|
GQM
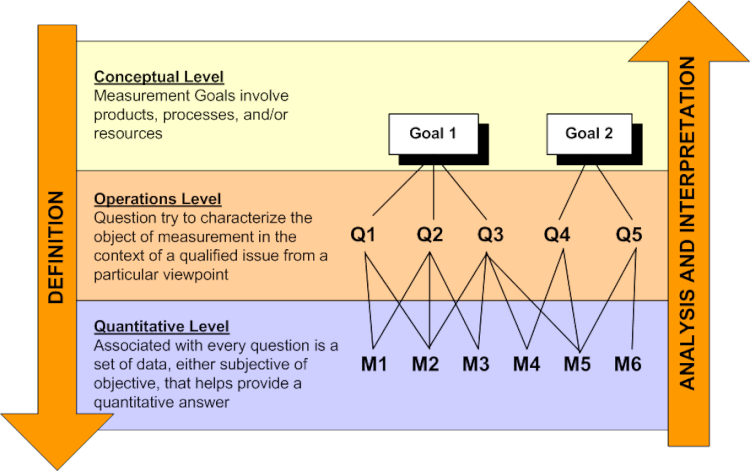
GQM, the initialism for "goal, question, metric", is an established goal-oriented approach to software metrics to improve and measure software quality. History GQM has been promoted by Victor Basili of the University of Maryland, College Park and the Software Engineering Laboratory at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center after supervising a Ph.D. thesis by Dr. David M. Weiss. Dr. Weiss' work was inspired by the work of Albert Endres at IBM Germany. Method GQM defines a measurement model on three levels: ; 1. Conceptual level (Goal): A goal is defined for an object, for a variety of reasons, with respect to various models of quality, from various points of view and relative to a particular environment. ; 2. Operational level (Question): A set of questions is used to define models of the object of study and then focuses on that object to characterize the assessment or achievement of a specific goal. ; 3. Quantitative level (Metric): A set of metrics, based on the models, is assoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GQM+Strategies
GQM+Strategies is a method that provides concepts and actionable steps for creating the link between goals and strategies across an organization and allows for measurement-based decision-making. It was developed by Victor Basili, Jens Heidrich, Mikael LindvallJürgen Münch Myrna Regardie, Carolyn B. Seaman, and Adam Trendowicz. The method was originally developed for organizations having a strong focus on IT and the development of software systems, but the method's popularity has grown to other domains and can be applied to any organization. The booAligning Organizations through Measurementgives a comprehensive overview of the method, provides actionable guidance, case studies, and practical applications. Background In today's competitive markets organizational survival and growth requires effective means of aligning the large variety of organizational goals and strategies to achieve business objectives. Effective alignment helps all parts of the organization move in the same dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal Question Metric Paradigm
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines. A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or aim, the anticipated result which guides reaction, or an end, which is an object, either a physical object or an abstract object, that has intrinsic value. Goal setting Goal-setting theory was formulated based on empirical research and has been called one of the most important theories in organizational psychology. Edwin A. Locke and Gary P. Latham, the fathers of goal-setting theory, provided a comprehensive review of the core findings of the theory in 2002. In summary, Locke and Latham found that specific, difficult goals lead to higher performance than either easy goals or instructions to "do your best", as long as feedback about progress is provided, the person is committed to the goal, and the person has the ability and knowledge to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal
A goal is an idea of the future or desired result that a person or a group of people envision, plan and commit to achieve. People endeavour to reach goals within a finite time by setting deadlines. A goal is roughly similar to a purpose or aim, the anticipated result which guides reaction, or an end, which is an object, either a physical object or an abstract object, that has intrinsic value. Goal setting Goal-setting theory was formulated based on empirical research and has been called one of the most important theories in organizational psychology. Edwin A. Locke and Gary P. Latham, the fathers of goal-setting theory, provided a comprehensive review of the core findings of the theory in 2002. In summary, Locke and Latham found that specific, difficult goals lead to higher performance than either easy goals or instructions to "do your best", as long as feedback about progress is provided, the person is committed to the goal, and the person has the ability and knowle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal-oriented
Goal orientation, or achievement orientation, is an "individual disposition towards developing or validating one's ability in achievement settings". In general, an individual can be said to be ''mastery'' or ''performance'' oriented, based on whether one's goal is to develop one's ability or to demonstrate one's ability, respectively. A ''mastery'' orientation is also sometimes referred to as a ''learning'' orientation. Goal orientation refers to how an individual interprets and reacts to tasks, resulting in different patterns of cognition, affect and behavior. Developed within a social-cognitive framework, the orientation goal theory proposes that students' motivation and achievement-related behaviors can be understood by considering the reasons or purposes they adopt while engaged in academic work. The focus is on how students think about themselves, their tasks, and their performance. Goal orientations have been shown to be associated with individuals' academic achievement, adjus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Metric
In software engineering and development, a software metric is a standard of measure of a degree to which a software system or process possesses some property. Even if a metric is not a measurement (metrics are functions, while measurements are the numbers obtained by the application of metrics), often the two terms are used as synonyms. Since quantitative measurements are essential in all sciences, there is a continuous effort by computer science practitioners and theoreticians to bring similar approaches to software development. The goal is obtaining objective, reproducible and quantifiable measurements, which may have numerous valuable applications in schedule and budget planning, cost estimation, quality assurance, testing, software debugging, software performance optimization, and optimal personnel task assignments. Common software measurements Common software measurements include: * ABC Software Metric * Balanced scorecard * Bugs per line of code * Code coverage * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Basili
Victor R. Basili (born April 13, 1940 in Brooklyn, New York), is an emeritus professor at the Department of Computer Science, which is part of the University of Maryland College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences, and the Institute for Advanced Computer Studies. He holds a Ph.D. in computer science from the University of Texas at Austin and two honorary degrees. He is a fellow of both the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). From 1982 through 1988 he was chair of the Department of Computer Science at the University of Maryland. He is currently a senior research fellow at the Fraunhofer Center for Experimental Software Engineering - Maryland and from 1997 to 2004 was its executive director. He is well known for his works on measuring, evaluating, and improving the software development process, as a pioneer of empirical software engineering, especially through his papers on the Goal/Question/Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Quality
In the context of software engineering, software quality refers to two related but distinct notions: * Software functional quality reflects how well it complies with or conforms to a given design, based on functional requirements or specifications. That attribute can also be described as the fitness for purpose of a piece of software or how it compares to competitors in the marketplace as a worthwhile Product (business), product. It is the degree to which the Software verification and validation#Software validation, correct software was produced. * Software structural quality refers to how it meets non-functional requirements that support the delivery of the functional requirements, such as robustness or maintainability. It has a lot more to do with the degree to which the software works as Software verification and validation#Software verification, needed. Many aspects of structural quality can be evaluated only Static testing, statically through the analysis of the software inne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |