|
GJB2
Gap junction beta-2 protein (GJB2), also known as connexin 26 (Cx26) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJB2'' gene. Clinical significance Defects in this gene lead to the most common form of congenital deafness in developed countries, called DFNB1 (also known as connexin 26 deafness or ''GJB2''-related deafness). One fairly common mutation is the deletion of one guanine from a string of six, resulting in a frameshift and termination of the protein at amino acid number 13. Having two copies of this mutation results in deafness. Connexin 26 also plays a role in tumor suppression through mediation of the cell cycle. The abnormal expression of Cx26, correlated with several types of human cancers, may serve as a prognostic factor for cancers such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and bladder cancer. Furthermore, Cx26 over-expression is suggested to promote cancer development by facilitating cell migration and invasion and by stimulating the self-perpetuation abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connexin
Connexins (Cx)TC# 1.A.24, or gap junction proteins, are structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. An entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, form gap junctions in invertebrates. Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, or connexons, which consist of homo- or heterohexameric arrays of connexins, and the connexon in one plasma membrane docks end-to-end with a connexon in the membrane of a closely opposed cell. The hemichannel is made of six connexin subunits, each of which consist of four transmembrane segments. Gap junctions are essential for many physiological processes, such as the coordinated depolarization of cardiac muscle, proper embryonic development, and the conducted response in microvasculature. Connexins also have non-channel dependant functions relating to cytoskeleton and cell migration. For these reasons, mutations in connexin-encoding genes can lead to functional and developmental abnormalities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connexin
Connexins (Cx)TC# 1.A.24, or gap junction proteins, are structurally related transmembrane proteins that assemble to form vertebrate gap junctions. An entirely different family of proteins, the innexins, form gap junctions in invertebrates. Each gap junction is composed of two hemichannels, or connexons, which consist of homo- or heterohexameric arrays of connexins, and the connexon in one plasma membrane docks end-to-end with a connexon in the membrane of a closely opposed cell. The hemichannel is made of six connexin subunits, each of which consist of four transmembrane segments. Gap junctions are essential for many physiological processes, such as the coordinated depolarization of cardiac muscle, proper embryonic development, and the conducted response in microvasculature. Connexins also have non-channel dependant functions relating to cytoskeleton and cell migration. For these reasons, mutations in connexin-encoding genes can lead to functional and developmental abnormalities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bart–Pumphrey Syndrome
Bart–Pumphrey syndrome (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma with knuckle pads and leukonychia and deafness") is a cutaneous condition characterized by hyperkeratoses (knuckle pads) over the metacarpophalangeal, proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. It was characterized in 1967. It can be associated with GJB2. See also * Camisa disease * List of cutaneous conditions * Bart syndrome * Palmoplantar keratoderma Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal thickening of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles. Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been described. Types C ... References External links Palmoplantar keratodermas Syndromes {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regulated gate between cells. One gap junction channel is composed of two protein hexamers (or hemichannels) called connexons in vertebrates and innexons in invertebrates. The hemichannel pair connect across the intercellular space bridging the gap between two cells. Gap junctions are analogous to the plasmodesmata that join plant cells. Gap junctions occur in virtually all tissues of the body, with the exception of adult fully developed skeletal muscle and mobile cell types such as sperm or erythrocytes. Gap junctions are not found in simpler organisms such as sponges and slime molds. A gap junction may also be called a ''nexus'' or ''macula communicans''. While an ephapse has some similarities to a gap junction, by modern definition the two a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GJB1
Gap junction beta-1 protein (GJB1), also known as connexin 32 (Cx32) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJB1'' gene. Gap junction beta-1 protein is a member of the gap junction connexin family of proteins that regulates and controls the transfer of communication signals across cell membranes, primarily in the liver and peripheral nervous system. Mutations of the GJB1 gene affecting the signalling of and trafficking through gap junctions, resulting in an inherited peripheral neuropathy called X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Complications include the demyelination of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, causing delayed transmission rates of nerve communication in the peripheral nervous system, due to irregularities in the normal function of the cells. This condition leads to a number of symptoms, most commonly muscle weakness and sensory problems in the outer extremities of the limbs. As a result, muscle atrophy and soft tissue injuries due to delayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vohwinkel Syndrome
Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal thickening of the stratum corneum of the palms and soles. Autosomal recessive, dominant, X-linked, and acquired forms have all been described. Types Clinically, three distinct patterns of palmoplantar keratoderma may be identified: diffuse, focal, and punctate. Diffuse Diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is a type of palmoplantar keratoderma that is characterized by an even, thick, symmetric hyperkeratosis over the whole of the palm and sole, usually evident at birth or in the first few months of life. Restated, diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma is an autosomal dominant disorder in which hyperkeratosis is confined to the palms and soles. The two major types can have a similar clinical appearance: *''Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma'' (also known as "Palmoplantar keratoderma cum degeneratione granulosa Vörner," "Vörner's epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma", and "Vörn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written with a lower case ''d''. It later came to be used in a cultural context to refer to those who primarily communicate through sign language regardless of hearing ability, often capitalized as ''Deaf'' and referred to as "big D Deaf" in speech and sign. The two definitions overlap but are not identical, as hearing loss includes cases that are not severe enough to impact spoken language comprehension, while cultural Deafness includes hearing people who use sign language, such as children of deaf adults. Medical context In a medical context, deafness is defined as a degree of hearing difference such that a person is unable to understand speech, even in the presence of amplification. In profound deafness, even the highest intensity sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. This unsaturated arrangement means the bicyclic molecule is planar. Properties Guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA, and uracil only in RNA. Guanine has two tautomeric forms, the major keto form (see figures) and rare enol form. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. In cytosine, the amino group acts as the hydrogen bond donor and the C-2 carbonyl and the N-3 amine as the hydrogen-bond acceptors. Guanine has the C-6 carbonyl group that acts as the hydrogen bond acceptor, while a group at N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
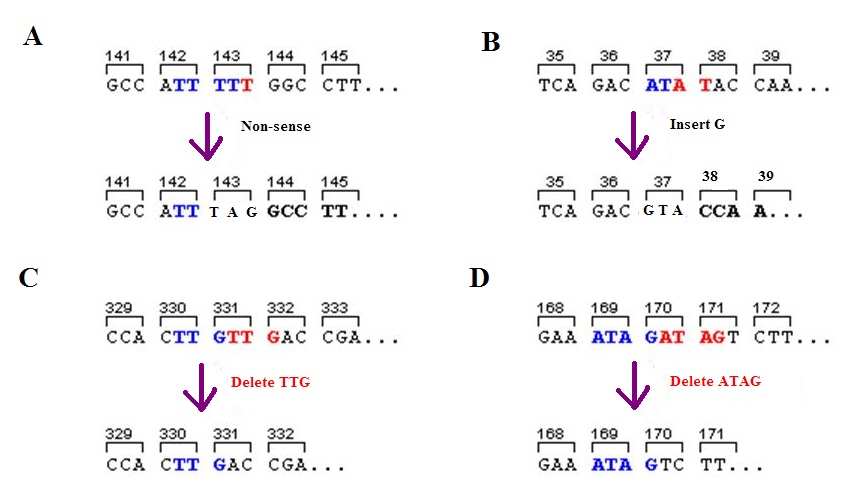
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor Gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding environment, when mutated can cause an envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |