|
Gabor Transform
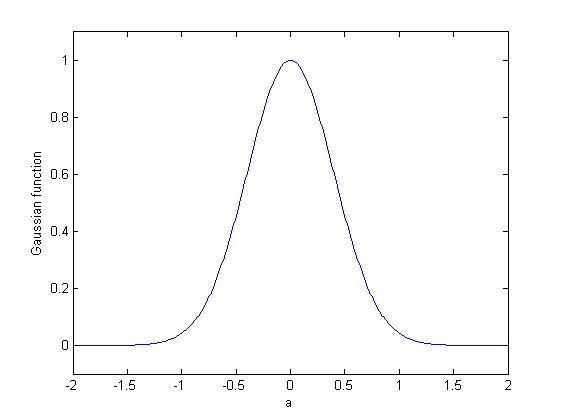
The Gabor transform, named after Dennis Gabor, is a special case of the short-time Fourier transform. It is used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. The function to be transformed is first multiplied by a Gaussian function, which can be regarded as a window function, and the resulting function is then transformed with a Fourier transform to derive the time-frequency analysis.E. Sejdić, I. Djurović, J. Jiang, “Time-frequency feature representation using energy concentration: An overview of recent advances,” ''Digital Signal Processing'', vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 153-183, January 2009. The window function means that the signal near the time being analyzed will have higher weight. The Gabor transform of a signal ''x''(''t'') is defined by this formula: : G_x(\tau,\omega) = \int_^\infty x(t)e^e^\,dt The Gaussian function has infinite range and it is impractical for implementation. However, a level of signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dennis Gabor
Dennis Gabor ( ; hu, Gábor Dénes, ; 5 June 1900 – 9 February 1979) was a Hungarian-British electrical engineer and physicist, most notable for inventing holography, for which he later received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics. He obtained British citizenship in 1934, and spent most of his life in England. Life and career Gabor was born as Günszberg Dénes, into a Jewish family in Budapest, Hungary. In 1918, his family converted to Lutheranism. Dennis was the first-born son of Günszberg Bernát and Jakobovits Adél. Despite having a religious background, religion played a minor role in his later life and he considered himself agnostic. In 1902, the family received permission to change their surname from Günszberg to Gábor. He served with the Hungarian artillery in northern Italy during World War I. He began his studies in engineering at the Technical University of Budapest in 1918, later in Germany, at the Charlottenburg Technical University in Berlin, now known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time–frequency Analysis
In signal processing, time–frequency analysis comprises those techniques that study a signal in both the time and frequency domains ''simultaneously,'' using various time–frequency representations. Rather than viewing a 1-dimensional signal (a function, real or complex-valued, whose domain is the real line) and some transform (another function whose domain is the real line, obtained from the original via some transform), time–frequency analysis studies a two-dimensional signal – a function whose domain is the two-dimensional real plane, obtained from the signal via a time–frequency transform. The mathematical motivation for this study is that functions and their transform representation are tightly connected, and they can be understood better by studying them jointly, as a two-dimensional object, rather than separately. A simple example is that the 4-fold periodicity of the Fourier transform – and the fact that two-fold Fourier transform reverses direction – can be int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-time Fourier Transform
The short-time Fourier transform (STFT), is a Fourier-related transform used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. In practice, the procedure for computing STFTs is to divide a longer time signal into shorter segments of equal length and then compute the Fourier transform separately on each shorter segment. This reveals the Fourier spectrum on each shorter segment. One then usually plots the changing spectra as a function of time, known as a spectrogram or waterfall plot, such as commonly used in software defined radio (SDR) based spectrum displays. Full bandwidth displays covering the whole range of an SDR commonly use fast Fourier transforms (FFTs) with 2^24 points on desktop computers. Forward STFT Continuous-time STFT Simply, in the continuous-time case, the function to be transformed is multiplied by a window function which is nonzero for only a short period of time. The Fourier transform (a o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Transform
''S'' transform as a time–frequency distribution was developed in 1994 for analyzing geophysics data.Stockwell, RG (1999). ''S''-transform analysis of gravity wave activity from a small scale network of airglow imagers. PhD thesis, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. In this way, the ''S'' transform is a generalization of the short-time Fourier transform (STFT), extending the continuous wavelet transform and overcoming some of its disadvantages. For one, modulation sinusoids are fixed with respect to the time axis; this localizes the scalable Gaussian window dilations and translations in ''S'' transform. Moreover, the ''S'' transform doesn't have a cross-term problem and yields a better signal clarity than Gabor transform. However, the ''S'' transform has its own disadvantages: the clarity is worse than Wigner distribution function and Cohen's class distribution function. A fast ''S'' transform algorithm was invented in 2010. It reduces the computational compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabor Atom
In applied mathematics, Gabor atoms, or Gabor functions, are functions used in the analysis proposed by Dennis Gabor in 1946 in which a family of functions is built from translations and modulations of a generating function. Overview In 1946, Dennis Gabor suggested the idea of using a granular system to produce sound. In his work, Gabor discussed the problems with Fourier analysis. Although he found the mathematics to be correct, it did not reflect the behaviour of sound in the world, because sounds, such as the sound of a siren, have variable frequencies over time. Another problem was the underlying supposition, as we use sine waves analysis, that the signal under concern has infinite duration even though sounds in real life have limited duration – see time–frequency analysis. Gabor applied ideas from quantum physics to sound, allowing an analogy between sound and quanta. He proposed a mathematical method to reduce Fourier analysis into cells. His research aimed at the infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabor Wavelet
Gabor wavelets are wavelets invented by Dennis Gabor using complex functions constructed to serve as a basis for Fourier transforms in information theory applications. They are very similar to Morlet wavelets. They are also closely related to Gabor filters. The important property of the wavelet is that it minimizes the product of its standard deviations in the time and frequency domain. Put another way, the uncertainty in information carried by this wavelet is minimized. However they have the downside of being non-orthogonal, so efficient decomposition into the basis is difficult. Since their inception, various applications have appeared, from image processing to analyzing neurons in the human visual system. Minimal uncertainty property The motivation for Gabor wavelets comes from finding some function f(x) which minimizes its standard deviation in the time and frequency domains. More formally, the variance in the position domain is: : (\Delta x)^2 = \frac where f^(x) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabor Filter
In image processing, a Gabor filter, named after Dennis Gabor, is a linear filter used for texture analysis, which essentially means that it analyzes whether there is any specific frequency content in the image in specific directions in a localized region around the point or region of analysis. Frequency and orientation representations of Gabor filters are claimed by many contemporary vision scientists to be similar to those of the human visual system. They have been found to be particularly appropriate for texture representation and discrimination. In the spatial domain, a 2-D Gabor filter is a Gaussian kernel function modulated by a sinusoidal plane wave (see Gabor transform). Some authors claim that simple cells in the visual cortex of mammalian brains can be modeled by Gabor functions. Thus, image analysis with Gabor filters is thought by some to be similar to perception in the human visual system. Definition Its impulse response is defined by a sinusoidal wave (a plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Gabor Simulation
Scale or scales may refer to: Mathematics * Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points * Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original * Scale factor, a number which scales, or multiplies, some quantity * Long and short scales, how powers of ten are named and grouped in large numbers * Scale parameter, a description of the spread or dispersion of a probability distribution * Feature scaling, a method used to normalize the range of independent variables or features of data * Scale (analytical tool) Measurements * Scale (map), the ratio of the distance on a map to the corresponding actual distance * Weighing scale, an instrument used to measure mass * Scale (ratio), the ratio of the linear dimension of the model to the same dimension of the original * Spatial scale, a classification of sizes * Scale ruler, a tool for measuring lengths and transferring measurements at a fixed ratio of length * Verni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Frequency
The concept of signed frequency (negative and positive frequency) can indicate both the rate and sense of rotation; it can be as simple as a wheel rotating clockwise or counterclockwise. The rate is expressed in units such as revolutions (a.k.a. ''cycles'') per second (hertz) or radian/second (where 1 cycle corresponds to 2''π'' radians). Sinusoids Let be a nonnegative angular frequency with units of radians/second. Then the function has slope , which is called a negative frequency. But when the function is used as the argument of a cosine operator, the result is indistinguishable from . Similarly, is indistinguishable from . Thus any sinusoid can be represented in terms of positive frequencies. The sign of the underlying phase slope is ambiguous. The ambiguity is resolved when the cosine and sine operators can be observed simultaneously, because leads by 1/4 cycle (= ''π''/2 radians) when , and lags by 1/4 cycle when . Similarly, a vector, , rotates counter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-time Fourier Transform
The short-time Fourier transform (STFT), is a Fourier-related transform used to determine the sinusoidal frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. In practice, the procedure for computing STFTs is to divide a longer time signal into shorter segments of equal length and then compute the Fourier transform separately on each shorter segment. This reveals the Fourier spectrum on each shorter segment. One then usually plots the changing spectra as a function of time, known as a spectrogram or waterfall plot, such as commonly used in software defined radio (SDR) based spectrum displays. Full bandwidth displays covering the whole range of an SDR commonly use fast Fourier transforms (FFTs) with 2^24 points on desktop computers. Forward STFT Continuous-time STFT Simply, in the continuous-time case, the function to be transformed is multiplied by a window function which is nonzero for only a short period of time. The Fourier transform (a o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |