|
Galtonia
''Galtonia'' is a genus of plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Native to Southern Africa, the genus is named after Sir Francis Galton. According to some authorities it has been subsumed into ''Ornithogalum'' as a subgenus, while others prefer to keep it as a separate genus. Description These are large, vigorous perennial bulbous geophytes, with numerous wide (>5 cm) and large tapering glabrous leaves that ascend and sheathe the stem. The inflorescences are racemose, and conical or cylindrical, but sometimes corymbose. They bear nodding (rarely erect) flowers with fleshy white or greenish yellow tepals that are fused (rarely free) into a campanulate (bell like) tube that extends about half the length of the flower, but are never fragrant. The bracts are membranous and linear-acuminate, while bracteoles are absent. The pedicels are patent The Stamens, which are hidden amongst the perianth lobes where they are inserted at the base have ovate-acumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
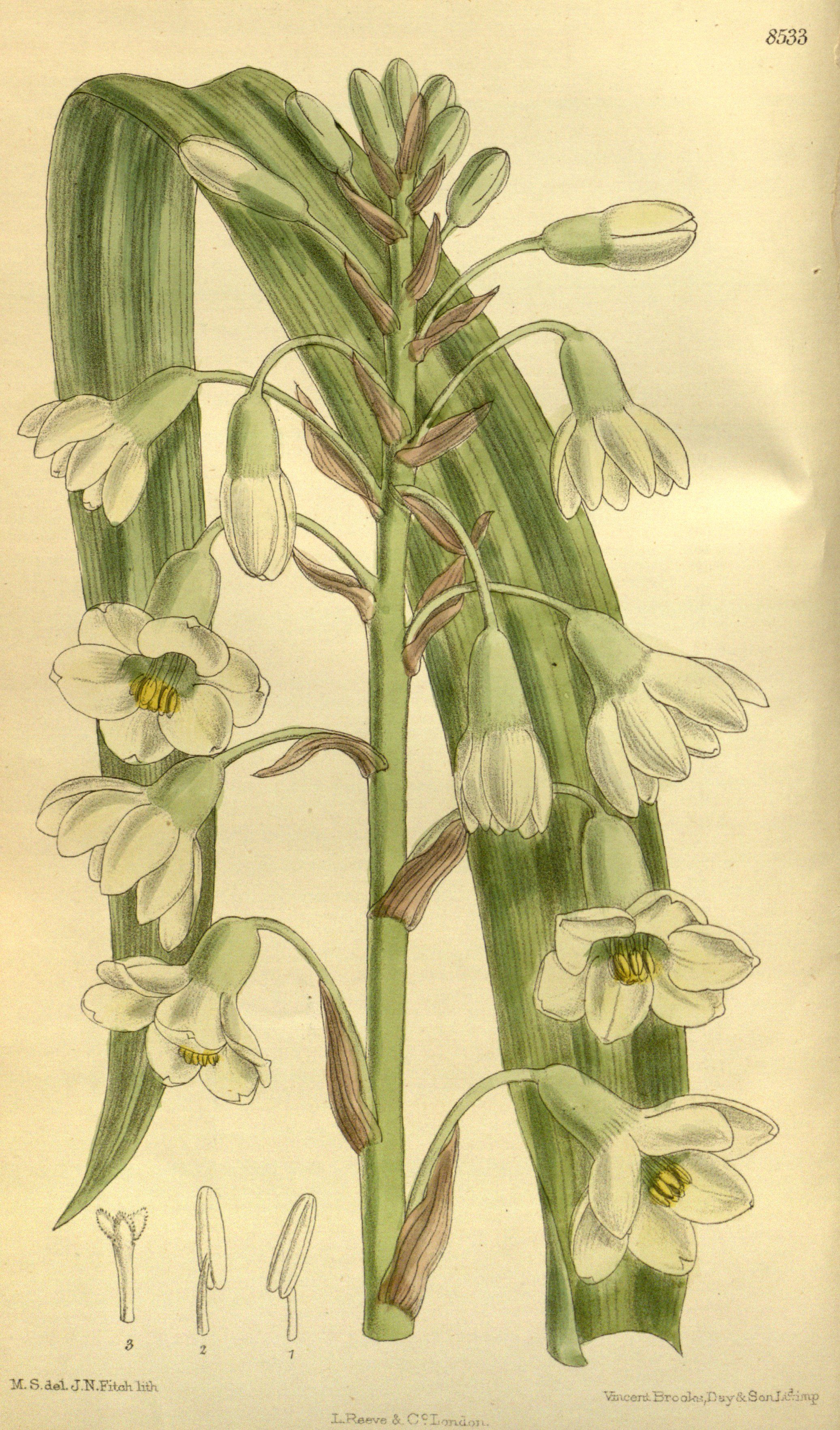
Galtonia Princeps 140-8533
''Galtonia'' is a genus of plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. Native to Southern Africa, the genus is named after Sir Francis Galton. According to some authorities it has been subsumed into ''Ornithogalum'' as a subgenus, while others prefer to keep it as a separate genus. Description These are large, vigorous perennial bulbous geophytes, with numerous wide (>5 cm) and large tapering Glossary of botanical terms#glabrous, glabrous leaves that ascend and sheathe the stem. The inflorescences are racemose, and conical or cylindrical, but sometimes corymbose. They bear nodding (rarely erect) flowers with fleshy white or greenish yellow tepals that are fused (rarely free) into a campanulate (bell like) floral tube, tube that extends about half the length of the flower, but are never fragrant. The bracts are membranous and linear-acuminate, while bracteoles are absent. The pedicels are patent The Stamens, which are hidden amongst the perianth lobes where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galtonia Candicans
''Ornithogalum candicans'', known as the summer hyacinth, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, native to moist grassland in South Africa (Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Free State, Kwazulu/Natal, Eastern Cape). It is a bulbous perennial growing to , with strap-shaped leaves and white snowdrop-like flowers in late summer. It is still widely referenced under its synonym ''Galtonia candicans''. Originally it had been designated as ''Hyacinthus candicans'', by Baker in 1870. This plant has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit The Award of Garden Merit (AGM) is a long-established annual award for plants by the British Royal Horticultural Society (RHS). It is based on assessment of the plants' performance under UK growing conditions. History The Award of Garden Merit .... Cultivation Hardiness: Z 7-10 References Bibliography * * * * candicans Taxa named by John Gilbert Baker Taxa named by John Charles Manning Taxa named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithogalum
