|
Gardner, Martin
Martin Gardner (October 21, 1914May 22, 2010) was an American popular mathematics and popular science writer with interests also encompassing scientific skepticism, micromagic, philosophy, religion, and literatureespecially the writings of Lewis Carroll, L. Frank Baum, and G. K. Chesterton.Martin (2010) He was also a leading authority on Lewis Carroll. ''The Annotated Alice'', which incorporated the text of Carroll's two Alice books, was his most successful work and sold over a million copies. He had a lifelong interest in magic and illusion and in 1999, MAGIC magazine named him as one of the "100 Most Influential Magicians of the Twentieth Century". He was considered the doyen of American puzzlers. He was a prolific and versatile author, publishing more than 100 books. Gardner was best known for creating and sustaining interest in recreational mathematicsand by extension, mathematics in generalthroughout the latter half of the 20th century, principally through his "Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulsa, Oklahoma
Tulsa () is the second-largest city in the state of Oklahoma and 47th-most populous city in the United States. The population was 413,066 as of the 2020 census. It is the principal municipality of the Tulsa Metropolitan Area, a region with 1,023,988 residents. The city serves as the county seat of Tulsa County, the most densely populated county in Oklahoma, with urban development extending into Osage, Rogers, and Wagoner counties. Tulsa was settled between 1828 and 1836 by the Lochapoka Band of Creek Native American tribe and most of Tulsa is still part of the territory of the Muscogee (Creek) Nation. Historically, a robust energy sector fueled Tulsa's economy; however, today the city has diversified and leading sectors include finance, aviation, telecommunications and technology. Two institutions of higher education within the city have sports teams at the NCAA Division I level: Oral Roberts University and the University of Tulsa. As well, the University of Oklaho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Evans Award
The Mathematical Association of America (MAA) is a professional society that focuses on mathematics accessible at the undergraduate level. Members include university, college, and high school teachers; graduate and undergraduate students; pure and applied mathematicians; computer scientists; statisticians; and many others in academia, government, business, and industry. The MAA was founded in 1915 and is headquartered at 1529 18th Street, Northwest in the Dupont Circle neighborhood of Washington, D.C. The organization publishes mathematics journals and books, including the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' (established in 1894 by Benjamin Finkel), the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Mission and Vision The mission of the MAA is to advance the understanding of mathematics and its impact on our world. We envision a society that values the power and beauty of mathematics and fully realizes its potential to promote human flourishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
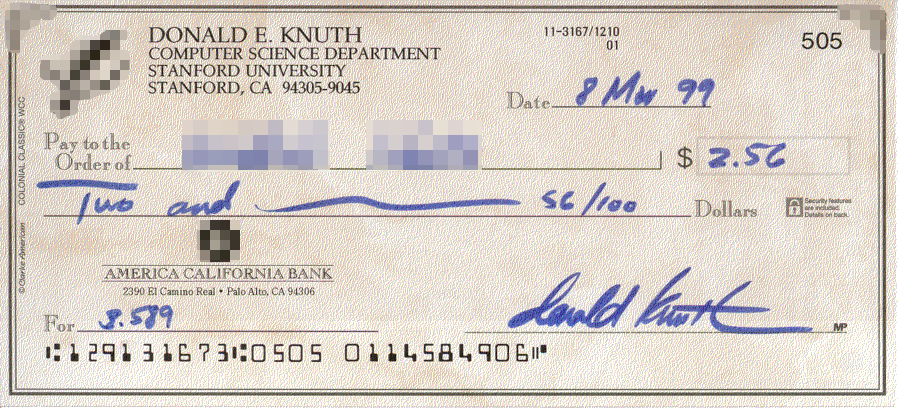
Donald Knuth
Donald Ervin Knuth ( ; born January 10, 1938) is an American computer scientist, mathematician, and professor emeritus at Stanford University. He is the 1974 recipient of the ACM Turing Award, informally considered the Nobel Prize of computer science. Knuth has been called the "father of the analysis of algorithms". He is the author of the multi-volume work ''The Art of Computer Programming'' and contributed to the development of the rigorous analysis of the computational complexity of algorithms and systematized formal mathematical techniques for it. In the process, he also popularized the asymptotic notation. In addition to fundamental contributions in several branches of theoretical computer science, Knuth is the creator of the TeX computer typesetting system, the related METAFONT font definition language and rendering system, and the Computer Modern family of typefaces. As a writer and scholar, Knuth created the WEB and CWEB computer programming systems designed to encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Shermer
