|
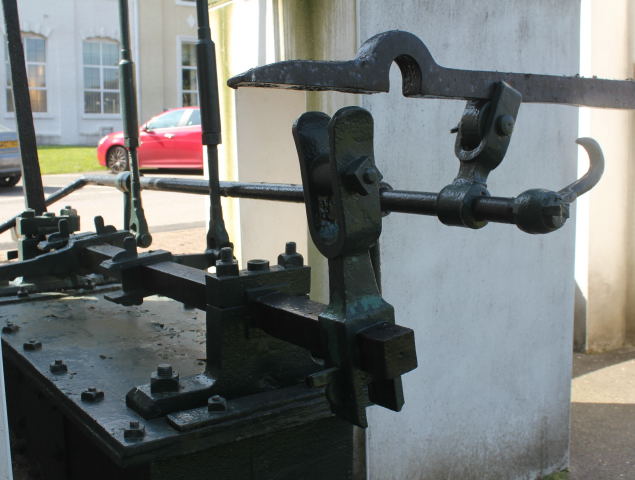
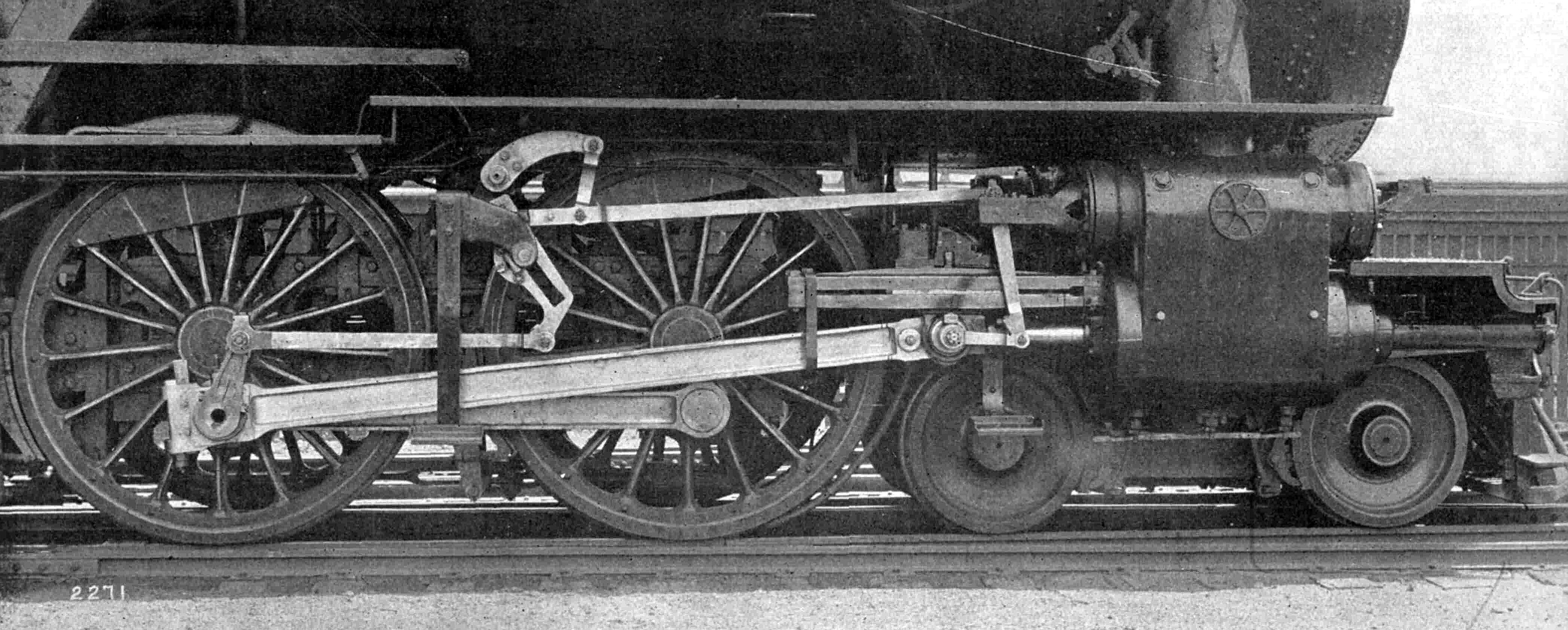
Gab Valve Gear
Gab valve gear was an early form of valve gear used on steam engines. Its simplest form allowed an engine to be stopped and started. A double form, mostly used on steam locomotives, allowed easy reversing. Etymology The word ''gab'' or ''gabb'' may derive from a word for mouth, recorded by the Oxford English Dictionary from 1724, and probably medieval in origin from other forms related to gossip or idle chatter. The OED also gives the steam engine sense of ''gab'' as a notch in the valvegear as possibly being of Flemish origin, from the word ''gabbe''. This is cited in the OED from 1792. The OED also cites the obviously derivative ''gab-lever'' from 1839. Origins One of the first self-acting valve gears used for steam engines was the eccentric valve gear. This placed an eccentric on the engine's crankshaft, that in turn drove a strap and a long rod to the valve's actuating spindle. This was a simple valve gear but worked well for rotative engines that ran continuously for l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JD Varteg02
JD or jd may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''JD'' (film), a 2016 Bollywood film * J.D. (''Scrubs''), nickname of Dr. John Dorian, fictional protagonist of the comedy-drama ''Scrubs'' * JD Fenix, a character from the ''Gears of War'' video game series * ''J. D.'s Revenge'', 1976 motion picture * ''Jade Dynasty'' (video game), a 2007 fantasy MMORPG * ''Just Dance'' (video game series), video game series *"J.D.", an episode of the sixth season of '' Fear the Walking Dead'' Businesses and organizations * JD.com, a Chinese electronic commerce company * Jack Daniel's, a whiskey brand, distilled in Tennessee, US * Janata Dal, a political party in India * John Deere, an agricultural machinery manufacturer * JD Edwards, a former computer software company * JD Sports, a UK retail company * JD Wetherspoon, a UK pub and restaurant chain * Justdial, an Indian local search agency * Dawson State Jail, operated by the Corrections Corporation of America and owned by the Texas Depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
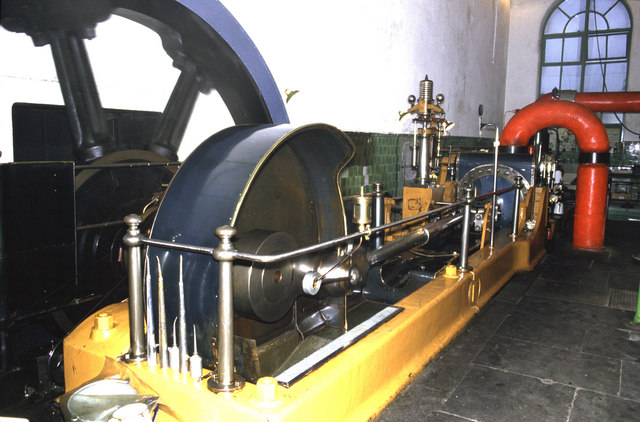
Winding Engine
A winding engine is a stationary engine used to control a cable, for example to power a mining hoist at a pit head. Electric hoist controllers have replaced proper winding engines in modern mining, but use electric motors that are also traditionally referred to as ''winding engines''. Early winding engines were hand, or more usually horse powered. The first powered winding engines were stationary steam engines. The demand for winding engines was one factor that drove James Watt to develop his rotative beam engine, with its ability continuously to turn a winding drum, rather than the early reciprocating beam engines that were only useful for working pumps. They differ from most other stationary steam engines in that, like a steam locomotive, they need to be able to stop frequently and also reverse. This requires more complex valve gear and other controls than are needed on engines used in mills or to drive pump A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. *Table engines have the crosshead above the vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansive Working
