogenomics. Background Initially, aDNA sequencing involved cloning small fragments into bacteria, which proceeded with low efficiency due to the oxidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
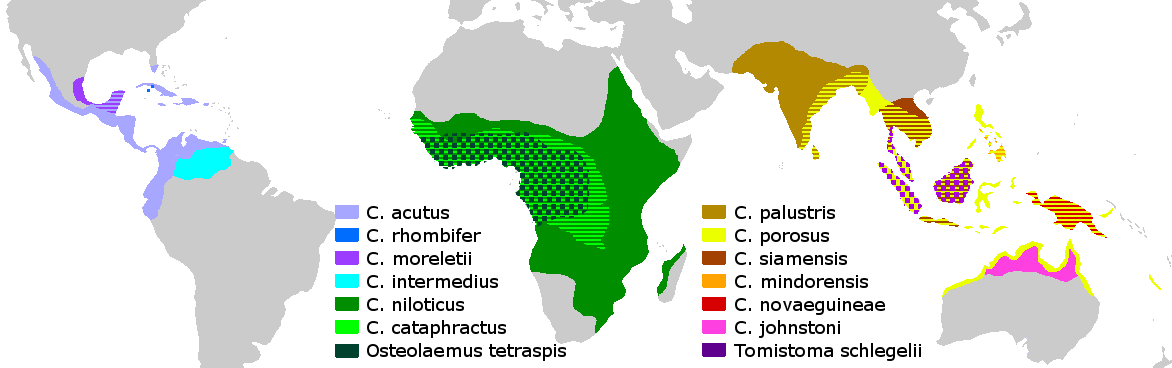
Crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living relatives of birds, as the two groups are the only known survivors of the Archosauria. Members of the order's total group, the clade Pseudosuchia, appeared about 250 million years ago in the Early Triassic period, and diversified during the Mesozoic era. The order Crocodilia includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term 'crocodiles' is sometimes used to refer to all of these, crocodilians is a less ambiguous vernacular term for members of this group. Large, solidly built, lizard-like reptiles, crocodilians have long flattened snouts, laterally compressed tails, and eyes, ears, and nostrils at the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geologic map o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip Dating
Tip dating is a technique used in molecular dating that allows the inference of time-calibrated phylogenetic trees. Its defining feature is that it uses the ages of the samples to provide time information for the analysis, in contrast with traditional 'node dating' methods that require age constraints to be applied to the internal nodes of the evolutionary tree. In tip dating, morphological data and molecular data are typically analysed together to estimate the evolutionary relationships (tree topology) and the divergence times among lineages (node times); this approach is also known as 'total-evidence dating'. However, tip dating can also be used to analyse data sets that only comprise morphological characters or that only comprise molecular characters (e.g., data sets that include samples of ancient DNA or of serially sampled viruses). Tip dating has been implemented in Bayesian phylogenetic software and typically draws on the fossilised birth-death model for evolution. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant taxon, extant members of the order (biology), order Crocodilia, which includes the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae) among other extinct taxa. Although they appear similar, crocodiles, alligators and the gharial belong to separate biological family (biology), families. The gharial, with its narrow snout, is easier to distinguish, while Morphology (biology), morphological differences are more difficult to spot in crocodiles and alligators. The most obvious external differences are visible in the head, with crocodiles having narrower and longer heads, with a more V-shaped than a U-shaped snout compared to alligators and caimans. Another obvious trait is that the upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodyloidea
Crocodyloidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodilians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Gavialoidea, and it includes the crocodiles. Crocodyloidea may also include the extinct Mekosuchinae, native to Australasia from the Eocene to the Holocene, although this is disputed. Classification Cladistically, it is defined as ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile) and all crocodylians more closely related to ''C. niloticus'' than to either ''Alligator mississippiensis'' (the American alligator) or ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial). This is a stem-based taxon, stem-based definition for crocodiles Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant memb ..., and is more inclusive than the crown group Crocodylidae. As a crown group, Crocodylidae only includes the last common anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialoidea
Gavialoidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodylians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Crocodyloidea. Although many extinct species are known, only the gharial ''Gavialis gangeticus'' and the false gharial ''Tomistoma schlegelii'' are alive today, with ''Hanyusuchus'' having become extinct in the last few centuries. Extinct South American gavialoids likely dispersed in the mid Tertiary from Africa and Asia. Fossil remains of the Puerto Rican gavialoid '' Aktiogavialis puertorisensis'' were discovered in a cave located in San Sebastián, Puerto Rico and dated to the Oligocene. This individual is thought to have crossed the Atlantic coming from Africa, indicating that this species was able to withstand saltwater. Classification Gavialoidea is cladistically defined as ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial) and all crocodylians closer to it than to ''Alligator mississippiensis'' (the American alligator) or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). This is a stem-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longirostres
Longirostres is a clade of crocodilians that includes the crocodiles and the gavialids, to the exclusion of the alligatoroids. Named in 2003 by Harshman ''et al.'', Longirostres is a crown group defined phylogenetically as including the last common ancestor of ''Crocodylus niloticus'' and ''Gavialis gangeticus'' and all of its descendants. Traditionally, crocodiles and alligators were considered more closely related and grouped together in the clade Brevirostres, to the exclusion of the gharials. This classification was based on morphological studies primarily focused on analyzing skeletal traits of living and extinct fossil species. However, recent molecular studies using DNA sequencing DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Th ... have rejected Brevirostres upon finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics And Evolution
''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of evolutionary biology and phylogenetics. The journal is edited by E.A. Zimmer. Indexing The journal is indexed in: *EMBiology *Journal Citation Reports *Scopus Scopus is Elsevier's abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles (22,794 active titles and 13,583 inactive titles) from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-l ... * Web of Science External links * Elsevier academic journals Evolutionary biology journals Phylogenetics Molecular biology Publications established in 1992 Monthly journals {{biology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |