|
Gynecologic Cancer Disparities In The United States
Gynecologic cancer disparities in the United States refer to differences in incidence, prevalence, and mortality from gynecologic cancers between population groups. The five main types of gynecologic cancer include cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, vaginal cancer, and vulvar cancer. For patients with these and other gynecologic malignancies within the United States, disparities across the care continuum by socioeconomic status and racial/ethnic background have been previously identified and studied. The causes behind these disparities are multifaceted and a complex interplay of systemic differences in health as well as individual patient factors such as cultural, educational, and economic barriers. Cervical cancer disparities Since the development of the Papanicolou smear or Pap smear in 1941, cervical cancer has been highly preventable. The implementation of Pap smear screening programs has resulted in a steady decline in incidence and mortality rates from c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecologic Oncology
Gynecologic oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer. As specialists, they have extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of these cancers. In the United States, 82,000 women are diagnosed with gynecologic cancer annually. In 2013, an estimated 91,730 were diagnosed. The Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the European Society of Gynaecological Oncology are professional organizations for gynecologic oncologists, and the Gynecologic Oncology Group is a professional organization for gynecological oncologists as well as other medical professionals who deal with gynecologic cancersThe Foundation for Women's Canceris the major U.S. organization that raises awareness and research funding and provides educational programs and materials about gynecologic cancers. There is low quality evidence which demonstrates women with gyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most often vaginal bleeding not associated with a menstrual period. Other symptoms include pain with urination, pain during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain. Endometrial cancer occurs most commonly after menopause. Approximately 40% of cases are related to obesity. Endometrial cancer is also associated with excessive estrogen exposure, high blood pressure and diabetes. Whereas taking estrogen alone increases the risk of endometrial cancer, taking both estrogen and a progestogen in combination, as in most birth control pills, decreases the risk. Between two and five percent of cases are related to genes inherited from the parents. Endometrial cancer is sometimes loosely referred to as "uterine cancer", although it is distinct from other fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer is an extraordinarily rare form of cancer that develops in the tissue of the vagina. Primary vaginal cancer originates from the vaginal tissue – most frequently squamous cell carcinoma, but primary vaginal adenocarcinoma, sarcoma, and melanoma have also been reported – while secondary vaginal cancer involves the metastasis of a cancer that originated in a different part of the body. Secondary vaginal cancer is more common. Signs of vaginal cancer may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, dysuria, tenesmus, or pelvic pain, though as many as 20% of women diagnosed with vaginal cancer are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. Vaginal cancer occurs more frequently in women over age 50, and the mean age of diagnosis of vaginal cancer is 60 years. It often can be cured if found and treated in early stages. Surgery alone or surgery combined with pelvic radiation is typically used to treat vaginal cancer. Description Carcinoma of the vagina occurs in less than 2% of wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer is a cancer of the vulva, the outer portion of the female genitals. It most commonly affects the labia majora. Less often, the labia minora, clitoris, or vaginal glands are affected. Symptoms include a lump, itchiness, changes in the skin, or bleeding from the vulva. Risk factors include vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), HPV infection, genital warts, smoking, and many sexual partners. Most vulvar cancers are squamous cell cancers. Other types include adenocarcinoma, melanoma, sarcoma, and basal cell carcinoma. Diagnosis is suspected based on physical examination and confirmed by tissue biopsy. Routine screening is not recommended. Prevention may include HPV vaccination. Standard treatments may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and biologic therapy. Vulvar cancer newly affected about 44,200 people and resulted in 15,200 deaths globally in 2018. In the United States, it newly occurred in about 6,070 people with 1,280 deaths a year. Onset is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix Adenocarcinoma In Situ (1800597030)
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilize an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms, aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papanicolaou Smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cytobrush. A similar method is used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
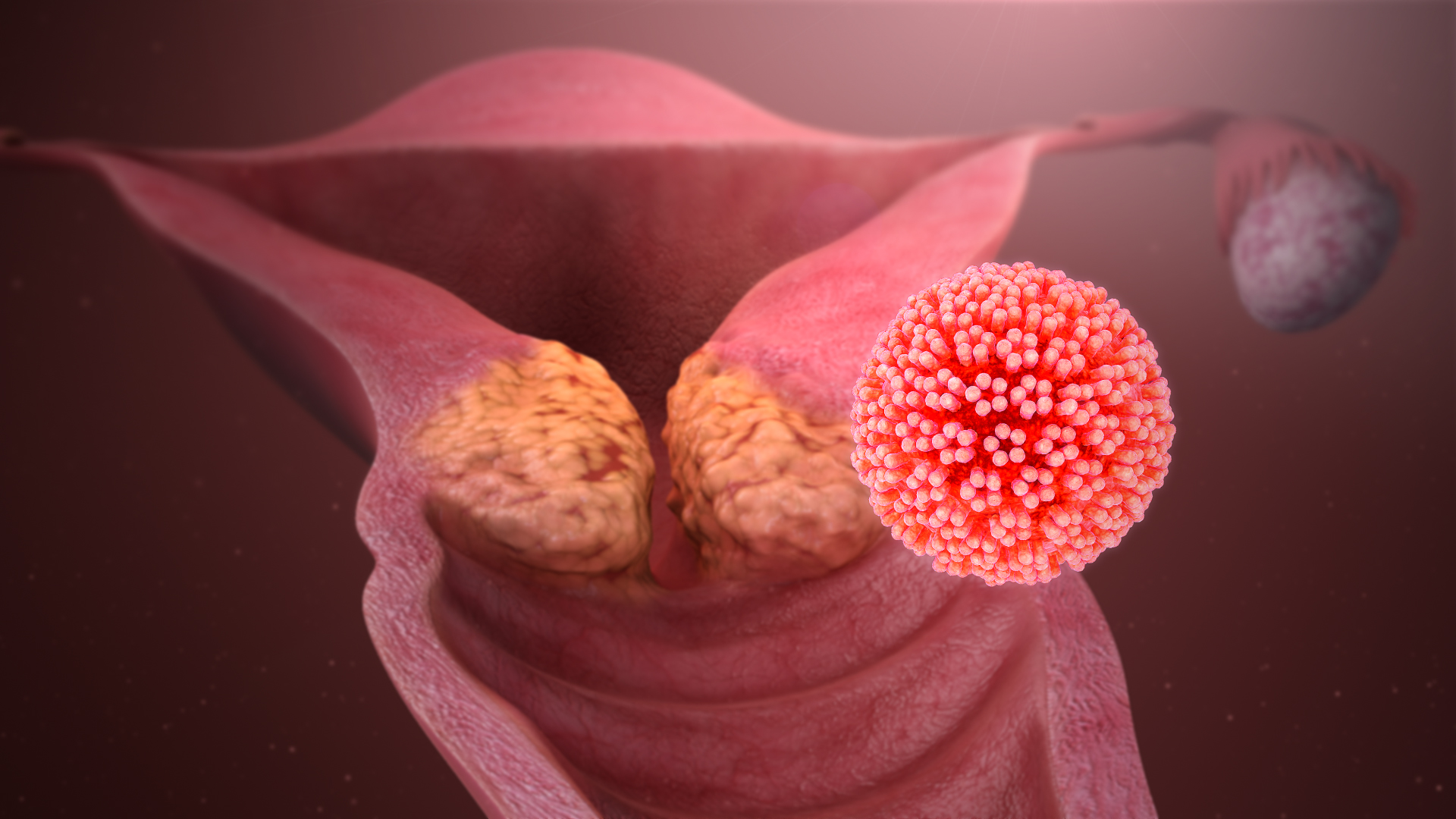
Human Papillomavirus Infection
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) or Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrial cancer (second most common), ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair. It is a type of cancer syndrome. Because patients with Lynch syndrome can have polyps, the term HNPCC has fallen out of favor. Signs and symptoms Risk of cancer ''Lifetime risk and mean age at diagnosis for Lynch syndrome associated cancers'' In addition to the types of cancer found in the chart above, it is understood that Lynch syndrome also contributes to an increased risk of small bowel cancer, pancreatic cancer, ureter/renal pelvis cancer, biliary tract cancer, brain cancer, and sebaceous neoplasms. Increased risk of prostate cancer and breast cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. Indications It is usually done because many types of cancer have a marked tendency to produce lymph node metastasis early in their natural history. This is particularly true of melanoma, head and neck cancer, differentiated thyroid cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Famed British surgeon Berkeley Moynihan once remarked that "the surgery of cancer is not the surgery of organs; it is the surgery of the lymphatic system". The better-known examples of lymphadenectomy are ''axillary lymph node dissection'' for breast cancer; ''radical neck dissection'' for head and neck cancer and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Health In The United States
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or Adolescence, adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving childbirth, birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14750388526).jpg)

.jpg)