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellcrank
A bellcrank is a type of crank that changes motion through an angle. The angle can be any angle from 0 to 360 degrees, but 90 degrees and 180 degrees are most common. The name comes from its first use, changing the vertical pull on a rope to a horizontal pull on the striker of a bell, used for calling staff in large houses or commercial establishments. Angles A typical 90 degree bellcrank consists of an "L" shaped crank pivoted where the two arms of the L meet. Moving rods (or cables or ropes) are attached to the ends of the L arms. When one is pulled, the L rotates around the pivot point, pulling on the other arm. A typical 180 degree bellcrank consists of a straight bar pivoted in the center. When one arm is pulled or pushed, the bar rotates around the pivot point, pulling or pushing on the other arm. Mechanical advantage Changing the length of the arms changes the mechanical advantage of the system. Many applications do not change the direction of motion but instead amplify a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephenson's Rocket
Stephenson's ''Rocket'' is an early steam locomotive of 0-2-2 wheel arrangement. It was built for and won the Rainhill Trials of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), held in October 1829 to show that improved locomotives would be more efficient than stationary steam engines. ''Rocket'' was designed and built by Robert Stephenson in 1829, and built at the Forth Street Works of his company in Newcastle upon Tyne. Though ''Rocket'' was by no means the first steam locomotive, it was the first to bring together several innovations to produce the most advanced locomotive of its day. It is the most famous example of an evolving design of locomotives by Stephenson that became the template for most steam engines in the following 150 years. The locomotive was preserved and displayed in the Science Museum in London until 2018, after which it was displayed at the National Railway Museum in York. Design Overall layout The locomotive had a tall smokestack chimney at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversing Lever
A Johnson Bar is a control lever on a steam locomotive, used to control the timing of the admission of steam into the locomotive's cylinders. By controlling this timing, the amount of power delivered to the wheels is regulated, as is the direction that the wheels rotate, giving the lever the alternate name of the reversing lever. This is the term employed in British English, while the term 'Johnson Bar' is the norm in the United States. History Historians have not identified the reasons why engineers called the reversing lever a Johnson Bar, but the reversing lever is described in both British, and American railway journals of the time. The best accreditation of the invention is documented under the Walschaerts valve gear. Reversing The reversing lever in locomotive history is documented from about 1842. The American Railway Master Mechanic's Association had members that published illustrations. Parts for the reversing lever are drawn in the "Locomotive Dictionary", 1st e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gab Motion Ja
Gab or GAB may refer to: * Gáb, a cuneiform sign * Gab (social network), an American social networking platform * "Gab" (song), an Occitan boasting song of the Middle Ages * Gab, Iran, a village in Hormozgan Province * Games and Amusements Board, a Philippine sports and gambling regulatory government agency * Georgia Academy for the Blind * German American Bund, a German-American pro-Nazi organization (1936–1941) * Government Accountability Board, a defunct (since 2016) Wisconsin political regulatory institution * The Great American Bash, a professional wrestling event * Great Artesian Basin, in Australia * Great Australian Bight, an open bay * Greater Atlantic Bank Greater Atlantic Bank (GAB) was an American community bank. The bank was founded in May 1887 and was closed in December 2009. It was the first bank failure of the Great Recession and was the first bank failure in Virginia since 1993. On October ..., a defunct American community bank See also * Gabb (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotion No 1
''Locomotion'' No. 1 (originally named ''Active'') is an early steam locomotive that was built in 1825 by the pioneering railway engineers George Stephenson, George and Robert Stephenson at their manufacturing firm, Robert Stephenson and Company. It became the first steam locomotive to haul a passenger-carrying train on a public railway, the Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR). ''Locomotion No. 1'' was ordered by the Stockton and Darlington Railway Company in September 1824; its design benefitted from George Stephenson's experience building his series of Killingworth locomotives. It is believed that ''Locomotion No. 1'' was the first locomotive to make use of coupling rods to link together its driving wheels, reducing the chance of the wheels slipping on the iron rails. However, the shell boiler#Centre-flue boilers, centre-flue boiler proved to be a weakness, providing for a poor heating surface compared to later fire-tube boiler, multi-flue boilers. In September 1825, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. Self-help advocate Samuel Smiles particularly praised his achievements. His chosen rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway line in the world to use locomotives, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip-eccentric Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft Mining
Shaft mining or shaft sinking is the action of excavating a mine shaft from the top down, where there is initially no access to the bottom. Shaft (civil engineering), Shallow shafts, typically sunk for civil engineering projects, differ greatly in execution method from deep shafts, typically sunk for mining projects. Shaft sinking is one of the most difficult of all mine development methods: restricted space, gravity, groundwater and specialized procedures make the task quite formidable. Shafts may be sunk by conventional drill and blast or mechanised means. Historically, mine shaft sinking has been among the most dangerous of all the mining occupations and the preserve of mining contractors called sinker (mining), sinkers. Today shaft sinking contractors are concentrated in Canada, Germany, China and South Africa. The modern shaft sinking industry is gradually shifting further towards greater mechanisation. Recent innovations in the form of full-face shaft boring (akin to a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |