|
GGSE-1
The Gravity Gradient Stabilization Experiment (GGSE-1) was a technology satellite launched simultaneously with four other satellites (including SOLRAD 7A and POPPY 3) on 11 January 1964 by the U.S. military from Vandenberg Air Force Base aboard a Thor Augmented Delta-Agena D rocket. It demonstrated a new oscillation damping system intended for use in reconnaissance satellites. Background GGSE-1 was the first in a series of technology satellites that tested designs and deployment techniques later applied to the Naval Ocean Surveillance System NOSS/Whitecloud reconnaissance satellites. Spacecraft GGSE-1 was an ovoid satellite based on a similar bus to SOLRAD 7A, with which it was launched into orbit. GGSE-1 was equipped with a passive oscillatory damping mechanism attached to the spacecraft via a rod of metal tape. The entire mechanism and rod together weighed less than 4.5 kg. The damping mechanism, developed by General Electric, comprised a metal sphere, 12.7&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOLRAD 7A
SOLRAD 7A was the seventh solar X-Ray monitoring satellite in the SOLRAD series, and the fourth to successfully orbit the Earth. It was boosted into orbit along with four other military satellites atop a Thor Augmented Delta-Agena D rocket on January 11, 1964. Data returned by SOLRAD 7A dramatically revised scientific models of the solar corona. History The SOLRAD science satellite program was conceived in 1958 to observe the Sun in the X-ray spectrum. It was quickly combined, to provide civilian cover (launches being unclassified at that time), with the concurrently conceived United States Naval Research Laboratory's GRAB satellite project, which would collect information on foreign radars and communications installations. There were five SOLRAD/GRAB missions between 1960 and 1962, with the scientific SOLRAD experiments sharing satellite space with GRAB's intelligence payload. Two of the missions were successful. In 1962, all U.S. overhead reconnaissance projects were consol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit (satellite)
The Transit system, also known as NAVSAT or NNSS (for ''Navy Navigation Satellite System''), was the first satellite navigation system to be used operationally. The radio navigation system was primarily used by the U.S. Navy to provide accurate location information to its Polaris ballistic missile submarines, and it was also used as a navigation system by the Navy's surface ships, as well as for hydrographic survey and geodetic surveying. Transit provided continuous navigation satellite service from 1964, initially for Polaris submarines and later for civilian use as well. In the Project DAMP Program, the missile tracking ship USAS American Mariner also used data from the satellite for precise ship's location information prior to positioning its tracking radars. History The Transit satellite system, sponsored by the Navy and developed jointly by DARPA and the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, under the leadership of Dr. Richard Kershner at Johns Hopkins, was the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, silicone grease, silicone rubber, silicone resin, and silicone caulk. Chemistry More precisely called polymerized siloxanes or polysiloxanes, silicones consist of an inorganic silicon–oxygen backbone chain (⋯−Si−O−Si−O−Si−O−⋯) with two organic groups attached to each silicon center. Commonly, the organic groups are methyl. The materials can be cyclic or polymeric. By varying the −Si−O− chain lengths, side groups, and crosslinking, silicones can be synthesized with a wide variety of properties and compositions. They can vary in consistency from liquid to gel to rubber to hard plastic. The most common siloxan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ocean Surveillance System