''Ornithogalum'' is a genus of perennial plants mostly native to southern Europe and southern Africa belonging to the family Asparagaceae. Some species are native to other areas such as the Caucasus. Growing from a bulb, species have linear basal leaves and a slender stalk, up to 30 cm tall, bearing clusters of typically white star-shaped flowers, often striped with green. The common name of the genus, star-of-Bethlehem, is based on its star-shaped flowers, after the Star of Bethlehem that appears in the biblical account of the birth of Jesus. The number of species has varied considerably, depending on authority, from 50 to 300. Description ''Ornithogalum'' species are perennial bulbous geophytes with basal leaves. ''Sensu lato'', the genus has the characteristics of the tribe Ornithogaleae as a whole, since the tribe is monotypic in that sense. ''Sensu stricto'', the genus is characterised by long linear to oblong-lanceolate (lance-shaped) leaves, sometimes with a whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scilloideae
Scilloideae (named after the genus '' Scilla'', "squill") is a subfamily of bulbous plants within the family '' Asparagaceae''. Scilloideae is sometimes treated as a separate family Hyacinthaceae, named after the genus '' Hyacinthus''. Scilloideae or Hyacinthaceae include many familiar garden plants such as '' Hyacinthus'' (hyacinths), '' Hyacinthoides'' (bluebells), '' Muscari'' (grape hyacinths) and '' Scilla'' and '' Puschkinia'' (squills or scillas). Some are important as cut flowers. Scilloideae are distributed mostly in Mediterranean climates, including South Africa, Central Asia and South America. Their flowers have six tepals and six stamens with a superior ovary, which previously placed them within the lily family (Liliaceae), and their leaves are fleshy, mucilaginous, and arranged in a basal rosette. The Scilloideae, like most lily-like monocots, were at one time placed in a very broadly defined lily family (Liliaceae). The subfamily is recognized in modern classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Decaisne
Joseph Decaisne (7 March 1807 – 8 January 1882) was a French botanist and agronomist. He became an ''aide-naturaliste'' to Adrien-Henri de Jussieu (1797-1853), who served as the chair of rural botany. It was during this time that he began to study plants brought back by various travelers like those of Victor Jacquemont (1801-1832) from Asia. Decaisne used applied research, most notably on the agronomy of the madder, the yam and the ramie. He was also interested in algae. Biography Although born in Brussels, Belgium, he exercised his activity exclusively in Paris. He entered in 1824 as a gardener at the ''Muséum national d'histoire naturelle'' (French museum of natural history) and became, in 1832, head of the ''carré des semis'' section. He also worked at the '' Jardin des Plantes'' and collaborated with Asa Gray. In 1847 he chaired Statistical Agriculture department in the College de France. In 1850, Decaisne followed Charles-François Brisseau de Mirbel (1776-1854) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton, FRS FRAI (; 16 February 1822 – 17 January 1911), was an English Victorian era polymath: a statistician, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto- geneticist, psychometrician and a proponent of social Darwinism, eugenics, and scientific racism. He was knighted in 1909. Galton produced over 340 papers and books. He also created the statistical concept of correlation and widely promoted regression toward the mean. He was the first to apply statistical methods to the study of human differences and inheritance of intelligence, and introduced the use of questionnaires and Statistical survey, surveys for collecting data on human communities, which he needed for genealogical and biographical works and for his anthropometrics, anthropometric studies. He was a pioneer of eugenics, coining the term itself in 1883, and also coined the phrase "nature versus nurture". His book ''Hereditary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagaceae
Asparagaceae, known as the asparagus family, is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots. The family name is based on the edible garden asparagus, '' Asparagus officinalis''. Those who live in the temperate climates may be surprised to learn that this family includes both common garden plants as well as common houseplants. The garden plants include asparagus, yucca, bluebell, and hosta, and the houseplants include snake plant, corn cane, spider plant and plumosus fern. Taxonomy In earlier classification systems, the species involved were often treated as belonging to the family Liliaceae. The APG II system of 2003 allowed two options as to the circumscription of the family: either Asparagaceae ''sensu lato'' ("in the wider sense") combining seven previously recognized families, or Asparagaceae ''sensu stricto'' ("in the strict sense") consisting of very few genera (notably '' Asparagus'', also '' Hemiphylacus''), but nevertheless to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style (botany)
The stigma () is the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the style and ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals (biotic pollination), or in rare cases from surrounding water ( hydrophily). Stigma can vary from long and slende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary (botany)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels (e.g. dicarpel or tricarpel), and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries. Fruits A fruit is the mature, ripened ovary of a flower following double fertilization in an angiosperm. Because gymnosperms do not have an ovary but reproduce through double fertilization of unprotected ovules, they produce naked seeds that do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bracts
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, especially one associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale. Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves. They may be smaller, larger, or of a different color, shape, or texture. Typically, they also look different from the parts of the flower, such as the petals or sepals. A plant having bracts is referred to as bracteate or bracteolate, while one that lacks them is referred to as ebracteate and ebracteolate, without bracts. Variants Some bracts are brightly-coloured and serve the function of attracting pollinators, either together with the perianth or instead of it. Examples of this type of bract include those of '' Euphorbia pulcherrima'' (poinsettia) and '' Bougainvillea'': both of these have large colourful bracts surrounding much smaller, less colourful flowers. In grasses, each floret (flower) is enclosed in a pair of papery bracts, called the lemma (lower bract) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma () is the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the style and ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals (biotic pollination), or in rare cases from surrounding water ( hydrophily). Stigma can vary from long and sle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adnation
Adnation in Angiosperms is the fusion of two or more whorls of a flower, e.g. stamens to petals". This is in contrast to connation, the fusion among a single whorl A whorl ( or ) is an individual circle, oval, volution or equivalent in a whorled pattern, which consists of a spiral or multiple concentric objects (including circles, ovals and arcs). Whorls in nature File:Photograph and axial plane flo .... References Plant anatomy {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(255_30)_Tulip;_cross-section.jpg)

