|
Gaius Crastinus
Gaius Crastinus (c. 85 BC – 48 BC) was a soldier in Julius Caesar's 10th legion during his Gallic Wars. He had first joined either the 8th or 9th legion in 65 BC, when Pompey Magnus had first raised these two legions in Spain. He transferred over to the 10th legion as a junior-grade centurion in 61 BC when it was first formed, after being handpicked by Caesar. After joining the 10th legion, he commanded a Century. Crastinus fought throughout Caesar's Gallic campaigns, and was present at the Battle of Alesia, where he witnessed the surrender of the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix to the forces of the Roman Republic. Early in the war, Crastinus commanded his unit as it repelled an attempted crossing of a river by the Helvetii. Crastinus, whom Caesar considered to be amongst his best soldiers, was promoted by Caesar to the rank of Primus Pilus, or "First File" Centurion. This rank was one of exceptional prestige, since centurions of this rank commanded the first (''primus''), and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC – AD 476). Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 equites (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republican period of Rome (the infantry were split into 10 cohorts each of four maniples of 120 legionaries), to 4,800 legionaries (in 10 cohorts of 6 centuries of 80 legionaries) during Caesar's age, to 5,280 men plus 120 auxiliaries in the Imperial period (split into 10 cohorts, nine of 480 men each, with the first cohort being double-strength at 960 men). It should be noted the above numbers are typical field strengths while "paper strength" was sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
80s BC Births
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra. * the first number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Soldiers
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius. He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the province of Aegyptus (Egypt), he went to Rome c. 120, where he practised as an advocate, pleading cases before the emperors (probably as ''advocatus fisci'', an important official of the imperial treasury). It was in 147 at the earliest that he was appointed to the office of procurator, probably in Egypt, on the recommendation of his friend Marcus Cornelius Fronto, an influential rhetorician and advocate. Because the position of procurator was open only to members of the equestrian order (the "knightly" class), his possession of this office tells us about Appian's family background. His principal surviving work (Ρωμαϊκά ''Romaiká'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciano Canfora
Luciano Canfora (; born 5 June 1942) is an Italian classicist and historian. Born in Bari, Canfora obtained his first degree in Roman History in 1964 at Pisa University. He is currently Professor Emeritus of Classics at the University of Bari. His specialty is ancient libraries and his book ''The Vanished Library'' about Library of Alexandria has been translated into some 15 languages.*Cànfora, Luciano» in ''Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani'', Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana, Roma (on-line) He has also published a history of democracy under the title ''La Democrazia: Storia di un'Ideologia'' (Bari, 2004). Since 1975, he has edited the periodical ''Quaderni di storia''. Canfora stood in the 1999 European Parliament election for the Party of Italian Communists The Party of Italian Communists ( it, Partito dei Comunisti Italiani, PdCI) was a communist party in Italy established in October 1998 by splinters from the Communist Refoundation Party (PRC). The split was led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Cowan
Ross Cowan is a British historian and author specialising in Roman military history. Education and career Cowan studied at the University of Glasgow, completing an MA in classical civilisation in 1997 and a PhD in history in 2003. His doctoral thesis was on the Praetorian Guard and Legio II Parthica, entitled ''Aspects of the Severan Field Army AD 193–238''. Since earning his PhD Cowan has been an independent scholar, writing books on Roman military history for Osprey Publishing, Greenhill Books and Pen & Sword Books. Publications * ''For the Glory of Rome: A History of Warriors and Warfare '' * ''Roman Conquests: Italy '' * ''Roman Battle Tactics 109 BC–AD 313 '' * ''Roman Legionary 109-58 BC: The Age of Marius, Sulla and Pompey the Great '' * ''Roman Legionary 58 BC–AD 69 '' * ''Roman Legionary AD 69-161 '' * ''Imperial Roman Legionary AD 161-284 '' * ''Roman Legionary AD 284-337: The Age of Diocletian and Constantine the Great'' * ''Milvian Bridge AD 312: Constanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word meaning "sword" (of any type), but in its narrow sense it refers to the sword of ancient Roman foot soldiers. