|
Grevillea Eriobotrya
''Grevillea eriobotrya'', commonly called the woolly cluster grevillea, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is dense, erect, spreading shrub usually with linear leaves, and groups of white to creamy-white flowers. Description ''Grevillea eriobotrya'' is a dense, erect, spreading shrub that typically grows to a height of . It usually has linear leaves, sometimes divided with two or three linear lobes, long and wide. The edges of the leaves are rolled under and the upper surface has three to five longitudinal ridges. The flowers are arranged in dense, cylindrical groups long and are white to creamy-white, the pistil long. Flowering occurs from September to December and the fruit is a lens-shaped to more or less spherical follicle long. Taxonomy ''Grevillea eriobotrya'' was first formally described in 1876 by Ferdinand von Mueller in '' Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae'' from spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Morrison (botanist)
Alexander Morrison (15 March 1849 – 7 December 1913) was a Scottish Botanist who was the first Government Botanist of Western Australia. Morrison was born in western Dalmeny, Scotland the 8th of 10 children to Thomas Morrison (1809-1867) and Ann Geggie (1815-1867). He began a medicine degree at Edinburgh, but suffered from ill health, prompting him to break his studies and visit Australia. He spent two years in Melbourne before returning to Edinburgh to complete his degree. He then undertook post-graduate studies at Glasgow, Würzburg and Vienna. He returned to Australia in 1877 as a medical officer on a migrant ship. He practiced medicine in Melbourne for 15 years, but again ill health prompted him to travel. He visited the South Seas and spend some time living in the New Hebrides, where he collected plants for Ferdinand von Mueller. After returning to Australia, he was appointed the first Government Botanist of Western Australia, holding the position from 1897 to 1906. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
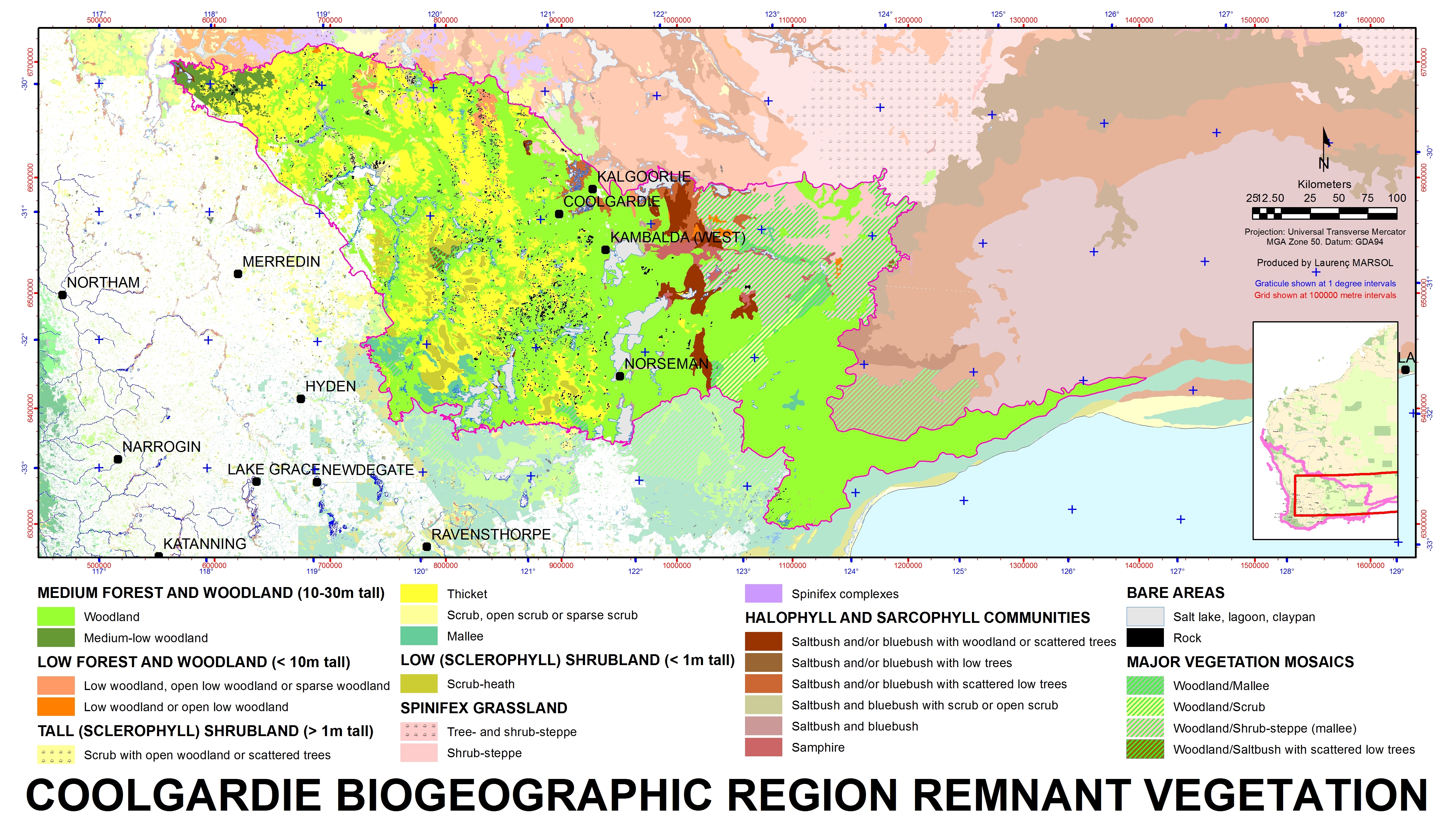
Coolgardie (biogeographic Region)
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteales Of Australia
Proteales is an order of flowering plants consisting of three (or four) families. The Proteales have been recognized by almost all taxonomists. The representatives of the Proteales are very different from each other. The order contains plants that do not look alike at all. What they have in common is seeds with little or no endosperm. The ovules are often atropic. Families In the classification system of Dahlgren the Proteales were in the superorder Proteiflorae (also called Proteanae). The APG II system of 2003 also recognizes this order, and places it in the clade eudicots with this circumscription: * order Proteales :* family Nelumbonaceae :* family Proteaceae family Platanaceae">Platanaceae.html" ;"title=" family Platanaceae"> family Platanaceae with "+ ..." = optionally separate family (that may be split off from the preceding family). The APG III system of 2009 followed this same approach, but favored the narrower circumscription of the three families, firmly reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicots Of Western Australia
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of Western Australia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grevillea
''Grevillea'', commonly known as spider flowers, is a genus of about 360 species of evergreen flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely trees, with the leaves arranged alternately along the branches, the flowers zygomorphic, arranged in racemes at the ends of branchlets, and the fruit a follicle that splits down one side only, releasing one or two seeds. Description Plants in the genus ''Grevillea'' are shrubs, rarely small trees with simple or compound leaves arranged alternately along the branchlets. The flowers are zygomorphic and typically arranged in pairs along a sometimes branched raceme at the ends of branchlets. The flowers are bisexual, usually with four tepals in a single whorl. There are four stamens and the gynoecium has a single carpel. The fruit is a thin-walled follicle that splits down only one side, releasing one or two seeds before the next growing season. Taxonomy The genus ''Grevillea'' was first forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Grevillea Species
This is a list of ''Grevillea'' species accepted by Plants of the World Online as of December 2021: A *'' Grevillea acacioides'' C.A.Gardner ex McGill. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acanthifolia'' A.Cunn. – Acanthus-leaved grevillea (N.S.W.) *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' A.Cunn. subsp. ''acanthifolia'' *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' subsp. ''paludosa'' Makinson & Albr. — bog grevillea *:''Grevillea acanthifolia'' subsp. ''stenomera'' (F.Muell. ex Benth.) McGill. *'' Grevillea acerata'' McGill. (N.S.W.) *'' Grevillea acrobotrya'' Meisn. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acropogon'' Makinson (W.A.) *'' Grevillea acuaria'' F.Muell. ex Benth. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea adenotricha'' McGill. (W.A.) *'' Grevillea agrifolia'' A.Cunn. ex R.Br. — blue grevillea (W.A., N.T.) *:''Grevillea agrifolia'' A.Cunn. ex R.Br. subsp. ''agrifolia'' *:''Grevillea agrifolia'' subsp. ''microcarpa'' (Olde & Marriott) Makinson *'' Grevillea albiflora'' C.T.White – white spider flower (N.S.W., Qld., S.A., N.T.) *'' Grevillea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalgoo (biogeographic Region)
Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of . The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund. Geography The Yalgoo bioregion extends southeastwards from the southern end of Shark Bay on Australia's west coast nearly to Lake Barlee in the interior of Western Australia. The western portion, known as the Edel subregion, includes the Edel Land peninsula and Dirk Hartog, Bernier, and Dorre islands, which enclose Shark Bay on the west. It also includes the coastal plain south of Shark Bay nearly to Kalbarri, where it transitions to the Geraldton Sandplains bioregion. The Edel subregion rests on the Carnarvon and Perth sedimentary basins. The Zuytdorp Cliffs line the coast from the northern end of Edel Land to the mouth of the Murchison River. Soils are generally white sands along the coast, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn Craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empty in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


