|
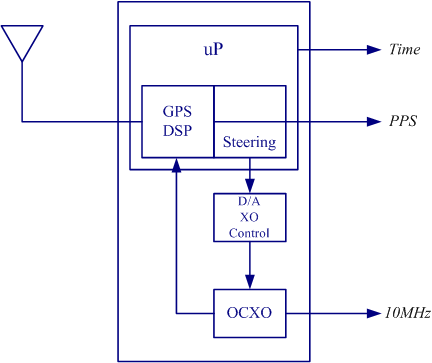
GPSDO
A GPS clock, or GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO), is a combination of a GPS receiver and a high-quality, stable oscillator such as a quartz or rubidium oscillator whose output is controlled to agree with the signals broadcast by GPS or other GNSS satellites. GPSDOs work well as a source of timing because the satellite time signals must be accurate in order to provide positional accuracy for GPS in navigation. These signals are accurate to nanoseconds and provide a good reference for timing applications. Applications GPSDOs serve as an indispensable source of timing in a range of applications, and some technology applications would not be practical without them. GPSDOs are used as the basis for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) around the world. UTC is the official accepted standard for time and frequency. UTC is controlled by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Timing centers around the world use GPS to align their own time scales to UTC. GPS based standards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPSDO
A GPS clock, or GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO), is a combination of a GPS receiver and a high-quality, stable oscillator such as a quartz or rubidium oscillator whose output is controlled to agree with the signals broadcast by GPS or other GNSS satellites. GPSDOs work well as a source of timing because the satellite time signals must be accurate in order to provide positional accuracy for GPS in navigation. These signals are accurate to nanoseconds and provide a good reference for timing applications. Applications GPSDOs serve as an indispensable source of timing in a range of applications, and some technology applications would not be practical without them. GPSDOs are used as the basis for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) around the world. UTC is the official accepted standard for time and frequency. UTC is controlled by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Timing centers around the world use GPS to align their own time scales to UTC. GPS based standards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holdover In Synchronization Applications
Two independent clocks, once synchronized, will walk away from one another without limit. To have them display the same time it would be necessary to re-synchronize them at regular intervals. The period between synchronizations is referred to as holdover and performance under holdover relies on the quality of the reference oscillator, the PLL design, and the correction mechanisms employed. Importance The quote above suggests that one can think of holdover in synchronization applications as analogous to running on backup power. Modern wireless communication systems require at least knowledge of frequency and often knowledge of phase as well in order to work correctly. Base stations need to know what time it is, and they usually get this knowledge from the outside world somehow (from a GPS Time and Frequency receiver, or from a synchronization source somewhere in the network they are connected to). But if the connection to the reference is lost then the base station will be on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Oven
A crystal oven is a temperature-controlled chamber used to maintain the quartz crystal in electronic crystal oscillators at a constant temperature, in order to prevent changes in the frequency due to variations in ambient temperature. An oscillator of this type is known as an ''oven-controlled crystal oscillator'' (OCXO, where "XO" is an old abbreviation for "crystal oscillator".) This type of oscillator achieves the highest frequency stability possible with a crystal. They are typically used to control the frequency of radio transmitters, cellular base stations, military communications equipment, and for precision frequency measurement. Description Quartz crystals are widely used in electronic oscillators to precisely control the frequency produced. The frequency at which a quartz crystal resonator vibrates depends on its physical dimensions. A change in temperature causes the quartz to expand or contract due to thermal expansion, changing the frequency of the signal produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock signal for digital integrated circuits, and to stabilize frequencies for radio transmitters and receivers. The most common type of piezoelectric resonator used is a quartz crystal, so oscillator circuits incorporating them became known as crystal oscillators. However, other piezoelectricity materials including polycrystalline ceramics are used in similar circuits. A crystal oscillator relies on the slight change in shape of a quartz crystal under an electric field, a property known as inverse piezoelectricity. A voltage applied to the electrodes on the crystal causes it to change shape; when the voltage is removed, the crystal generates a small voltage as it elastically returns to its original shape. The quartz oscillates at a stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerically Controlled Oscillator
A numerically-controlled oscillator (NCO) is a digital signal generator which creates a synchronous (i.e. clocked), discrete-time, discrete-valued representation of a waveform, usually sinusoidal. NCOs are often used in conjunction with a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) at the output to create a direct digital synthesizer (DDS). Numerically-controlled oscillators offer several advantages over other types of oscillators in terms of agility, accuracy, stability and reliability. NCOs are used in many communications systems including digital up/down converters used in 3G wireless and software radio systems, digital phase-locked loops, radar systems, drivers for optical or acoustic transmissions, and multilevel FSK/ PSK modulators/demodulators. Operation An NCO generally consists of two parts: *A ''phase accumulator'' (PA), which adds to the value held at its output a frequency control value at each clock sample. *A ''phase-to-amplitude converter'' (PAC), which uses the phase accum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipath Interference
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflection from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings. When the same signal is received over more than one path, it can create interference and phase shifting of the signal. Destructive interference causes fading; this may cause a radio signal to become too weak in certain areas to be received adequately. For this reason, this effect is also known as multipath interference or multipath distortion. Where the magnitudes of the signals arriving by the various paths have a distribution known as the Rayleigh distribution, this is known as Rayleigh fading. Where one component (often, but not necessarily, a line of sight component) dominates, a Rician distribution provides a more accurate model, and this is known as R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. ''Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Line of sight transmission is used for medium-distance radio transmission, such as cell phones, cordless phones, walkie- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-per-second Signal
A pulse per second (PPS or 1PPS) is an electrical signal that has a width of less than one second and a sharply rising or abruptly falling edge that accurately repeats once per second. PPS signals are output by radio beacons, frequency standards, other types of precision oscillators and some GPS receivers. 'ICD-GPS-060B: GPS User Equipment (Phase III) Interface Control Document for the Pecise Time and Time Interval (PTTI) Interface'', Global Positioning System Joint Program Office, 2002 Precision clocks are sometimes manufactured by interfacing a PPS signal generator to processing equipment that aligns the PPS signal to the UTC second and converts it to a useful display. |
Allan Variance
The Allan variance (AVAR), also known as two-sample variance, is a measure of frequency stability in clock A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the ...s, oscillators and amplifiers. It is named after David W. Allan and expressed mathematically as \sigma_y^2(\tau). The Allan deviation (ADEV), also known as sigma-tau, is the square root of the Allan variance, \sigma_y(\tau). The ''M-sample variance'' is a measure of frequency stability using ''M'' samples, time ''T'' between measurements and observation time \tau. ''M''-sample variance is expressed as :\sigma_y^2(M, T, \tau). The Allan variance is intended to estimate stability due to noise processes and not that of systematic errors or imperfections such as frequency drift or temperature effects. The Allan variance and Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). An SoC may connect the external microcontroller chips as the motherboard components, but an SoC usually integrates the advanced peripherals like graphics processing unit (GPU) and Wi-Fi interface controller as its internal microcontroller unit circuits. Microcontrollers are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase-locked Loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector in a feedback loop. The oscillator's frequency and phase are controlled proportionally by an applied voltage, hence the term voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The oscillator generates a periodic signal of a specific frequency, and the phase detector compares the phase of that signal with the phase of the input periodic signal, to adjust the oscillator to keep the phases matched. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and output frequencies the same. Consequently, in addition to synchronizing signals, a phase-locked loop can track an input frequency, or it can generate a frequency that is a multiple of the input frequency. These properties are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
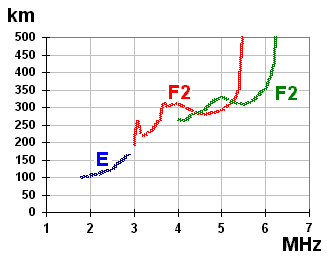
Ionosonde
An ionosonde, or chirpsounder, is a special radar for the examination of the ionosphere. The basic ionosonde technology was invented in 1925 by Gregory Breit and Merle A. Tuve and further developed in the late 1920s by a number of prominent physicists, including Edward Victor Appleton. The term ''ionosphere'' and hence, the etymology of its derivatives, was proposed by Robert Watson-Watt. Components An ionosonde consists of: * A high frequency (HF) radio transmitter, automatically tunable over a wide range. Typically the frequency coverage is 0.5–23 MHz or 1–40 MHz, though normally sweeps are confined to approximately 1.6–12 MHz. * A tracking HF receiver which can automatically track the frequency of the transmitter. * An antenna with a suitable radiation pattern, which transmits well vertically upwards and is efficient over the whole frequency range used. * Digital control and data analysis circuits. The transmitter sweeps all or part of the HF frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |