|
Gannet Oil And Gas Field
Gannet is an oil and gas field located in the United Kingdom's continental shelf in the North Sea. It is east of Aberdeen, and the water depth at the Gannet offshore installation is . The field is located in Blocks 22/21, 22/25, 22/26 and 21/30. It is half-owned by Royal Dutch Shell (50%) and partly by ExxonMobil (50%) and has been operated by Shell UK Ltd since ‘first oil’ in November 1993. The Gannet A installation is the host platform for subsea tiebacks designated Gannet B to G. Like most Shell fields in the central and northern North Sea the field is named after a sea bird the gannet. The Gannet reservoirs The Gannet reservoirs are located at a depth of between and extend over several blocks. They comprises good quality turbiditic sands of a Tertiary age (Tay, Rogaland, Forties, Lista and Andrew Formations) and were discovered in 1973. The formation comprises a mixture of hydrocarbon reservoirs. : Design The topsides for Gannet were designed by Matthew Hall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and access t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulmar Oil Field
The Fulmar Oilfield is situated 312 km east of Dundee, Scotland, United Kingdom in block number 30/16 and 30/11b. It is operated by Repsol Sinopec who took over from the previous operator, Shell at the end of 2006. At this time Talisman also purchased the equity of the other partners ExxonMobil and Amerada Hess. The field was discovered in December 1975 by well 30/16-6 in a water depth of 82 metres. Estimated ultimate recovery is 544 million barrels (86.5 m3) of oil. It is named after the fulmar, a sea bird. The oil reservoir is located at a depth of 3,050 metres. The "Fulmar A platform" operates above the oilfield. Production started in February 1982 from the Fulmar 'A' platform. This platform is a steel, 8 legged jacket designed by McDermott Engineering and constructed at Nigg, Easter Ross, Scotland. This jacket weighs 12,400 tonnes and supports a topside weight of around 22,560 tonnes. The jacket and platform were installed in July 1979 and June 1980. Design data for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Use And Conservation In The United Kingdom
Energy in the United Kingdom came mostly from fossil fuels in 2021. Total World energy supply and consumption, energy consumption in the United Kingdom was 142.0millionTonne of oil equivalent, tonnes of oil equivalent (1,651TWh) in 2019. In 2014, the UK had an energy consumption ''per capita'' of 2.78tonnes of oil equivalent (32.3MWh) compared to a world average of 1.92tonnes of oil equivalent (22.3MWh). Demand for electricity in 2014 was 34.42Watt, GW on average (301.7TWh over the year) coming from a total electricity generation of 335.0TWh. Successive UK governments have outlined numerous commitments to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. One such announcement was the low-carbon economy, Low Carbon Transition Plan launched by the Brown ministry in July 2009, which aimed to generate 30% electricity from renewable sources, and 40% from low carbon content fuels by 2020. Notably, the UK is Wind power in the United Kingdom, one of the best sites in Europe for wind energy, and wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Policy Of The United Kingdom
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist (due to the decline of North Sea oil production). The United Kingdom historically has a good policy record of encouraging public transport links with cities, despite encountering problems with high speed trains, which have the potential to reduce dramatically domestic and short-haul European flights. The policy does not, however, significantly encourage hybrid vehicle use or ethanol fuel use, options ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Quahog
The ocean quahog (''Arctica islandica'') is a species of edible clam, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Arcticidae. This species is native to the North Atlantic Ocean, and it is harvested commercially as a food source. This species is also known by a number of different common names, including Icelandic cyprine, mahogany clam, mahogany quahog, black quahog, and black clam. The typical ''Arctica islandica'' resembles the quahog, but the shell of the ocean quahog is rounder, the periostracum is usually black, and on the interior of the shell, the pallial line has no indentation, or sinus. Unlike the quahog, which lives intertidally and can be collected by clam digging, this species lives subtidally, and can only be collected by dredging. They grow to sizes exceeding 50 mm or two inches shell height. An individual specimen was reported to have lived 507 years, making it the longest-lived non-colonial metazoan whose age was accurately known. Life cycle and lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
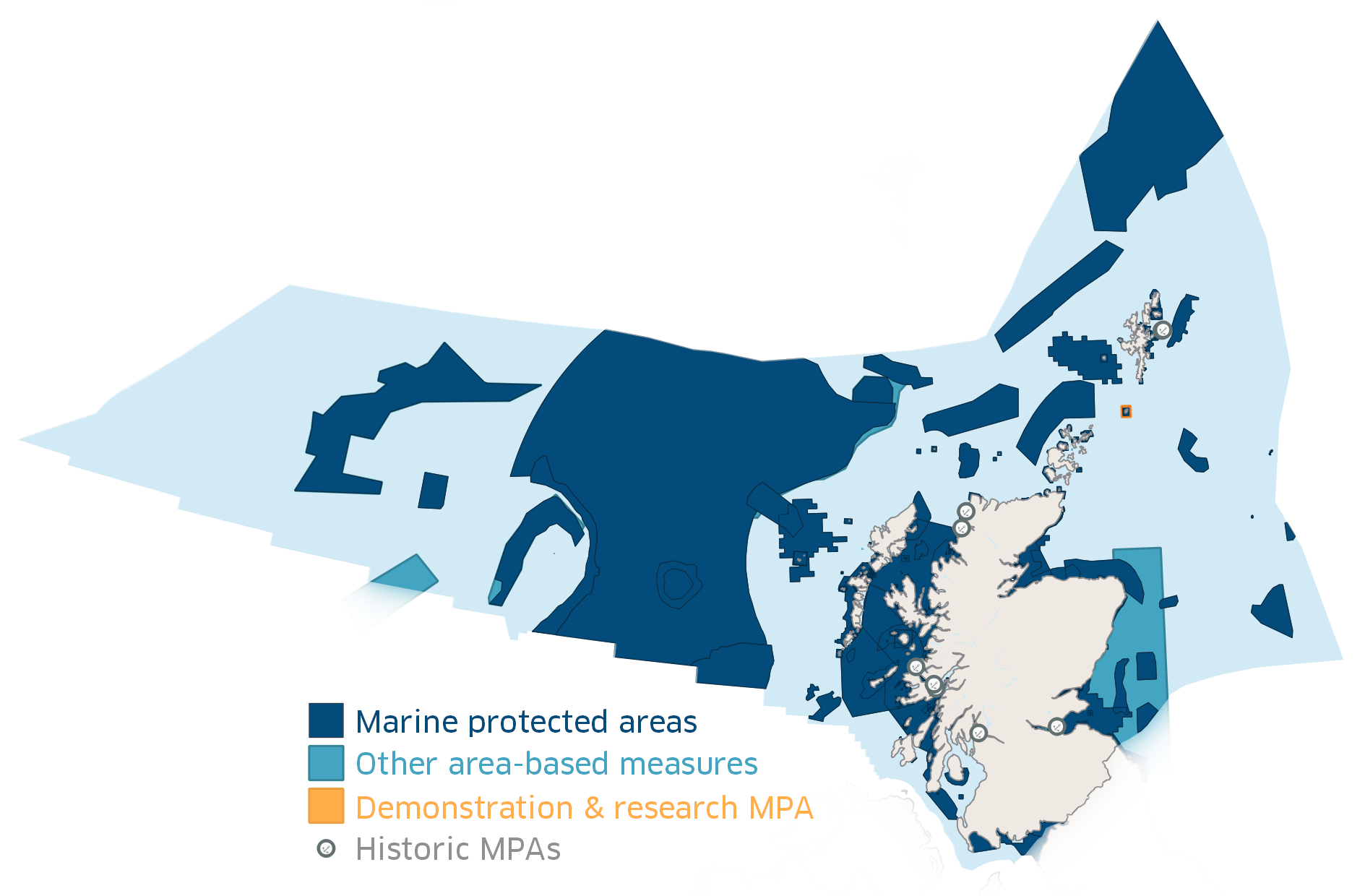
Marine Protected Areas In Scotland
In Scotland, Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are areas of sea defined so as to protect to habitats, wildlife, geology, undersea landforms, historic shipwrecks, and to demonstrate sustainable management of the sea. As of December 2020, approximately 37% of Scotland's seas are covered by the Scottish MPA network, which comprises 244 sites in total. Designation As of December 2020 Scotland's MPA network comprises 244 sites protected by a variety of different conservation designations, many of which are the same as those used on land, such as Special Protection Areas (SPA) and Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI).Scottish MPA network - Parliamentary Report. p. 11.Scottish MPA network - Parliamentary Report. p. 32. This figure includes four sites designated in December 2020: North-east Lewis; Shiant East Bank; Sea of the Hebrides; and the Southern Trench. The legal framework for designating MPAs depends on the designation: for example SSSIs are designated under the Nature Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montrose Oil Field
The Montrose oil field is a significant crude oil producing field in the UK sector of the central North Sea, 210 km east of Aberdeen. Production of oil started in 1976 and a major upgrade in 2016 extended the field life to beyond 2030. The field The Montrose oil field is located in Blocks 22/17 and 22/18 of the UK North Sea. It is named after the Scottish east coast town of Montrose. The field was discovered in November 1971 and is a Palaeocene sandstone at a depth of 8,000 feet (2,438 m). The reservoir has the following characteristics: Owners and operators The field was originally licensed to a joint venture comprising Amoco UK Petroleum Limited (30.77%), Enterprise Oil plc (30.77%), Amerada Hess Exploration Ltd (23.00%), and Texas Eastern (UK) Ltd (15.38%). The field was originally operated by Amoco (UK) Exploration Company. Ownership of the Montrose field passed from Amoco to BP to Paladin Resources, until Talisman Energy took over, then in 2012 Talisman formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Scotland
The Marine Scotland Directorate ( gd, Cùisean Mara na h-Alba) is a directorate of the Scottish Government. Marine Scotland manages Scotland's seas and freshwater fisheries along with delivery partners NatureScot and the Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Marine Scotland provides management and research of devolved responsibilities such as: * Licensing of marine activities. * Sea fisheries. * Salmon and recreational fishing. * Marine renewable energy. * Marine conservation. * Marine spatial planning. * Scientific research including sea and freshwater fisheries. * Enforcement of marine and fisheries law. History The Marine Scotland directorate was established on 1 April 2009, merging two executive agencies (Fisheries Research Services and the Scottish Fisheries Protection Agency) and the Scottish Government marine and fishery policy divisions. Staff, assets and budget Marine Scotland has around 700 staff, covering a range of professions including scientists, sea fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Produced Water
Produced water is a term used in the oil industry or geothermal industry to describe water that is produced as a byproduct during the extraction of Petroleum, oil and natural gas, or used as a medium for heat extraction. Produced water is the kind of brackish and saline water from underground formations that are brought to the surface. Oil and gas reservoirs often have water as well as hydrocarbons, sometimes in a zone that lies under the hydrocarbons, and sometimes in the same zone with the oil and gas. In geothermal plays, the produced water is usually hot. It contains steam with dissolved solutes and gases, providing important information on the geological, chemical, and hydrological characteristics of geothermal systems. Oil wells sometimes produce large volumes of water with the oil, while gas wells tend to produce water in smaller proportions. To achieve maximum Petroleum extraction, oil recovery, waterflooding is often implemented, in which water is Water injection (oil pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Fergus Gas Terminal
The St Fergus Gas Terminal is a large gas terminal found near St Fergus, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The other main UK gas terminals are at Bacton, Norfolk and the Easington, East Riding of Yorkshire. History The plant was initially developed by British Gas (now National Grid) and Total Oil Marine. The three main plants have three main pipelines each coming ashore. The National Grid plant receives gas from the other main three plants. In total, St Fergus receives around 25% of the UK's gas. The land was purchased from the historical Mess family of St. Fergus Total The Total part of the refinery opened in September 1977 for the Frigg pipeline, with another section opening in 1978 for the Vesterled pipeline. The Queen opened this plant officially on May 9, 1978. Vesterled is owned by the Gassled partners. Shell The Shell plant opened in April 1982, being officially opened by Prince Charles in October 1982, taking gas from the Brent field, via the FLAGS pipeline. Gas came from the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |