|
Gustav Karl Theodor Friedrich Baermann
Gustav Karl Theodor Friedrich Baermann (7 February 1877-1950), was a medical doctor and researcher into public health in the early 20th century. He worked for the former Dutch East Indies administration as a foreign scientist. He was the originator of the Baermann Technique for the extraction of larval roundworms and published his seminal work in 1917. Biography Baermann was born in Breslau, former Prussia, now Poland to Heinrich Baermann (1841-1918) and Anna Mathilde Carolina née Dompierre (1843-1931). In 1897 he became lifetime member of the Corps Bavaria in Munich, with the reception number 1254. Baermann married his first wife, Eva Helene Emilie Erika Weinbach on 31 December 1904 in Breslau, former Prussia, now Poland. He studied for his PhD at Universität Breslau, and graduated in 1905. Baermann worked with and contributed to the work of Albert Neisser whom he accompanied on his expeditions to Java in 1905 and 1907 to study venereal diseases in humans. In 1905 Neisser o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baermann
Heinrich Joseph Baermann (also spelled Bärmann; 14 February 1784 – 11 June 1847) was a German clarinet virtuoso of the Romantic era who is generally considered as being not only an outstanding performer of his time, but highly influential in the creation of several important composers' works for his instrument. Life Baermann was born in Potsdam. In his youth, Baermann took lessons from Joseph Beer (1744–1811) at the military school in Potsdam. After his prowess came to the attention of the Berlin court in 1804, Prince Louis Ferdinand of Prussia had the 20-year-old musician pursue his training in Berlin under the guidance of Franz Tausch (1762–1817). He played in the court orchestra of Munich from 1807 until his retirement in 1834, when his son Carl Baermann succeeded him. Parallel to Baermann's rise, the clarinet was undergoing a series of developments in key construction and embouchure that allowed greater agility and flexibility in playing. The growing custom was to pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary). The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter) though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. In latent syphilis, which can last for years, there are few or no symptoms. In tertiary syphilis, there are gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as " the great imitator" as it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through sexual activity. It may also be tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Public Health Doctors
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1950 Deaths
Year 195 ( CXCV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scrapula and Clemens (or, less frequently, year 948 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 195 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus has the Roman Senate deify the previous emperor Commodus, in an attempt to gain favor with the family of Marcus Aurelius. * King Vologases V and other eastern princes support the claims of Pescennius Niger. The Roman province of Mesopotamia rises in revolt with Parthian support. Severus marches to Mesopotamia to battle the Parthians. * The Roman province of Syria is divided and the role of Antioch is diminished. The Romans annexed the Syrian cities of Edessa and Nisibis. Severus re-establish his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1877 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Queen Victoria is proclaimed '' Empress of India'' by the '' Royal Titles Act 1876'', introduced by Benjamin Disraeli, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom . * January 8 – Great Sioux War of 1876 – Battle of Wolf Mountain: Crazy Horse and his warriors fight their last battle with the United States Cavalry in Montana. * January 20 – The Conference of Constantinople ends, with Ottoman Turkey rejecting proposals of internal reform and Balkan provisions. * January 29 – The Satsuma Rebellion, a revolt of disaffected samurai in Japan, breaks out against the new imperial government; it lasts until September, when it is crushed by a professionally led army of draftees. * February 17 – Major General Charles George Gordon of the British Army is appointed Governor-General of the Sudan. * March – '' The Nineteenth Century'' magazine is founded in London. * March 2 – Compromise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
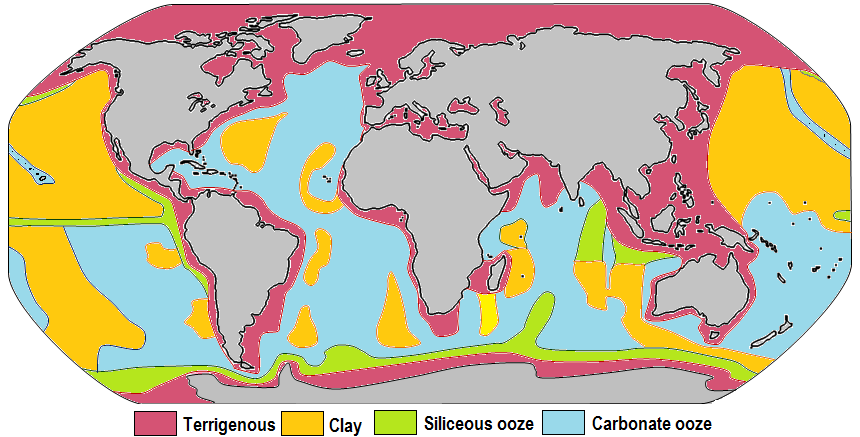
Marine Sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea. Additional deposits come from marine organisms and chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris. Except within a few kilometres of a mid-ocean ridge, where the volcanic rock is still relatively young, most parts of the seafloor are covered in sediment. This material comes from several different sources and is highly variable in composition. Seafloor sediment can range in thickness from a few millimetres to several tens of kilometres. Near the surface seafloor sediment remains unconsolidated, but at depths of hundreds to thousands of metres the sediment becomes lithified (turned to rock). Rates of sedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulter Counter
A Coulter counter is an apparatus for counting and sizing particles suspended in electrolytes. The Coulter counter is the commercial term for the technique known as resistive pulse sensing or electrical zone sensing, the apparatus is based on The Coulter principle named after its inventor, Wallace H. Coulter. A typical Coulter counter has one or more microchannels that separate two chambers containing electrolyte solutions. As fluid-containing particles or cells are drawn through each microchannel, each particle causes a brief change to the electrical resistance of the liquid. The counter detects these changes in the electrical resistance. Coulter principle The ''Coulter principle'' states that particles pulled through an orifice, concurrent with an electric current, produce a change in impedance that is proportional to the volume of the particle traversing the orifice. This pulse in impedance originates from the displacement of electrolyte caused by the particle. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemocytometer
The hemocytometer (or haemocytometer) is a counting-chamber device originally designed and usually used for counting blood cells. The hemocytometer was invented by Louis-Charles Malassez and consists of a thick glass microscope slide with a rectangular indentation that creates a precision volume chamber. This chamber is engraved with a laser-etched grid of perpendicular lines. The device is carefully crafted so that the area bounded by the lines is known, and the depth of the chamber is also known. By observing a defined area of the grid, it is therefore possible to count the number of cells or particles in a specific volume of fluid, and thereby calculate the concentration of cells in the fluid overall. A well used type of hemocytometer is the ''Neubauer'' counting chamber. Other types of hemocytometers with different rulings are in use for different applications. Fuchs-Rosenthal rulings, commonly used for spinal fluid counting, Howard Mold rulings used for mold on food an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullgren Funnel
A Berlese funnel, also known as Tullgren funnel, Berlese trap, or Berlese-Tullgren funnel, is an apparatus used to extract living organisms, particularly arthropods, from samples of soil. The Tullgren funnel works by creating a desiccation gradient over the sample such that mobile organisms will move away from the dry environment and fall into a collecting vessel, where they perish and are preserved for examination. The illustration shows how it works: a funnel (E) contains the soil or litter (D), and a heat source (F) such as an electric lamp (G) heats the litter. Animals escaping from the desiccation of the litter descend through a filter (C) into a preservative liquid (A) in a receptacle (B). This illustration is merely a schematic, since usually the soil sample will not be crumbled and poured into the funnel (this would inevitably lead to a high amount of soil particles in the preservation fluid requiring laborious work to sort out the soil organisms). In fact, the soil sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baermann Atlas
Heinrich Joseph Baermann (also spelled Bärmann; 14 February 1784 – 11 June 1847) was a German clarinet virtuoso of the Romantic era who is generally considered as being not only an outstanding performer of his time, but highly influential in the creation of several important composers' works for his instrument. Life Baermann was born in Potsdam. In his youth, Baermann took lessons from Joseph Beer (1744–1811) at the military school in Potsdam. After his prowess came to the attention of the Berlin court in 1804, Prince Louis Ferdinand of Prussia had the 20-year-old musician pursue his training in Berlin under the guidance of Franz Tausch (1762–1817). He played in the court orchestra of Munich from 1807 until his retirement in 1834, when his son Carl Baermann succeeded him. Parallel to Baermann's rise, the clarinet was undergoing a series of developments in key construction and embouchure that allowed greater agility and flexibility in playing. The growing custom was to pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medan
Medan (; English: ) is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of North Sumatra, as well as a regional hub and financial centre of Sumatra. According to the National Development Planning Agency, Medan is one of the four main central cities of Indonesia, alongside Jakarta, Surabaya, and Makassar. As of the 2020 Census, Medan has a population of 2,435,252 within its city limits,Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. and over 3.4 million in its built-up urban area, making it the fourth largest urban area in Indonesia. The Medan metropolitan area—which includes neighbouring Binjai, Deli Serdang Regency, and a part of Karo Regency—is the largest metropolitan area outside of Java, with 4,744,323 residents counted in the 2020 Census. Medan is a multicultural metropolis and a busy trading city bordered by the Strait of Malacca, making it one of the major economic cities in Indonesia. A gateway to the western part of Indonesia, Medan is supported by the Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
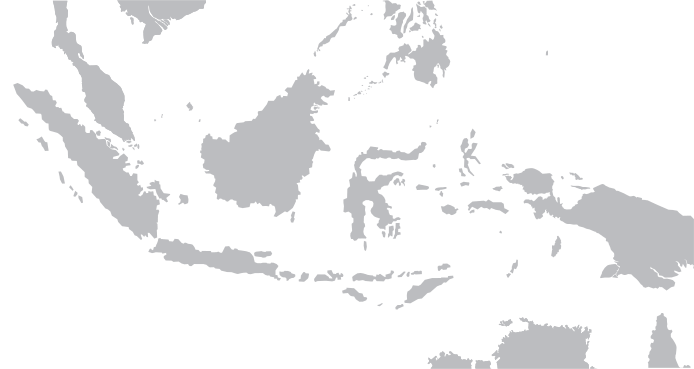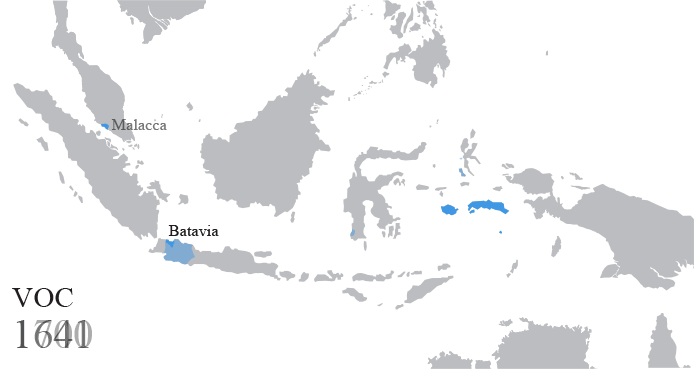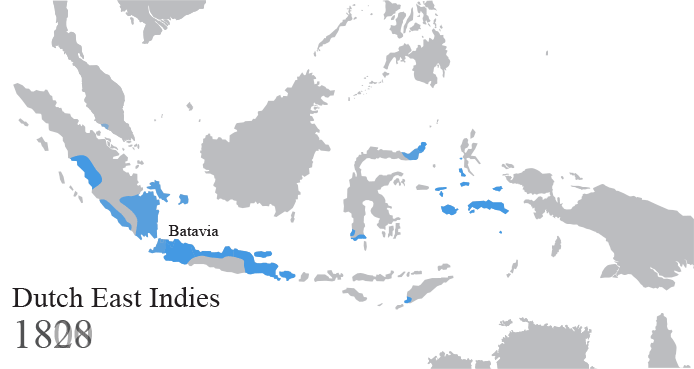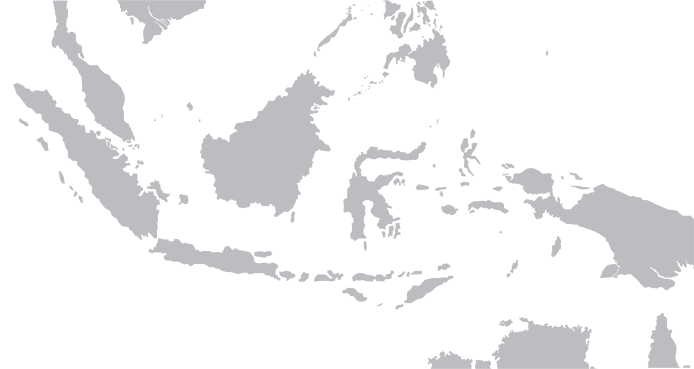
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |