|
GPM Core Observatory
Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is a joint mission between JAXA and NASA as well as other international space agencies to make frequent (every 2–3 hours) observations of Earth's precipitation. It is part of NASA's Earth Systematic Missions program and works with a satellite constellation to provide full global coverage. The project provides global precipitation maps to assist researchers in improving the forecasting of extreme events, studying global climate, and adding to current capabilities for using such satellite data to benefit society. GPM builds on the notable successes of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM), which was also a joint NASA-JAXA activity. The project is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, and consists of a GPM Core Observatory satellite assisted by a constellation of spacecraft from other agencies and missions. The Core Observatory satellite measures the two and three dimensional structure of Earth's precipitation patterns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
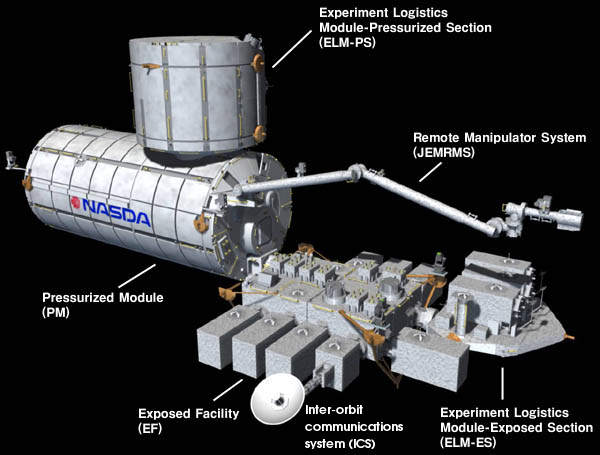
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPM Examines East Coast Snow Storm
GPM may refer to: * GPM (software), software providing support for mouse devices in Linux virtual consoles *Graphical path method, a mathematically based algorithm used in project management * Gallons per minute, a unit of volumetric flow rate *Gallons per mile, a unit of fuel efficiency * General Purpose Macrogenerator, an early macro processor * Global Marshall Plan, specific ideas on how to save the global environment *Global Precipitation Measurement, a NASA and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency project to measure global rainfall *Graduated payment mortgage, a type of loan *Graham Patrick Martin, an American actor *Grand Prairie Municipal Airport, a public-use airfield in Grand Prairie, Texas, United States (Federal Aviation Administration identification code) * Grand Prix Masters, an auto racing series for retired Formula One drivers *Gross profit margin, a calculation of revenue and cost of products *Protestant Church in the Moluccas The Protestant Church of Maluku is a Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched By H-II Rockets
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather satellite, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, Planetary science, planetary exploration, and Space transport, transportation of Human spaceflight, humans and cargo spacecraft, cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters outer space, space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 2014
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condensed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Programs
This is a list of NASA missions, both crewed and robotic, since the establishment of NASA in 1958. There are over 80 currently active science missions. X-Plane program Since 1945, NACA (NASA's predecessor) and, since 1958, NASA have conducted the X-Plane Program. The program was originally intended to create a family of experimental aircraft not intended for production beyond the limited number of each design built solely for flight research. The first X-Plane, the Bell X-1, was the first rocket-powered airplane to break the sound barrier on October 14, 1947. X-Planes have set numerous milestones since then, both crewed and unpiloted. Human spaceflight NASA has successfully launched 166 crewed flights. Three have ended in failure, causing the deaths of seventeen crewmembers in total: Apollo 1 (which never launched) killed three crew members in 1967, STS-51-L ( the ''Challenger'' disaster) killed seven in 1986, and STS-107 ( the ''Columbia'' disaster) killed seven more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We, The People
The Preamble to the United States Constitution, beginning with the words We the People, is a brief introductory statement of the Constitution's fundamental purposes and guiding principles. Courts have referred to it as reliable evidence of the Founding Fathers' intentions regarding the Constitution's meaning and what they hoped the Constitution would achieve. The preamble was mainly written by Founding Father Gouverneur Morris, a Pennsylvania delegate to the 1787 Constitutional Convention held at Independence Hall in Philadelphia. Text Drafting The Preamble was placed in the Constitution during the last days of the Constitutional Convention by the Committee on Style, which wrote its final draft, with Gouverneur Morris leading the effort. It was not proposed or discussed on the floor of the convention beforehand. The initial wording of the preamble did not refer to the people of ''the United States''; rather, it referred to people of the various states, which was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Rukh Khan
Shah Rukh Khan (; born 2 November 1965), also known by the initialism SRK, is an Indian actor, film producer, and television personality who works in Hindi films. Referred to in the media as the " Baadshah of Bollywood", "King of Bollywood" and "King Khan", he has appeared in more than 80 films, and earned numerous accolades, including 14 Filmfare Awards. He has been awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India, as well as the Ordre des Arts et des Lettres and Legion of Honour by the Government of France. Khan has a significant following in Asia and the Indian diaspora worldwide. In terms of audience size and income, he has been described as one of the most successful film stars in the world. Khan began his career with appearances in several television series in the late 1980s. He made his Bollywood debut in 1992 with '' Deewana''. Early in his career, Khan was recognised for portraying villainous roles in the films ''Baazigar'' (1993), ''Darr'' (1993), and ''Anjaam'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Social
NASA has hosted many events for its social media enthusiasts called NASA Socials (formerly NASA Tweetups) beginning in 2009. These events are targeted at the social media followers of NASA through platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, Google Plus, Instagram, YouTube and more. They provide guests with VIP access to NASA facilities and speakers with the goal of leveraging participants' social networks to further the outreach requirements of NASA as laid out in the National Aeronautics and Space Act. NASA re-branded these events as "Socials" in March 2012 as it expanded participation to services beyond just Twitter. As of 2015, all NASA field centers and NASA Headquarters have hosted NASA Tweetup/Social events. There were 5 NASA Tweetups in 2009, 10 in 2010, 16 in 2011, 21 in 2012, 22 in 2013, and 23 in 2014. In August 2011, over 2,000 participants had been part of official NASA Tweetups. By July 2014, that number had swelled to over 6,000 total participants in over 5 years of NASA Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, saline water (salt water) and atmospheric water is variable depending on a wide range of climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different forms: liquid, solid (ice) and vapor. The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle as it is the source of 86% of global evaporation. The water cycle involves the exchange of energy, which leads to temperature changes. When water evaporates, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |