|
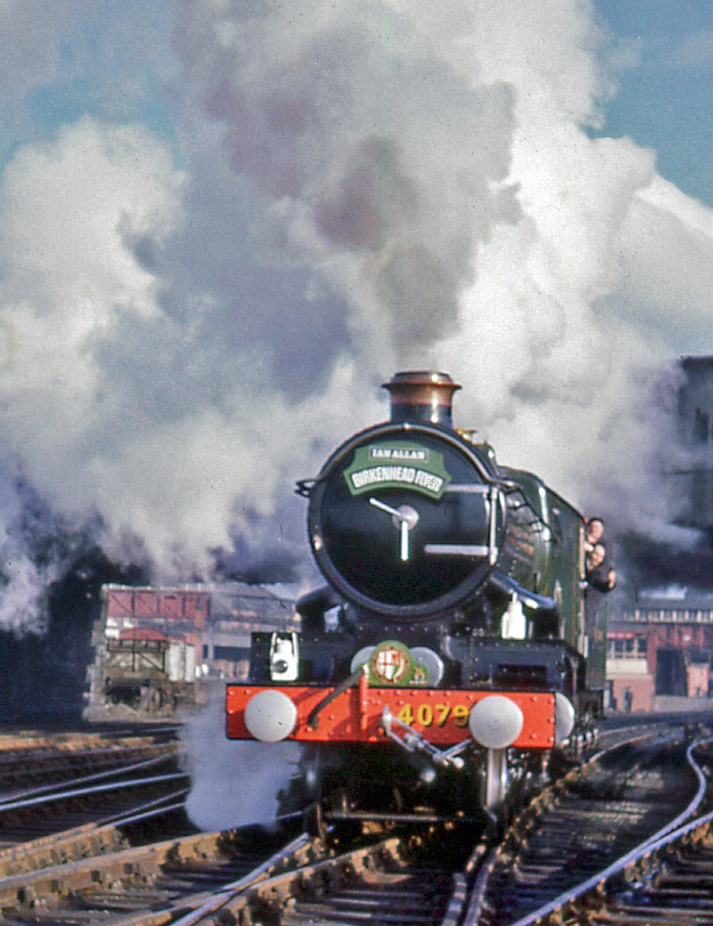
GWR 4073 Class 7027 Thornbury Castle
7027 ''Thornbury Castle'' was built in August 1949. Its first shed allocation was Plymouth Laira. Its March 1959 shed allocation was Old Oak Common. Its last shed allocation was Reading. It was withdrawn in December 1963 and arrived at Woodham Brothers scrapyard in Barry, South Wales in May 1964. The locomotive was not scrapped and was being restored in 2022. Preservation 7027 was sold to the then Birmingham Railway Museum and left as the 23rd departure from Barry in August 1972. After being purchased by Pete Waterman's Transport Trust, she was stored outside the Crewe Heritage Centre in her Barry Scrapyard condition. Some parts of 7027 are currently in use on elder sibling 5043 ''Earl of Mount Edgcumbe'' and one set of name and number plates for 7027 are mounted on a wall of the main hall of The Castle School in Thornbury, South Gloucestershire. Following the removal of Waterman's railway equipment from the former LNWR site in 2016, she was moved to Peak Rail in April 2016. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare, also known simply as Weston, is a seaside town in North Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. It includes the suburbs of Mead Vale, Milton, Oldmixon, West Wick, Worlebury, Uphill and Worle. Its population at the 2011 census was 76,143. Since 1983, Weston has been twinned with Hildesheim in Germany. The local area has been occupied since the Iron Age. It was still a small village until the 19th century when it developed as a seaside resort. A railway station and two piers were built. In the second half of the 20th century it was connected to the M5 motorway but the number of people holidaying in the town declined and some local industries closed, although the number of day visitors has risen. Attractions include The Helicopter Museum, Weston Museum, and the Grand Pier. Cultural venues include The Playhouse, the Winter Gardens and the Blakehay Theatre. The Bristol Channel has a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crewe Heritage Centre
Crewe Heritage Centre is a railway museum located in Crewe, England. Managed by the Crewe Heritage Trust, the museum is located between the railway station and the town centre; the site was the location of the 'Old Works' which was demolished in the early 1980s. History The centre was established in the old London, Midland and Scottish Railway yard, which was once part of Crewe Works, between the junction to Chester and the West Coast Main Line. It was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II, accompanied by the Duke of Edinburgh, on 24 July 1987. It was renamed in 1992 as Crewe Railway Age by the owning registered charity but, after the management of the centre was taken over by a new group of volunteers, the museum returned to its original name of Crewe Heritage Centre in early 2008. Exhibits The centre has a series of exhibits, ranging from the only surviving APT-P train, miniature railways, three open signal boxes (Crewe Station A, Crewe North Junction and Exeter West) and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preserved Great Western Railway Steam Locomotives
Preservation may refer to: Heritage and conservation * Preservation (library and archival science), activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record while making as few changes as possible * ''Preservation'' (magazine), published by the National Trust for Historic Preservation * Historic preservation, endeavor to preserve, conserve and protect buildings, objects, landscapes or other artifacts * Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage, protection and care of tangible cultural heritage Mathematics and computer science * Type preservation, property of a type system if evaluation of expressions does not cause their type to change * Case preservation, when computer storage preserves the distinction between upper and lower case * Digital preservation, endeavor to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable Arts and entertainment * ''Preservation'' (2018 novel), historical fiction by Jock Serong about the wreck of the '' Sydney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1949
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 4073 Class
The 4073 or Castle Class are 4-6-0 steam locomotives of the Great Western Railway, built between 1923 and 1950. They were designed by the railway's Chief Mechanical Engineer, Charles Collett, for working the company's express passenger trains. They could reach speeds of up to . Background The origins of this highly successful design date back to the Star Class of 1907 which introduced the basic 4-cylinder 4-6-0 layout with long-travel valves and Belpaire firebox that was to become characteristic of Great Western Railway (GWR) express passenger locomotives. The Star class was designed to take the top express trains on the GWR, with 61 in service by 1914, but after World War I there was a need for an improved design. To meet this need, Chief Mechanical Engineer George Churchward had in mind an enlarged Star class design with a standard No.7 boiler, as fitted to his GWR 4700 Class express freight 2-8-0. However, this combination would have taken the axle load over the 20-ton limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 4000 Class
The Great Western Railway 4000 or Star were a class of 4-cylinder 4-6-0 passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward for the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1906 and introduced from early 1907. The prototype was built as a 4-4-2 Atlantic (but converted to 4-6-0 during 1909). They proved to be a successful design which handled the heaviest long-distance express trains, reaching top speeds of 90 mph (145 km/h), and established the design principles for GWR 4-cylinder classes over the next twenty-five years. Background After finally converting the last broad gauge lines in 1892, the GWR began a period of modernisation as new cut-off lines shortened its routes to west of England, South Wales and Birmingham. During the first decade of the twentieth century, the new Chief Mechanical Engineer, George Jackson Churchward designed or acquired a number of experimental locomotives with different wheel arrangements and boiler designs to help him plan for the futu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 4700 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 4700 Class was a class of nine 2-8-0 steam locomotives, designed by George Jackson Churchward. They were introduced in 1919 for heavy mixed-traffic work. Although primarily designed for fast freight, the class also sometimes hauled passenger trains, notably heavy holiday expresses in the summer months. They were called "Night Owls" because they were primarily designed to haul goods during the night and that they could be seen simmering in the daylight, awaiting their nocturnal duties. Background At the end of the First World War, the running department of the GWR identified the need for a larger version of the successful GWR 4300 Class 2-6-0 incorporating the Swindon No. 1 boiler. They envisaged a smaller version of the successful Saint class 4-6-0 with driving wheels - the intermediate of Churchward's three standard wheel sizes, for express goods trains. However, Churchward preferred a 2-8-0 design for this purpose. Prototype The prototype of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didcot Railway Centre
Didcot Railway Centre is a railway museum and preservation engineering site in Didcot, Oxfordshire, England. The site was formerly a Great Western Railway engine shed and locomotive stabling point. Background The founders and commercial backers of the Great Western Railway (GWR) supported Isambard Kingdom Brunel's scheme to develop an integrated railway and steamship service which allowed trans-Atlantic passengers and freight quicker passage between London and New York City. However, whilst backing the scheme the railway had to make a profit, and so it took a number of detours and added both mainline and branch line traffic to increase its domestic earnings. This earned the railway the nickname ''The Great Way Round'' from its detractors. Whilst the route from London Paddington to Reading was relatively straight, the then obvious most direct route to Bristol would have taken the railway further south, thus avoiding both Didcot and Swindon. However, passenger and freight traffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway (heritage Railway)
The Great Central Railway (GCR) is a heritage railway in Leicestershire, named after the company that originally built this stretch of railway. It runs for between the town of Loughborough and a new terminus in the north of Leicester. It has period signalling, locomotives and rolling stock. The GCR is currently the only double track mainline heritage railway in the world with of working double track. Four stations are in operation, each restored to a period in the railway's commercial history: (the 1950s); Quorn & Woodhouse (Second World War and the remainder of the 1940s); (Edwardian Era); Leicester North (the 1960s). Background history In 1897, the Great Central Railway itself was formed, becoming the last steam mainline in the United Kingdom. Two years later in 1899, "The London Extension" was officially opened to passenger and freight traffic, allowing more direct journeys from the capital to Nottingham, Leicester, Sheffield and Manchester. The entire line w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Somerset Railway
The West Somerset Railway (WSR) is a heritage railway line in Somerset, England. The freehold of the line and stations is owned by Somerset County Council; the railway is leased to and operated by West Somerset Railway plc (WSR plc); which is supported and minority-owned by charitable trust the West Somerset Railway Association (WSRA) and the West Somerset Steam Railway Trust (WSSRT). The WSR plc operates services using both heritage steam and diesel trains. It originally opened in 1862 between and . In 1874 it was extended from Watchet to by the Minehead Railway. Although just a single line, improvements were needed in the first half of the twentieth century to accommodate the significant number of tourists that wished to travel to the Somerset coast. The line was closed by British Rail in 1971 and reopened in 1976 as a heritage line. It is the longest standard gauge independent heritage railway in the United Kingdom. Services normally operate over just the between Mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosville Motor Services (Weston-super-Mare)
Crosville Motor Services operated both contract hire and stage carriage bus services between 2011 and 2018 from its base in Weston-super-Mare, North Somerset, England. It also operated a fleet of heritage vehicles and continues to do so as 'Crosville Vintage'. History The original Crosville Motor Services was a major bus operator, covering Mid and North Wales and North West England. The name fell out of use after that company was privatised but was resurrected by this new operator. Some of the heritage fleet were once used by the original Crosville. Although contract and private hire work had been undertaken from 2011, Crosville's first four commercial bus routes commenced operation in April 2012. These included routes from Weston-super-Mare to Sand Bay and Burnham-on-Sea, also a sea front tour to Uphill which was operated by heritage buses on summer Sundays and public holidays. In April 2013 Crosville commenced operating a further two routes, 4 and 83. In 2016, Crosville's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornbury, South Gloucestershire
Thornbury is a market town and civil parish in the South Gloucestershire Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area of England, about 12 miles (19 km) north of Bristol. It had a population of 12,063 at the 2011 UK census, 2011 Census. The population has risen to 14,496 in the 2021 Census. Thornbury is a Britain in Bloom award-winning town, with its own competition: Thornbury in Bloom. The earliest documentary evidence of a village at "Thornbyrig" dates from the end of the 9th century. Domesday Book noted a manor of "Turneberie" belonging to William the Conqueror's consort, Matilda of Flanders, with 104 residents. History There is evidence of human activity in the Thornbury area in the Neolithic and Bronze Ages, but evidence of the Roman presence is confined to the Thornbury hoard of 11,460 Roman coins dating from 260–348 CE, found in 2004 during the digging of a fishpond. The earliest documentary evidence of a village at "Thornbyrig" dates from the end of the 9th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



Oct2001.jpg)
