|
Gag Rule
A gag rule is a rule that limits or forbids the raising, consideration, or discussion of a particular topic, often but not always by members of a legislative or decision-making body. A famous example of gag rules is the series of rules concerning the discussion of slavery in effect in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1836 to 1844. By country England A gag rule may be formally neutral, that is, forbidding discussions or arguments either for or against a particular policy. For example, William Laud, the Archbishop of Canterbury during the reign of King Charles I of England:forbade ministers to discuss the sublime mysteries associated with Calvin's doctrine of predestination. They could not preach it, nor could they preach against it. They could not mention it at all ... For Laud, what was at stake was not so much the promotion of his own theological opinions as the suppression of the furor theologicus that had caused so much devastation in England and throughout Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery Gag Rule
In United States history, the gag rule was a series of rules that forbade the raising, consideration, or discussion of Slavery in the United States, slavery in the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives from 1836 to 1844. Background Congress regularly received petitions asking for various types of relief or action. Before the gag rules, House rules required that the first thirty days of each session of Congress be devoted to the reading of petitions from constituents. Each petition was read aloud, printed, and assigned to an appropriate committee, which could choose to address or ignore it. After those thirty days, petitions were read in the House every other Monday. This procedure became unworkable in 1835, when, at the instigation of the new American Anti-Slavery Society, petitions arrived in Congress in quantities never before seen. Over the gag rule period, well over 1,000 petitions, with 130,000 signatures, poured into the United States House of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Laud
William Laud (; 7 October 1573 – 10 January 1645) was a bishop in the Church of England. Appointed Archbishop of Canterbury by Charles I in 1633, Laud was a key advocate of Charles I's religious reforms, he was arrested by Parliament in 1640 and executed towards the end of the First English Civil War in January 1645. A firm believer in episcopalianism, or rule by bishops, "Laudianism" refers to liturgical practices designed to enforce uniformity within the Church of England, as outlined by Charles. Often highly ritualistic, these were precursors to what are now known as high church views. In theology, Laud was accused of Arminianism, favouring doctrines of the historic church prior to the Reformation and defending the continuity of the English Church with the primitive and medieval church, and opposing Calvinism. On all three grounds, he was regarded by Puritan clerics and laymen as a formidable and dangerous opponent. His use of the Star Chamber to persecute opponents su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justin Welby, who was enthroned at Canterbury Cathedral on 21 March 2013. Welby is the 105th in a line which goes back more than 1400 years to Augustine of Canterbury, the "Apostle to the English", sent from Rome in the year 597. Welby succeeded Rowan Williams. From the time of Augustine until the 16th century, the archbishops of Canterbury were in full communion with the See of Rome and usually received the pallium from the pope. During the English Reformation, the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope. Thomas Cranmer became the first holder of the office following the English Reformation in 1533, while Reginald Pole was the last Roman Catholic in the position, serving from 1556 to 1558 during the Counter-Reformation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles I Of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after his father inherited the English throne in 1603, he moved to England, where he spent much of the rest of his life. He became heir apparent to the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland in 1612 upon the death of his elder brother, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales. An unsuccessful and unpopular attempt to marry him to the Spanish Habsburg princess Maria Anna of Spain, Maria Anna culminated in an eight-month visit to Spain in 1623 that demonstrated the futility of the marriage negotiation. Two years later, he married the House of Bourbon, Bourbon princess Henrietta Maria of France. After his 1625 succession, Charles quarrelled with the Parliament of England, English Parliament, which sought to curb his royal prerogati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predestination In Calvinism
Predestination is a doctrine in Calvinism dealing with the question of the control that God exercises over the world. In the words of the Westminster Confession of Faith, God "freely and unchangeably ordained whatsoever comes to pass." The second use of the word "predestination" applies this to the salvation, and refers to the belief that God appointed the eternal destiny of some to salvation by grace, while leaving the remainder to receive eternal damnation for all their sins, even their original sin. The former is called "unconditional election", and the latter "reprobation". In Calvinism, some people are predestined and effectually called in due time ( regenerated/born again) to faith by God, all others are reprobated. Calvinism places more emphasis on election compared to other branches of Christianity. Origins Predestination of the elect and non-elect was taught by the Jewish Essene sect, Gnosticism, and Manichaeism. In Christianity, the doctrine that God unilaterally pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Wars Of Religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic Church, Catholic countries of Europe, or Christendom. Other motives during the wars involved revolt, territorial ambitions and European balance of power, great power conflicts. By the end of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), Catholic France had allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia (1648), which established a new political order that is now known as Westphalian sovereignty. The conflicts began with the minor Knights' Revolt (1522), followed by the larger German Peasants' War (1524–1525) in the Holy Roman Empire. Warfare intensified after the Catholic Church began the Counter-Reformation in 1545 against the growth of Protestantism. The conflicts cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Weekly Standard
''The Weekly Standard'' was an American neoconservative political magazine of news, analysis and commentary, published 48 times per year. Originally edited by founders Bill Kristol and Fred Barnes, the ''Standard'' had been described as a "redoubt of neoconservatism" and as "the neocon bible." Its founding publisher, News Corporation, debuted the title on September 18, 1995. In 2009, News Corporation sold the magazine to a subsidiary of the Anschutz Corporation. On December 14, 2018, its owners announced that the magazine was ceasing publication, with the last issue published on December 17. Sources attribute its demise to an increasing divergence between Kristol and other editors' shift towards anti-Trump positions, and the magazine's audience's shift towards Trumpism. Many of the magazine's articles were written by members of conservative think tanks located in Washington, including the American Enterprise Institute, the Ethics and Public Policy Center, the Foundation for Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewan Negara
The Dewan Negara (English language, English: Senate; Literal translation, lit. "State Council") is the upper house of the Parliament of Malaysia, consisting of 70 senators of whom 26 are elected by the State legislative assemblies of Malaysia, state legislative assemblies, with two senators for each state, while the other 44 are appointed by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King), including four who are appointed to represent the Federal Territories (Malaysia), federal territories. The ''Dewan Negara'' usually reviews legislation that has been passed by the lower house, the ''Dewan Rakyat''. All bills must usually be passed by both the ''Dewan Rakyat'' and the ''Dewan Negara'' (the Senate), before they are sent to the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, King for royal assent. However, if the ''Dewan Negara'' rejects a bill, it can only delay the bill's passage by a maximum of a year before it is sent to the King, a restriction similar to that placed on the House of Lords in the United Kingdom. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
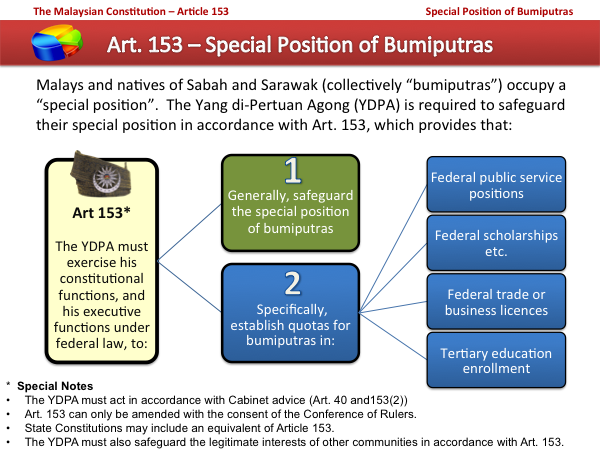
Malaysian Constitution
The Federal Constitution of Malaysia ( ms, Perlembagaan Persekutuan Malaysia) which was promulgated on 16 September 1963, is the supreme law of Malaysia and contains a total of 183 articles. It is a written legal document which was preceded by two previous documents, the Federation of Malaya Agreement 1948 and the ''Merdeka'' () Constitution of 1957 of the Federation of Malaya (). The Constitution of the Federation of Malaya was used as the basis for the establishment of a new Federation known in both English and Malay as Malaysia, when the Federation of Malaya federated with the self-governing State of Singapore and the Colonies of North Borneo (now Sabah) and Sarawak as the States of Malaya, the State of Singapore, and the Borneo States of Sabah and Sarawak. The new State of Malaysia was established through the amendment 87 out of 181 Articles and 10 out of 13 Schedules of The Constitution pursuant to the Malaysia Agreement 1963 as recommended by the 1961 White Paper on Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bumiputra
''Bumiputera'' or ''Bumiputra'' ( Jawi: ) is a term used in Malaysia to describe Malays, the Orang Asli of Peninsular Malaysia, and various indigenous peoples of East Malaysia (see official definition below). The term is sometimes controversial, and has similar usage in the Malay world, used similarly in Indonesia and Brunei. The term is derived from the Sanskrit which was later absorbed into the classical Malay word ( sa, भूमिपुत्र, bhū́miputra), which can be translated literally as "son of the land" or "son of the soil". In Indonesia, this term is known as "Pribumi". In the 1970s, the Malaysian government implemented policies designed to favour bumiputras (including affirmative action in public education and in the public sector) to elevate the socioeconomic status of the economically disadvantaged bumiputera community and to defuse interethnic tensions following the 13 May Incident in 1969 by placating the Malay majority through granting them a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahasa Malaysia
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as opposed to the variety used in Indonesia, which is referred to as the "Indonesian" language). Malaysian Malay is standardized from the Johore-Riau dialect of Malay. It is spoken by much of the Malaysian population, although most learn a vernacular form of Malay or another native language first. Malay is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary schools. Status In Malaysia Article 152 of the Federation designates "Malay" as the official language, but the term "Malaysian" or ''bahasa Malaysia'' is used on official contexts from time to time. The choice of name can be politically contentious; in 1999 the Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka rejected the publication of some short stories as the preface to the publication used the term ''bahasa Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery Gag Rule
In United States history, the gag rule was a series of rules that forbade the raising, consideration, or discussion of Slavery in the United States, slavery in the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives from 1836 to 1844. Background Congress regularly received petitions asking for various types of relief or action. Before the gag rules, House rules required that the first thirty days of each session of Congress be devoted to the reading of petitions from constituents. Each petition was read aloud, printed, and assigned to an appropriate committee, which could choose to address or ignore it. After those thirty days, petitions were read in the House every other Monday. This procedure became unworkable in 1835, when, at the instigation of the new American Anti-Slavery Society, petitions arrived in Congress in quantities never before seen. Over the gag rule period, well over 1,000 petitions, with 130,000 signatures, poured into the United States House of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |