|
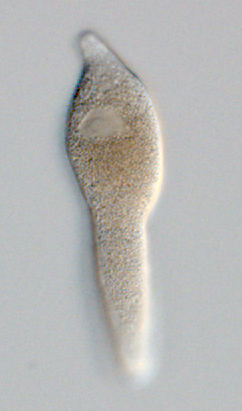
Ganymedidae
The Ganymedidae are a family of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. Taxonomy There is one genus in this family - ''Ganymedes''. The type species for this family and genus is ''Ganymedes anaspidis''. Other species in this genus include ''Ganymedes oaklandi'' and ''Ganymedes themistos''. History This family was created by Huxley in 1910.Huxley JS (1910) On ''Ganymedes anaspidis'' (''nov. gen''., ''nov. sp''.), a gregarine from the digestive tract of ''Anaspides tasmaniæ'' (Thompson). J Cell Sci s2-55: 155-175 Description Species in this taxon infect crustaceans. They are spread by the orofaecal route. The trophozoites inhabit the gut lumen. They are cylindrical in shape with folds along the surface of the cell. The nucleus is central. The nucleus is off center. A spherical ball like structure may be present at the anterior end of the cell and connected to the body of the cell by a narrow neck. A cup like depression is present at the posterior end. After undergoing syzyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aseptatorina
''Aseptatorina'' is a suborder of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia Taxonomy There are eleven families recognised in this suborder. There are ~400 species in these families. Five families — ''Allantocystidae'', ''Diplocystidae'', ''Enterocystidae'', ''Ganymedidae'' and ''Schaudinnellidae'' — have only one genus. ''Aikinetocystidae'' has two genera. Two families in this suborder — ''Ganymedidae'' and ''Thiriotiidae'' — infect crustacean Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...s. The taxonomy of this suborder may be in need of revision as it has been shown based on SSU 18S rDNA sequences that four families — ''Ganymedidae'' from the Aseptatorina and ''Cephalolobidae'', ''Porosporidae'' and ''Uradiophoridae'' from the Septatorina appear to form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganymedes (protozoa)
Ganymede most commonly refers to: *Ganymede (mythology), Trojan prince in Greek mythology * Ganymede (moon), Jupiter's largest moon, named after the mythological character Ganymede, Ganymed or Ganymedes may also refer to: *Ganymede (band), a 2000s American band *Ganymed (band), a 1970s Austrian disco band *Ganymedes (eunuch), tutor of Arsinoe IV of Egypt and adversary to Julius Caesar * "Ganymed" (Goethe), a poem by Goethe *Ganymede (software), a GPL-licensed network directory management system *1036 Ganymed, an asteroid * , British prison hulk that was moored in Chatham Harbour, Kent, England * , a United States Navy vessel in World War II * Rosalind (''As You Like It'') or Ganymede, a character in ''As You Like It'' by William Shakespeare * Ganymede, a Marvel Comics character See also *Ganymede City, a term coined by Arthur C. Clarke in his science fiction novel ''3001: The Final Odyssey'' *Ganymede Heights, rounded ridges with extensive rock outcrops on the eastern side of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis (''Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis (''Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis (''Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis (''Cystoisosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conoidasida
Conoidasida is a class of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses – the coccidia and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated conoid. Gregarines tend to parasitize invertebrates with the mature gamonts being extracellular, the coccidia mostly infect vertebrates and have intracellular gamonts. Description A conoid is found in most species and when present forms complete but truncated cone. Sexual and asexual reproduction are present in life cycle of all species. Each zygote normally forms an oocyst wall within which it undergoes meiosis. This is sometimes followed by mitosis. This process of sporogony produces mobile vermiform infectious sporozoites. Multiple mitotic divisions ( schizogony) also occur during merogony of the feeding stages (trophozoites) and during gametogony. Motility Microgametes of some species are flagellated. Locomotion of other gametes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. However, gregarines are closely related to both ''Toxoplasma'' and ''Plasmodium'', which cause toxoplasmosis and malaria, respectively. Both protists use protein complexes similar to those that are formed by the gregarines for gliding motility and invading target cells. This makes them excellent models for studying gliding motility with the goal of developing treatment options for toxoplasmosis and malaria. Thousands of different species of gregarines are expected to be found in insects, and 99% of these gregarines still need to be described. Each insect can be the host of multiple species. One of the most studied gregarines is ''Gregarina garnhami''. In general, gregarines are regarded as very successful parasites, as their hosts are spread over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugregarinorida
The ''Eugregarinorida'' are the most large and diverse order of gregarines — parasitic protists belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa. Eugregarines are found in marine, freshwater and terrestrial habitats. These species possess large trophozoites that are significantly different in morphology and behavior from the sporozoites. This taxon contains most of the known gregarine species. These protozoa are common parasites of many invertebrates including insects and polychete worms. Taxonomy Eugregarinorida has three recognised suborders: Aseptatorina, Blastogregarinorina and Septatorina. The intestinal eugregarines are separated into septate — suborder Septatina — and aseptate — suborder Aseptatina — depending on whether the trophozoite is superficially divided by a transverse septum. The marine gregarines are the most poorly studied members of this order. The eugregarines have been classified into 27 families with ~244 genera, 14 of which have more than 25 species each. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contained unity" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoites
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing '' Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the '' Giardia'' group. (The complement of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled cyst form). Life cycle stages Trophozoite and cyst stages are shown in the life cycle of '' Balantidium coli'' the causative agent of balantidiasis. In the apicomplexan life cycle the trophozoite undergoes schizogony (asexual reproduction) and develops into a schizont which contains merozoites Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is .... The trophozoite life stage of '' Giardia'' colonizes and proliferates in the small intestine. Trophozoites develop during the course of the infection into cysts wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |