|
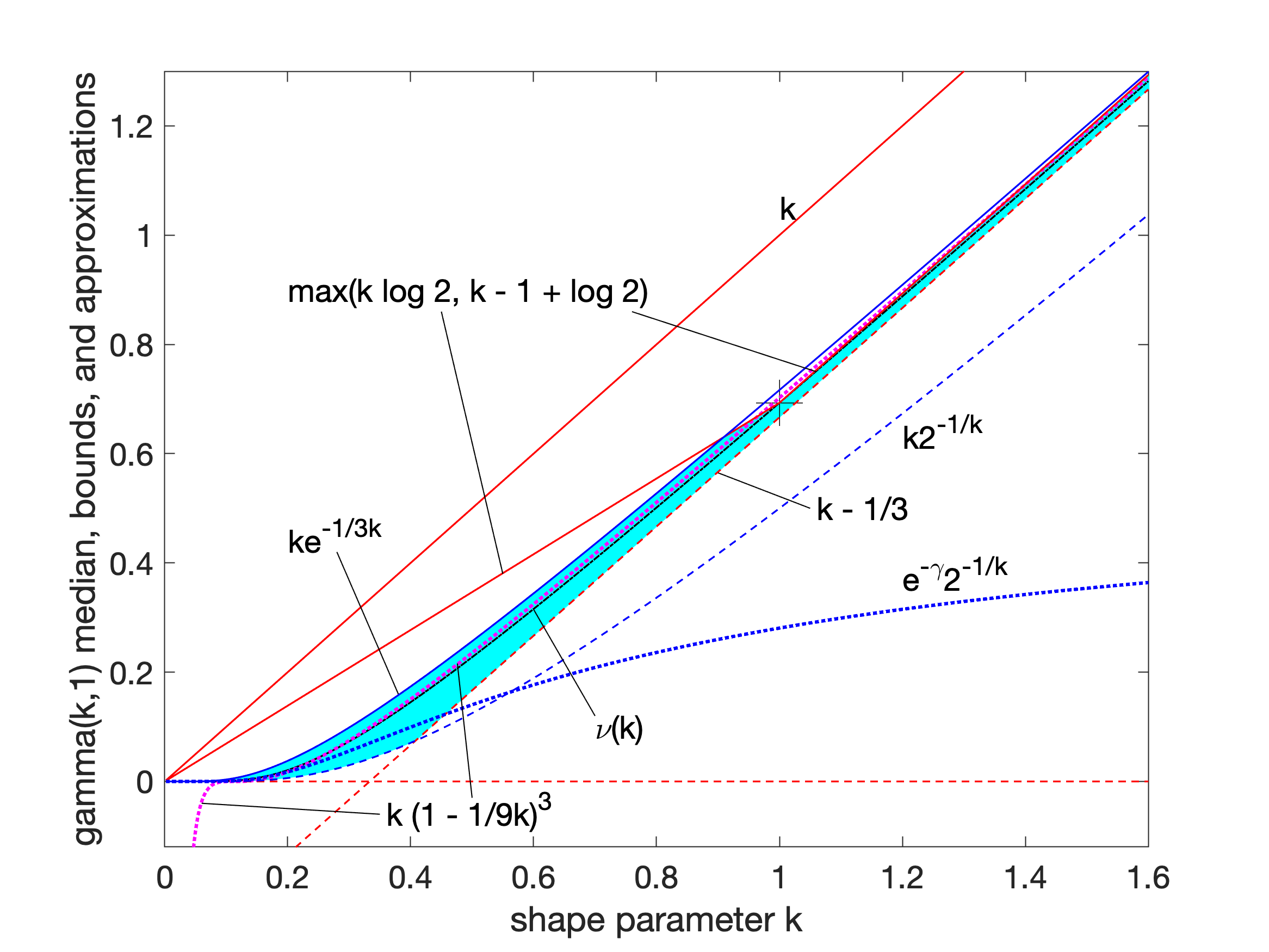
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: #With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter \theta. #With a shape parameter \alpha = k and an inverse scale parameter \beta = 1/ \theta , called a rate parameter. In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The gamma distribution is the maximum entropy probability distribution (both with respect to a uniform base measure and a 1/x base measure) for a random variable X for which E 'X''= ''kθ'' = ''α''/''β'' is fixed and greater than zero, and E n(''X'')= ''ψ''(''k'') + ln(''θ'') = ''ψ''(''α'') − ln(''β'') is fixed (''ψ'' is the digamma function). Definitions The parameterization with ''k'' and ''θ'' appears to be more common in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Distribution Pdf
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter represents either a voiced velar fricative or a Voiced palatal fricative#Palatal, voiced palatal fricative (while /g/ in foreign words is instead commonly transcribed as γκ). In the International Phonetic Alphabet and other modern Latin-alphabet based phonetic transcription#Alphabetic, phonetic notations, it represents the voiced velar fricative. History The Greek letter Gamma Γ is a grapheme derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter (''gīml'') which was rotated from the right-to-left script of Canaanite to accommodate the Greek language's writing system of left-to-right. The Canaanite grapheme represented the /g/ phoneme in the Canaanite language, and as such is cognate with ''gimel'' ג of the Hebrew alphabet. Based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Statistics
Bayesian statistics is a theory in the field of statistics based on the Bayesian interpretation of probability where probability expresses a ''degree of belief'' in an event. The degree of belief may be based on prior knowledge about the event, such as the results of previous experiments, or on personal beliefs about the event. This differs from a number of other interpretations of probability, such as the frequentist interpretation that views probability as the limit of the relative frequency of an event after many trials. Bayesian statistical methods use Bayes' theorem to compute and update probabilities after obtaining new data. Bayes' theorem describes the conditional probability of an event based on data as well as prior information or beliefs about the event or conditions related to the event. For example, in Bayesian inference, Bayes' theorem can be used to estimate the parameters of a probability distribution or statistical model. Since Bayesian statistics treats probabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Variation
In probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation (CV), also known as relative standard deviation (RSD), is a standardized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution or frequency distribution. It is often expressed as a percentage, and is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation \sigma to the mean \mu (or its absolute value, The CV or RSD is widely used in analytical chemistry to express the precision and repeatability of an assay. It is also commonly used in fields such as engineering or physics when doing quality assurance studies and ANOVA gauge R&R, by economists and investors in economic models, and in neuroscience. Definition The coefficient of variation (CV) is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation \ \sigma to the mean \ \mu , c_ = \frac. It shows the extent of variability in relation to the mean of the population. The coefficient of variation should be computed only for data measured on scales that have a meaningful zer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |