|
GFRα3
GDNF family receptor alpha-3 (GFRα3), also known as the artemin receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GFRA3'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-linked cell surface receptor and a member of the GDNF receptor family. It forms a signaling receptor complex with RET tyrosine kinase receptor and binds the artemin ligand. In mouse models of osteoarthritis, GFRα3 was upregulated in sensory nerves. Treating arthritic mice with monoclonal antibodies that bind to GFRα3 prevents artemin from binding there and signaling pain. Treated mice were able to use their limbs again two hours post-treatment. See also * GFRα The GDNF family receptor-α (GFRα) proteins are a group of co-receptors which form complexes with GDNF-family ligands (GFLs) to activate RET, the receptor of the GFLs. The GFRα co-receptors include the following: * GFRα1 – preference for ... References Further reading * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemin
Artemin, also known as enovin or neublastin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARTN'' gene. Function Artemin is a neurotrophic factor in the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor family of ligands which are a group of ligands within the TGF-beta superfamily of signaling molecules. GDNFs are unique in having neurotrophic properties and have potential use for gene therapy in neurodegenerative disease. Artemin has been shown in culture to support the survival of a number of peripheral neuron populations and at least one population of dopaminergic CNS neurons. Its role in the PNS and CNS is further substantiated by its expression pattern in the proximity of these neurons. This protein is a ligand for the RET receptor and uses GFR-alpha 3 as a coreceptor. Role in Axonal Development Artemin, along with other GDNF family of ligands, has been implicated in the structural development and plasticity of several types of neurons, including ventral mesencephalic dop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Cell Line-derived Neurotrophic Factor
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''GDNF'' gene. GDNF is a small protein that potently promotes the survival of many types of neurons. It signals through GFRα receptors, particularly GFRα1. It is also responsible for the determination of spermatogonia into primary spermatocytes, i.e. it is received by RET proto-oncogene (RET) and by forming gradient with SCF it divides the spermatogonia into two cells. As the result there is retention of spermatogonia and formation of spermatocyte. GDNF family of ligands (GFL) GDNF was discovered in 1991, and is the first member of the GDNF family of ligands (GFL) found. Function GDNF is highly distributed throughout both the peripheral and central nervous system. It can be secreted by astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, motor neurons, and skeletal muscle during the development and growth of neurons and other peripheral cells. The GDNF gene encodes a highly conserved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
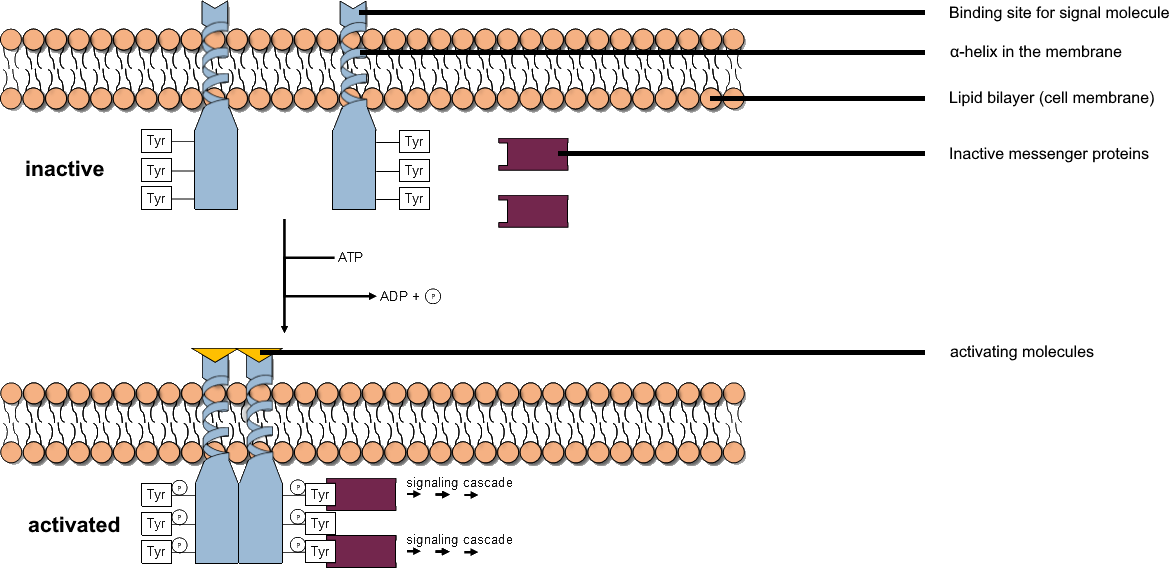
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time. Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs; the knee and hip joints; and the joints of the neck and lower back. Joints on one side of the body are often more affected than those on the other. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and therapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


4-3D-balls.png)