The Naval Ocean Surveillance System (NOSS) is a series of signals-intelligence satellites that have conducted electronic signals intelligence for the U.S. Navy since the early 1970s. The first series of satellites were codenamed "White Cloud" or "PARCAE", while second- and third-generation satellites have used the codenames "Ranger" and "Intruder". The system is operated by the United States Navy, and its main purpose was tactical geolocation of Soviet Navy assets during the Cold War. NOSS involves satellite clusters operating in low Earth orbit to detect radar and other electronic transmissions from ships at sea and locate them using the time difference of arrival technique. Satellites :''* One satellite from each third generation pair is officially catalogued as debris''. :data fro Cost |
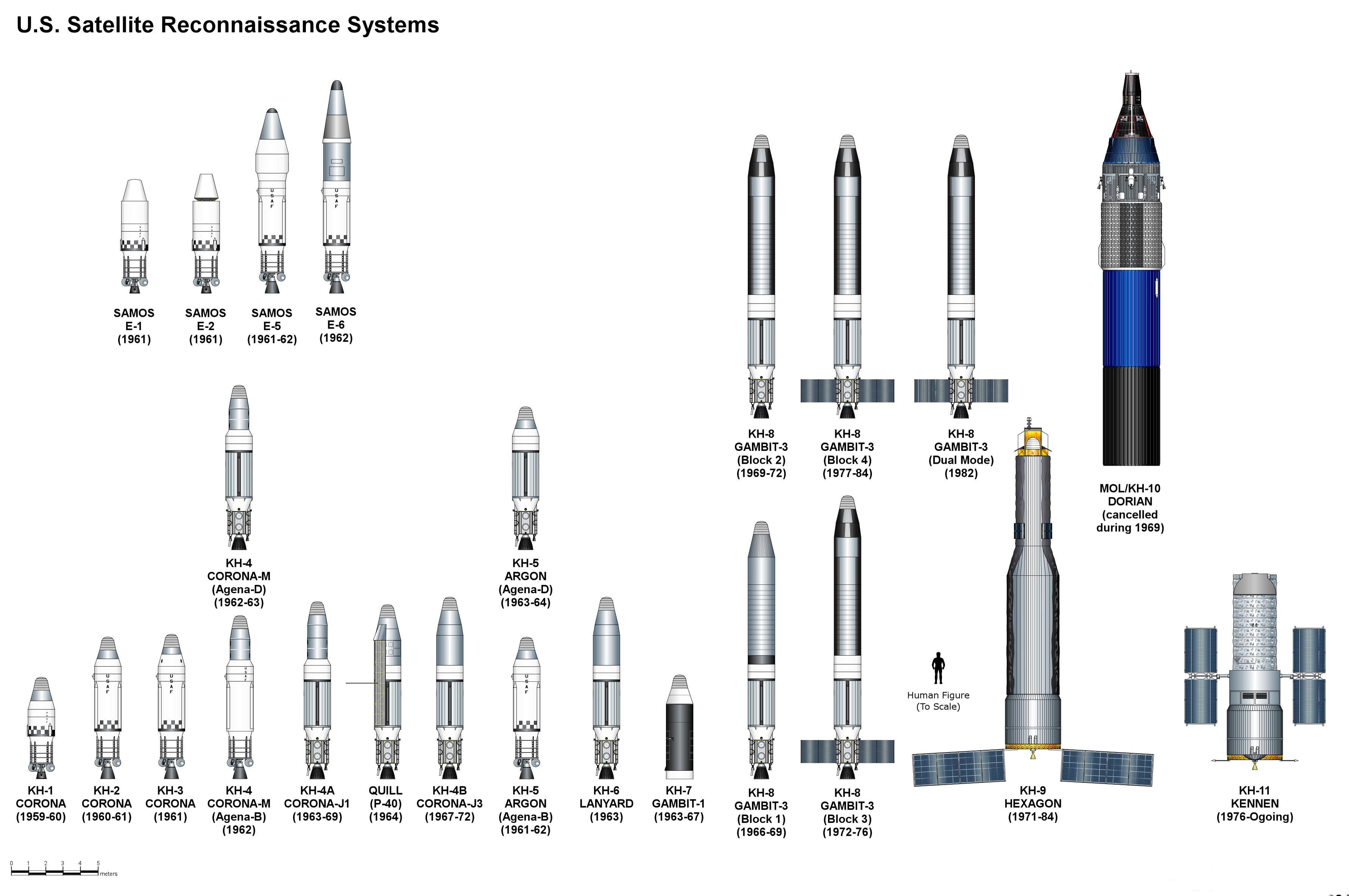
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poppy (satellite)
POPPY is the code name given to a series of U.S. intelligence satellites operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. The POPPY satellites recorded electronic signals intelligence (ELINT) data, targeting radar installations in the Soviet Union and Soviet naval ships at sea. The POPPY program was a continuation within NRO's Program C of the Naval Research Laboratory's Galactic Radiation and Background (GRAB) ELINT program, also known as ''Tattletale''. The National Security Agency was given the responsibility of collecting, interpreting, and reporting the signals intercepted. The existence of the POPPY program was declassified by the NRO in September 2005, although most of the details about its capabilities and operation are still classified. The NRO revealed, though, that the POPPY satellites, like other US signals intelligence (SIGINT) systems, used the principle of signals time difference of arrival, which enables precise locating of an object. All POPPY launches orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity-gradient Stabilization
Gravity-gradient stabilization (a.k.a. "tidal stabilization") is a method of stabilizing artificial satellites or space tethers in a fixed orientation using only the orbited body's mass distribution and gravitational field. The main advantage over using active stabilization with propellants, gyroscopes or reaction wheels is the low use of power and resources. It can also reduce or prevent the risk of propellant contamination of sensitive components. The idea is to use the Earth's gravitational field and tidal forces to keep the spacecraft aligned in the desired orientation. The gravity of the Earth decreases according to the inverse-square law, and by extending the long axis perpendicular to the orbit, the "lower" part of the orbiting structure will be more attracted to the Earth. The effect is that the satellite will tend to align its axis of minimum moment of inertia vertically. The first experimental attempt to use the technique on a human spaceflight was performed on Sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)




.jpg)