|
Galton Laboratory
The Galton Laboratory was a laboratory for research into eugenics and then into human genetics based at University College London in London, England. It was originally established in 1904, and became part of UCL's biology department in 1996. The ancestor of the Galton Laboratory was the Eugenics Record Office founded by Francis Galton in 1904. In 1907 the Office was reconstituted as the Galton Eugenics Laboratory as part of UCL and under the direction of Karl Pearson the Professor of Applied Mathematics. Galton financed the Laboratory and on his death left UCL enough money to create a chair in National Eugenics which Pearson filled. The Laboratory published a series of memoirs and in 1925 Pearson created the ''Annals of Eugenics'', which continues as the ''Annals of Human Genetics''. The journal has always been edited at the Galton. Pearson was succeeded as Galton Professor by R. A. Fisher in 1934. When Fisher moved to Cambridge in 1944 the laboratory was incorporated in an enlarge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
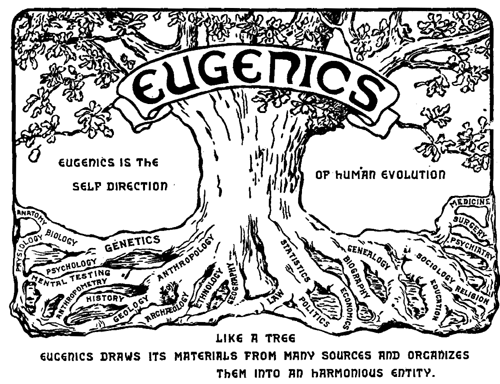
Eugenics
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRC Mammalian Development Unit
MRC may refer to Government * Medical Research Council (United Kingdom) * Medical Reserve Corps, a US network of volunteer organizations * Municipalité régionale de comté (regional county municipality), Quebec, Canada * Military Revolutionary Committee, in revolutionary Russia * Virginia Marine Resources Commission * Mail recovery center, or postal dead letter office * The Mississippi River Commission Organizations * Malaysian Red Crescent Society, a humanitarian organisation * Media Research Center, a US organization * Media Rating Council, a US organization * Medicare Rights Center, a US nonprofit organization * Migrant Resource Centre, an Australian organisation Politics * Mombasa Republican Council, a Kenyan separatist organization * Movement for the Rehabilitation of Citizens–Rurenzangemero, a Burundi political party * Mouvement républicain et citoyen (Citizen and Republican Movement), a French political party * Mouvement Révolutionnaire Congolais (Congolese Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Institutes Established In 1904
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratories In The United Kingdom
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Genetics
The history of genetics dates from the classical era with contributions by Pythagoras, Hippocrates, Aristotle, Epicurus, and others. Modern genetics began with the work of the Augustinian friar Gregor Johann Mendel. His work on pea plants, published in 1866, provided the initial evidence that, on its rediscovery in 1900, helped to establish the theory of Mendelian inheritance. In ancient Greece, Hippocrates suggested that all organs of the body of a parent gave off invisible “seeds,” miniaturized components, that were transmitted during sexual intercourse and combined in the mother’s womb to form a baby. In the Early Modern times, William Harvey's book ''On Animal Generation'' contradicted Aristotle's theories of genetics and embryology. The 1900 rediscovery of Mendel's work by Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns and Erich von Tschermak led to rapid advances in genetics. By 1915 the basic principles of Mendelian genetics had been studied in a wide variety of organisms — most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics Or Genomics Research Institutions
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics In The United Kingdom
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the context ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenics Organizations
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugenics In The United Kingdom
Eugenics ( ; ) is a fringe set of beliefs and practices that aim to improve the genetic quality of a human population. Historically, eugenicists have attempted to alter human gene pools by excluding people and groups judged to be inferior or promoting those judged to be superior. In recent years, the term has seen a revival in bioethical discussions on the usage of new technologies such as CRISPR and genetic screening, with a heated debate on whether these technologies should be called eugenics or not. The concept predates the term; Plato suggested applying the principles of selective breeding to humans around 400 BC. Early advocates of eugenics in the 19th century regarded it as a way of improving groups of people. In contemporary usage, the term ''eugenics'' is closely associated with scientific racism. Modern bioethicists who advocate new eugenics characterize it as a way of enhancing individual traits, regardless of group membership. While eugenic principles have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bette Robson
{{disambig, surname ...
Bette may refer to: People and fictional characters * Bette (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Jean-Christophe Bette, French competitive rower * The noble House of Bette: the Marquess of Lede: ** Guillaum de Bette, 1st Marquess of Lede ** Ambroise de Bette, 2nd Marquess of Lede ** Jean François de Bette, 3rd Marquess of Lede ** Emannuel de Bette, 4th Marquess of Lede ** Françoise de Bette * Bette people, a Bantu people in Nigeria Other uses * ''Bette'' (album), by Bette Midler * ''Bette'' (TV series), starring Bette Midler * Bikku Bitti, formerly Bette Peak, the highest point in Libya See also * Bete (other) * Bet (other) Black Entertainment Television (acronym BET) is an American basic cable channel targeting African-American audiences. It is owned by the CBS Entertainment Group unit of Paramount Global via BET Networks and has offices in New York City, Los An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruth Sanger
Ruth Ann Sanger (6 June 1918 – 4 June 2001) was an Australian immunogeneticist, haematologist and serologist. She was known for her work on human red cell antigens and for the genetic mapping of the human X chromosome. She was Director of the Medical Research Council Blood Group Unit, of the Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine from 1973-1983. She worked closely with Robert Russell Race from the 1940s, and they married in 1956. They co-authored many papers after 1948, and co-wrote six editions of a leading work on blood groups, ''Blood Groups in Man'', which helped make blood transfusions safer. The book was known as "Race and Sanger", which were published between 1950 and 1975. Education and early life Sanger was born in Southport, Queensland, Australia and had four siblings. Her father, Rev. Hubert Sanger, became headmaster of Armidale School in New South Wales. She was first cousins with Frederick Sanger, the biochemist and two-time winner of the Nobel prize. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRC Blood Group Unit
The MRC Blood Group Unit, originally the Blood Group Research Unit, was a research unit of the British Medical Research Council from 1946 to 1995. Initially established in the Lister Institute, it transferred to the Galton Laboratory (the Genetics department) of University College, London in 1975, the original home of its predecessor. The unit mainly used serological techniques to discover blood group antigens. Only in the last 15 years of its existence were monoclonal antibodies and molecular approaches adopted. Blood groups were used to study many aspects of human genetics: including those related to blood transfusion, linkage analysis, mosaicism and chimaerism. Directors * R.R. Race FRS, 1946–1973 * Ruth Sanger FRS, 1973–1983 * Dr Patricia Tippett, 1983–1995 Scientific achievements These are listed roughly in chronological order of the start of the research. Research on most topics was on-going with significant publications spanning several decades: for instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |