|
Gail Carpenter
Gail Alexandra Carpenter (born 1948) is an American cognitive scientist, neuroscientist and mathematician. She is now a "Professor Emerita of Mathematics and Statistics, Boston University." She had also been a Professor of Cognitive and Neural Systems at Boston University, and the director of the Department of Cognitive and Neural Systems (CNS) Technology Lab at Boston University. Early life Gail Carpenter is the only daughter of Chadwick Hunter "Chad" Carpenter (1920-1996) and Ruth M. (née Stevenson) Carpenter (1920-2010). She has four brothers. Carpenter attended the International School of Geneva (1961-1966) then went to the University of Colorado in Boulder earning a B.A. in 1970 (summa cum laude, mathematics). She then earned a Ph.D. in mathematics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. Carpenter then taught at MIT and Northeastern University before moving to Boston University.https://techlab.bu.edu/members/gail/, CNS Technology Website, Accessed 18 January 2022 Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International School Of Geneva
The International School of Geneva (in French: ''Ecole Internationale de Genève''), also known as "Ecolint" or "The International School", is a private, non-profit international school based in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1924 in the service of the League of Nations and the International Labour Organization (the world's first international organizations), it is the oldest international school in the world, and the largest one with 'international' in its name. It was the result of a partnership between parents (Arthur Sweetser and Ludwik Rajchman) and educators from the Institut Jean-Jacques Rousseau (Adolphe Ferrière and Paul Meyhoffer). In the mid-1960s, a group of teachers from Ecolint (La Grande Boissière campus) created the International Schools Examinations Syndicate (ISES), which later became the International Baccalaureate Organization (IBO) and then the International Baccalaureate (IB). Since its inception, the school's mission was conceived as educating for peace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning (SL) is a machine learning paradigm for problems where the available data consists of labelled examples, meaning that each data point contains features (covariates) and an associated label. The goal of supervised learning algorithms is learning a function that maps feature vectors (inputs) to labels (output), based on example input-output pairs. It infers a function from ' consisting of a set of ''training examples''. In supervised learning, each example is a ''pair'' consisting of an input object (typically a vector) and a desired output value (also called the ''supervisory signal''). A supervised learning algorithm analyzes the training data and produces an inferred function, which can be used for mapping new examples. An optimal scenario will allow for the algorithm to correctly determine the class labels for unseen instances. This requires the learning algorithm to generalize from the training data to unseen situations in a "reasonable" way (see inductive b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network (machine Learning)
In machine learning Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine ..., a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a Machine learning#Models, model inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks in animal brains. An ANN consists of connected units or nodes called ''artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in a brain. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in a brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the ''activation function''. The strength of the sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
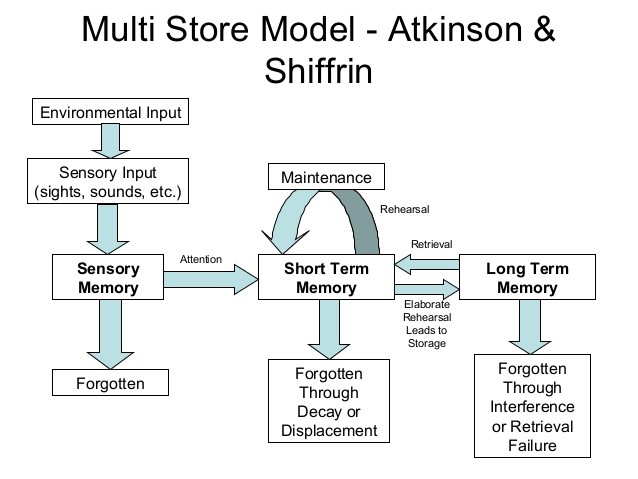
Information Processing Theory
Information processing theory is the approach to the study of cognitive development evolved out of the American experimental tradition in psychology. Developmental psychologists who adopt the information processing perspective account for mental development in terms of maturational changes in basic components of a child's mind. The theory is based on the idea that humans process the information they receive, rather than merely responding to stimuli. This perspective uses an analogy to consider how the mind works like a computer. In this way, the mind functions like a biological computer responsible for analyzing information from the environment. According to the standard information-processing model for mental development, the mind's machinery includes attention mechanisms for bringing information in, working memory for actively manipulating information, and long-term memory for passively holding information so that it can be used in the future. This theory addresses how as chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed ART Model (dART)
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value * Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space * Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for * Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burst Suppression
Burst suppression is an electroencephalography (EEG) pattern that is characterized by periods of high-voltage electrical activity alternating with periods of no activity in the brain. The pattern is found in patients with inactivated brain states, such as from general anesthesia, coma, or hypothermia. This pattern can be physiological, as during early development, or pathological, as in diseases such as Ohtahara syndrome. History The burst suppression pattern was first observed by Derbyshire et al. while studying effects of anesthetics on feline cerebral cortices in 1936, where the researchers noticed mixed slow and fast electrical activity with decreasing amplitude as anesthesia deepened. In 1948, Swank and Watson coined the term "burst-suppression pattern" to describe the alternation of spikes and flatlines in electrical activity in deep anesthesia. It wasn't until after the early 1960s that the burst suppression pattern began being used in medical settings; it had been primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut [Massachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət],'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York (state), New York to the west. The state's capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban area, urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American History of the United States, history, academia, and the Economy of the United States, research economy. Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and including Providence, Rhode Island, is home to approximately 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States. Boston is one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |