|
Gallium Halides
There are three sets of gallium halides, the trihalides where gallium has oxidation state +3, the intermediate halides containing gallium in oxidation states +1, +2 and +3 and some unstable monohalides, where gallium has oxidation state +1. Trihalides All four trihalides are known. They all contain gallium in the +3 oxidation state. Their proper names are gallium(III) fluoride, gallium(III) chloride, gallium(III) bromide and gallium(III) iodide. ; GaF3 :GaF3 is a white solid which sublimes before it melts, with an estimated melting point above 1000 °C. It contains 6 co-ordinate gallium atoms with a three-dimensional network of GaF6 octahedra sharing common corners. ; GaCl3, GaBr3 and GaI3 :These all have lower melting points than GaF3, ( GaCl3 mp 78 °C, GaBr3 mp 122 °C, GaI3 mp 212 °C) reflecting the fact that their structures all contain dimers with 4 coordinate gallium atoms and 2 bridging halogen atoms. Thus, this halides have molecular formula Ga2Cl6, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation State
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" formal charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystal, crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of Three-dimensional space (mathematics), three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive Translation (geometry), translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Compounds
Gallium compounds compounds containing the element gallium. These compounds are found primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The +1 oxidation state is also found in some compounds, although it is less common than it is for gallium's heavier congeners indium and thallium. For example, the very stable GaCl2 contains both gallium(I) and gallium(III) and can be formulated as GaIGaIIICl4; in contrast, the monochloride is unstable above 0 °C, disproportionating into elemental gallium and gallium(III) chloride. Compounds containing Ga–Ga bonds are true gallium(II) compounds, such as GaS (which can be formulated as Ga24+(S2−)2) and the dioxan complex Ga2Cl4(C4H8O2)2.Greenwood and Earnshaw, p. 240 Aqueous chemistry Strong acids dissolve gallium, forming gallium(III) salts such as (gallium nitrate). Aqueous solutions of gallium(III) salts contain the hydrated gallium ion, . Gallium(III) hydroxide, , may be precipitated from gallium(III) solutions by adding ammonia. Dehydrating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Halides
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide. The intermediate halides contain indium with oxidation states, +1, +2 and +3. Indium trihalides In all of the trihalides the oxidation state of indium is +3, and their proper names are indium(III) fluoride, indium(III) chloride, indium(III) bromide, and indium(III) iodide. The trihalides are Lewis acidic. Indium trichloride is a starting point in the production of trimethylindium which is used in the semiconductor industry. Indium(III) fluoride InF3 is a white solid, m.p. 1170 °C. Its structure contains 6 coordinate indium. Indium(III) chloride InCl3 is a white solid, m.p. 586 °C. It is obtained by oxidation of indium with chlorine. It is isostructural with AlCl3. Indium(III) bromide InB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
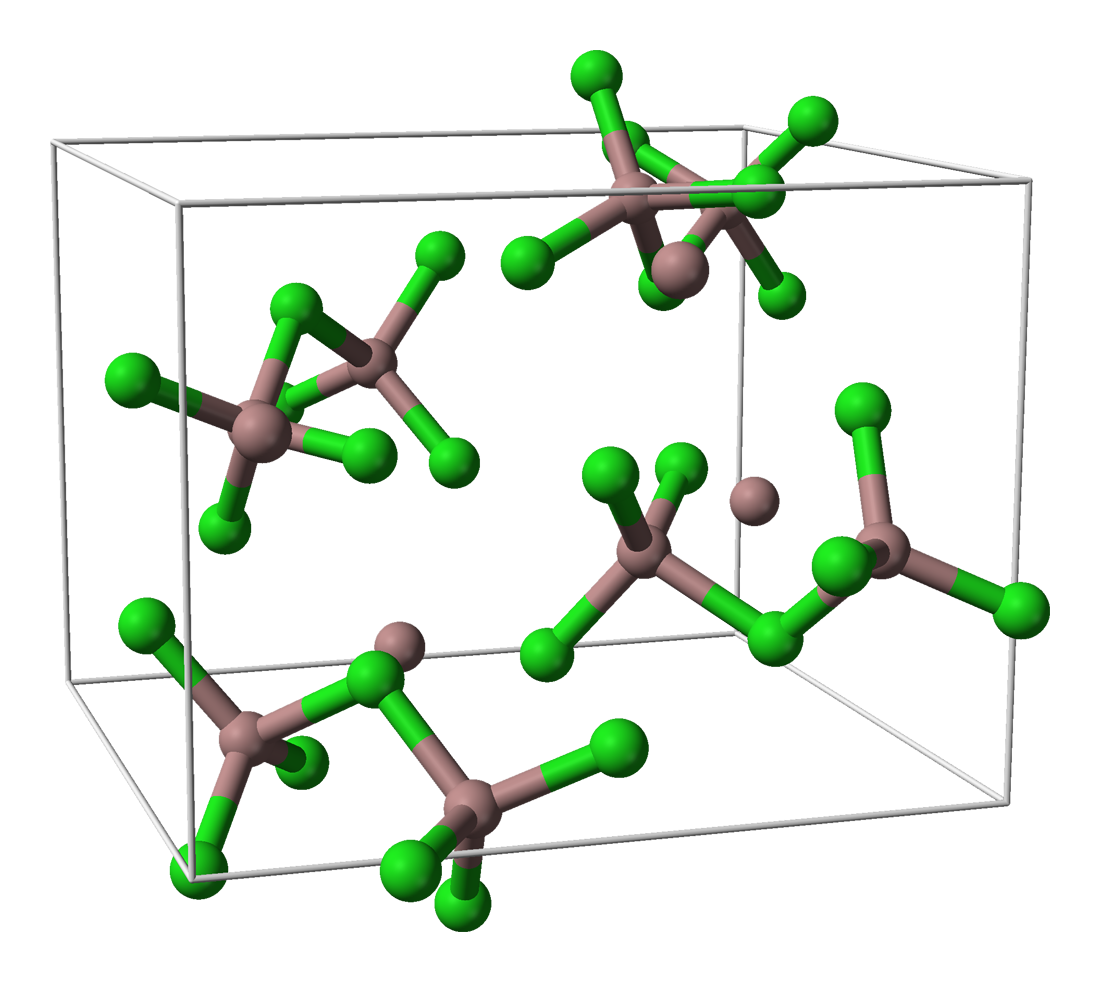
Solid "GaI" Precursor
Gallium monoiodide (GaI or Ga4I4) is a low-valent gallium species that acts as a reactive intermediate for many gallium-based products. Gallium(I) halides were first crystallographically characterized by Schnöckel and coworkers and have allowed a synthetic route to many low-valent gallium species. However, chemical syntheses that employ “GaI” rather than gallium(I) halide precursors have been increasingly investigated given the ease of synthesis of this reagent. While the synthetic method of Schnöckel and coworkers to synthesize gallium(I) halides require extraordinarily high temperatures, the straightforward preparation of “GaI” at near room temperature has allowed for the exploration of new gallium-based chemistries. Synthesis In 1990, Malcolm Green and coworkers synthesized a “GaI” species, whose method of preparation is most widely followed. They found that ultrasonication of liquid gallium metal with iodine in a toluene solvent yields a new pale green powder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Monoiodide
Gallium monoiodide (GaI or Ga4I4) is a low-valent gallium species that acts as a reactive intermediate for many gallium-based products. Gallium(I) halides were first crystallographically characterized by Schnöckel and coworkers and have allowed a synthetic route to many low-valent gallium species. However, chemical syntheses that employ “GaI” rather than gallium(I) halide precursors have been increasingly investigated given the ease of synthesis of this reagent. While the synthetic method of Schnöckel and coworkers to synthesize gallium(I) halides require extraordinarily high temperatures, the straightforward preparation of “GaI” at near room temperature has allowed for the exploration of new gallium-based chemistries. Synthesis In 1990, Malcolm Green and coworkers synthesized a “GaI” species, whose method of preparation is most widely followed. They found that ultrasonication of liquid gallium metal with iodine in a toluene solvent yields a new pale green powder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium(III) Nitride
Gallium nitride () is a binary III/ V direct bandgap semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes since the 1990s. The compound is a very hard material that has a Wurtzite crystal structure. Its wide band gap of 3.4 eV affords it special properties for applications in optoelectronic, high-power and high-frequency devices. For example, GaN is the substrate which makes violet (405 nm) laser diodes possible, without requiring nonlinear optical frequency-doubling. Its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it a suitable material for solar cell arrays for satellites. Military and space applications could also benefit as Radiation hardening, devices have shown stability in high radiation environments. Because GaN transistors can operate at much higher temperatures and work at much higher voltages than gallium arsenide (GaAs) transistors, they make ideal power amplifiers at microwave frequencies. In addition, GaN offers p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-iodide-3D-balls.png)