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called '' xiphe'' (plural; singular ''xiphos''). From the 3rd century BC, however, the soldiers of the Roman Republic adopted a sword based on the celtic sword used by the Celtiberians in Hispania late into the Punic Wars, known in Latin as the ''gladius hispaniensis'', meaning "Hispanic-type sword". New variants of the gladius, such as the "Mainz gladius" and the "Pompeii gladius", were used from the first century AD and during the early centuries of the Roman Empire; in the third century AD the gladius was replaced by the " spatha". A fully equipped Roman legionary after the reforms of Gaius Marius was armed with a shield (''scutum''), one or two javelins ('' pila''), a sword (''gladius''), often a dagger ('' pugio''), and, perhaps in the later empire period, darts (''plumbat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Civili
''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' ''(Commentaries on the Civil War)'', or ''Bellum Civile'', is an account written by Julius Caesar of his war against Gnaeus Pompeius and the Roman Senate. It consists of three books covering the events of 49–48 BC, from shortly before Caesar's invasion of Italy to Pompey's defeat at the Battle of Pharsalus and flight to Egypt. It was preceded by the much longer account of Caesar's campaigns in Gaul and was followed by similar works covering the ensuing wars against the remnants of Pompey's armies in Egypt, North Africa, and Spain. Caesar's authorship of the ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' is not disputed, while the three later works are believed to have been written by contemporaries of Caesar. Title The Latin title "Commentarii de Bello Civili" is often retained as the title of the book in English translations of the work. The title itself is Latin for "Commentaries on the Civil War". It is sometimes shortened to just "Civil Wars", "About th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
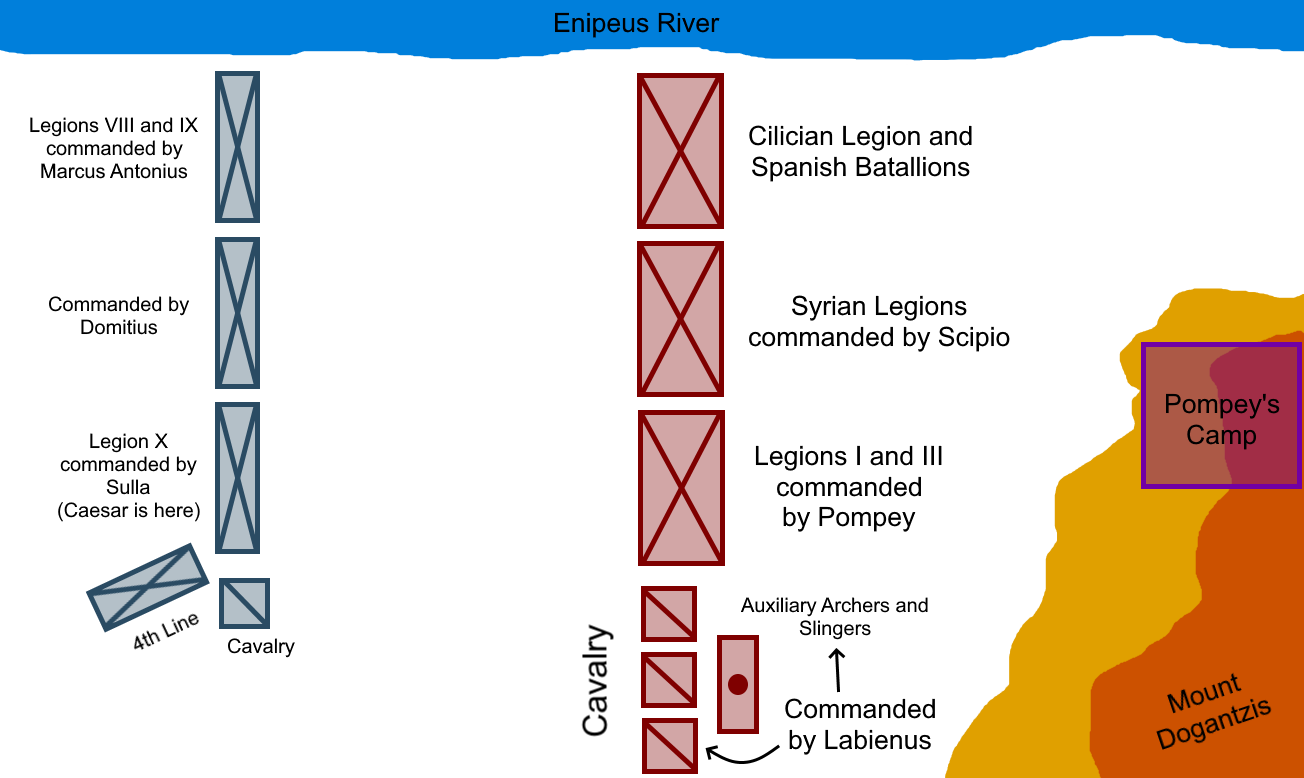
Battle Of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions. Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII. Prelude Following the start of the Civil War, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated. Caesar then withdrew east into Thessaly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primus Pilus
The ''primus pilus'' or ''primipilus'' was the senior centurion of the first cohort in a Roman legion, a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men, was called the ''primus pilus''; he was a career soldier and advisor to the legate. The ''Primus Pilus'' would remain in command for one year. They could continue to serve in the army after their term ended if there was a vacancy in command or if they wished to become an independent commander of an ''auxilia'' unit or the ''praefectus castrorum''. During the Roman Empire, emperor Claudius created the office of ''primus pilus iterum''. To become the ''primus pilus iterum'' an officer must have formerly served as a tribune in the ''vigiles'', ''cohortes urbanae'', or Praetorian Guard. The ''primus pilus iterum'' would hold the responsibility of a Praefectus castrorum but with higher pay. The ''primus pilus'' was a well paid position. They could accumulate enough wealth to become part of the equestrian class. Even if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio X Equestris
Legio X ''Equestris'', a Roman legion, was levied by Julius Caesar in 61 BC when he was the Governor of Hispania Ulterior. The Tenth was the first legion levied personally by Caesar and was consistently his most trusted. Legio X was famous in its day and throughout history, because of its portrayal in Caesar's Commentaries and the prominent role the Tenth played in his Gallic campaigns.Julius Caesar, I.42. Its soldiers were discharged in 45 BC. Its remnants were reconstituted, fought for Mark Antony and Octavian, disbanded, and later merged into X ''Gemina''.See, for example, Keppie. History Founding When Gaius Julius Caesar arrived as Governor in the province of Baetica or Hispania Ulterior (modern Andalusia), as it was in 61 BC, he immediately decided to subdue the west and northwest areas (modern day Portugal). He already had two legions based in the province, the 8th and 9th Legions, which had been enlisted by Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (Pompey the Great) in 65 BC. Caesar n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



-Segunda_Edad_del_Hierro.jpg)