Michael Brant Shermer (born September 8, 1954) is an American science writer, historian of science, executive director of The Skeptics Society, and founding publisher of ''Skeptic'' magazine, a publication focused on investigating pseudoscientific and supernatural claims. The author of over a dozen books, Shermer is known for engaging in debates on pseudoscience and religion in which he emphasizes scientific skepticism. Shermer was the co-producer and co-host of ''Exploring the Unknown'', a 13-hour Fox Family television series broadcast in 1999. From April 2001 to January 2019, he contributed a monthly ''Skeptic'' column to ''Scientific American'' magazine. Shermer was raised in a non-religious household, before converting to christian fundamentalism as a teenager. He stopped believing in God during graduate school, influenced by a traumatic accident that left his then-girlfriend paralyzed. He identifies as an agnostic and an atheist,Shermer, Michael (June 2005)"Why I Am An Ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Hofstadter
Douglas Richard Hofstadter (born February 15, 1945) is an American scholar of cognitive science, physics, and comparative literature whose research includes concepts such as the sense of self in relation to the external world, consciousness, analogy-making, artistic creation, literary translation, and discovery in mathematics and physics. His 1979 book '' Gödel, Escher, Bach: An Eternal Golden Braid'' won both the Pulitzer Prize for general nonfiction"General Nonfiction" . ''Past winners and finalists by category''. The Pulitzer Prizes. Retrieved March 17, 2012. and a (at that time called The American Book Award) for Science. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, (18 May 1872 – 2 February 1970) was a British mathematician, philosopher, logician, and public intellectual. He had a considerable influence on mathematics, logic, set theory, linguistics, artificial intelligence, cognitive science, computer science and various areas of analytic philosophy, especially philosophy of mathematics, philosophy of language, epistemology, and metaphysics.Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy"Bertrand Russell" 1 May 2003. He was one of the early 20th century's most prominent logicians, and a founder of analytic philosophy, along with his predecessor Gottlob Frege, his friend and colleague G. E. Moore and his student and protégé Ludwig Wittgenstein. Russell with Moore led the British "revolt against idealism". Together with his former teacher A. N. Whitehead, Russell wrote ''Principia Mathematica'', a milestone in the development of classical logic, and a major attempt to reduce the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sam Loyd
Samuel Loyd (January 30, 1841 – April 10, 1911), was an American chess player, chess composer, puzzle author, and recreational mathematics, recreational mathematician. Loyd was born in Philadelphia but raised in New York City. As a chess composer, he authored a number of chess problems, often with interesting themes. At his peak, Loyd was one of the best chess players in the US, and was ranked 15th in the world, according to chessmetrics.com. He played in the strong Paris 1867 chess tournament (won by Ignatz von Kolisch) with little success, placing near the bottom of the field. Following his death, his book ''Cyclopedia of 5000 Puzzles'' was published (1914) by his son. His son, named after his father, dropped the "Jr" from his name and started publishing reprints of his father's puzzles. Loyd (senior) was inducted into the US Chess Hall of Fame in 1987. Reputation Loyd is widely acknowledged as one of America's great puzzle writers and popularizers, often mentioned as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dudeney
Henry Ernest Dudeney (10 April 1857 – 23 April 1930) was an English author and mathematician who specialised in logic puzzles and mathematical games. He is known as one of the country's foremost creators of mathematical puzzles. Early life Dudeney was born in the village of Mayfield, East Sussex, England, one of six children of Gilbert and Lucy Dudeney. His grandfather, John Dudeney, was well known as a self-taught mathematician and shepherd; his initiative was much admired by his grandson. Dudeney learned to play chess at an early age, and continued to play frequently throughout his life. This led to a marked interest in mathematics and the composition of puzzles. Chess problems in particular fascinated him during his early years. Career Although Dudeney spent his career in the Civil Service, he continued to devise various problems and puzzles. Dudeney's first puzzle contributions were submissions to newspapers and magazines, often under the pseudonym of "Sphinx." Much of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Gödel
Kurt Friedrich Gödel ( , ; April 28, 1906 – January 14, 1978) was a logician, mathematician, and philosopher. Considered along with Aristotle and Gottlob Frege to be one of the most significant logicians in history, Gödel had an immense effect upon scientific and philosophical thinking in the 20th century, a time when others such as Bertrand Russell,For instance, in their "Principia Mathematica' (''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' edition). Alfred North Whitehead, and David Hilbert were using logic and set theory to investigate the foundations of mathematics, building on earlier work by the likes of Richard Dedekind, Georg Cantor and Frege. Gödel published his first incompleteness theorem in 1931 when he was 25 years old, one year after finishing his doctorate at the University of Vienna. The first incompleteness theorem states that for any ω-consistent recursive axiomatic system powerful enough to describe the arithmetic of the natural numbers (for example P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Carnap
Rudolf Carnap (; ; 18 May 1891 – 14 September 1970) was a German-language philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a major member of the Vienna Circle and an advocate of logical positivism. He is considered "one of the giants among twentieth-century philosophers." Biography Carnap's father had risen from being a poor ribbon-weaver to be the owner of a ribbon-making factory. His mother came from an academic family; her father was an educational reformer and her oldest brother was the archaeologist Wilhelm Dörpfeld. As a ten-year-old, Carnap accompanied Wilhelm Dörpfeld on an expedition to Greece. Carnap was raised in a profoundly religious Protestant family, but later became an atheist. He began his formal education at the Barmen Gymnasium and the Gymnasium in Jena. From 1910 to 1914, he attended the University of Jena, intending to write a thesis in physics. He also intently studied Immanuel Kant's '' Critique of Pure Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel De Unamuno
Miguel de Unamuno y Jugo (29 September 1864 – 31 December 1936) was a Spanish essayist, novelist, poet, playwright, philosopher, professor of Greek and Classics, and later rector at the University of Salamanca. His major philosophical essay was ''The Tragic Sense of Life'' (1912), and his most famous novel was '' Abel Sánchez: The History of a Passion'' (1917), a modern exploration of the Cain and Abel story. Biography Miguel de Unamuno was born in Bilbao, a port city of the Basque Country, Spain, the son of Félix de Unamuno and Salomé Jugo. As a young man, he was interested in the Basque language, which he could speak, and competed for a teaching position in the ''Instituto de Bilbao'' against Sabino Arana. The contest was finally won by the Basque scholar Resurrección María de Azkue. Unamuno worked in all major genres: the essay, the novel, poetry, and theater, and, as a modernism, modernist, contributed greatly to dissolving the boundaries between genres. There i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 – April 19, 1914) was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism". Educated as a chemist and employed as a scientist for thirty years, Peirce made major contributions to logic, a subject that, for him, encompassed much of what is now called epistemology and the philosophy of science. He saw logic as the formal branch of semiotics, of which he is a founder, which foreshadowed the debate among logical positivists and proponents of philosophy of language that dominated 20th-century Western philosophy. Additionally, he defined the concept of abductive reasoning, as well as rigorously formulated mathematical induction and deductive reasoning. As early as 1886, he saw that logic gate, logical operations could be carried out by electrical switching circuits. The same idea was used decades later to produce digital computers. See Also In 1934, the philosopher Paul W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |