|
Green V. Biddle
''Green v. Biddle'', 1 U.S. (8 Wheat.) 1 (1823), is a 6-to-1 ruling by the Supreme Court of the United States that held that the state of Virginia had properly entered into a compact with the United States federal government under Clause One of Article Four of the United States Constitution. This compact surrendered Virginia's claim to the area that eventually became the state of Kentucky, but imposed restrictions on Kentucky's ability to upset title to land sold or otherwise granted by the state of Virginia at the time of the compact. The Supreme Court held that legislation enacted by Kentucky that restricted these rights unconstitutionally infringed on Virginia's right to surrender the land in accordance with Article Four, Clause One. Background During European colonization of the Americas, James I of England granted the Charter of 1606 to the newly established Virginia Company, asserting royal title to Native American-occupied land between the 34th and 45th latitudes and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Wheaton
Henry Wheaton (November 27, 1785 – March 11, 1848) was a United States lawyer, jurist and diplomat. He was the third Reporter of Decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States, reporter of decisions for the United States Supreme Court, the first U.S. minister to Denmark, and the second U.S. minister to Prussia. Biography He was born at Providence, Rhode Island. He graduated from Brown University (then called Rhode Island College) in 1802, was admitted to the bar in 1805, and, after two years' study abroad in Poictiers, Poitiers and London, practiced law at Providence (1807-1812) and at New York City (1812-1827). From 1812 to 1815, he edited ''National Advocate'', the organ of the administration party. There he published notable articles on the question of neutral rights in connection with the then-existing war with England. On 26 October 1814, he became division judge advocate of the United States Army, army. He was a justice of the Marine Court of New York City from 1815 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Johnson (judge)
William Johnson Jr. (December 27, 1771 – August 4, 1834) was an American attorney, state legislator, and jurist who served as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1804 until his death in 1834. When he was 32 years old, Johnson was appointed to the Supreme Court by President Thomas Jefferson. He was the first Jeffersonian Republican member of the Court as well as the second Justice from the state of South Carolina. During his tenure, Johnson restored the act of delivering seriatim opinions. He wrote about half of the dissents during the Marshall Court, leading historians to nickname him the "first dissenter". Johnson wrote the majority opinion for two major cases (including '' United States v. Hudson'') and hundreds of majority opinions in minor admiralty, land, and insurance cases. He supported a strong federal government in economic matters, leading him to join the majority in cases such as '' McCulloch v. Maryland'', ''Gibbons v. Ogden'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresence in the sky, but the articulate voice of some sovereign or quasi sovereign that can be identified," ''Southern Pacific Company v. Jensen'', 244 U.S. 205, 222 (1917) (Oliver Wendell Holmes, dissenting). By the early 20th century, legal professionals had come to reject any idea of a higher or natural law, or a law above the law. The law arises through the act of a sovereign, whether that sovereign speaks through a legislature, executive, or judicial officer. The defining characteristic of common law is that it arises as precedent. Common law courts look to the past decisions of courts to synthesize the legal principles of past cases. '' Stare decisis'', the principle that cases should be decided according to consistent principled rules so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushrod Washington
Bushrod Washington (June 5, 1762 – November 26, 1829) was an American attorney and politician who served as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1798 to 1829. On the Supreme Court, he was a staunch ally of Chief Justice John Marshall. Washington was a co-founder and president of the American Colonization Society, which promoted the emigration of freed slaves to Africa. The nephew of American founding father and President George Washington, he inherited his uncle's papers and Mount Vernon, taking possession in 1802 after the death of Martha Washington, his uncle's widow, and with Marshall's help, published a biography of the first president. Early life Bushrod Washington was born on June 5, 1762, at Bushfield Manor, a plantation located at Mount Holly in Westmoreland County, Virginia.. He was a son of John Augustine Washington (1736–1787), the brother of George Washington, and John's heiress wife, Hannah Bushrod (1735–1801). He had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Story
Joseph Story (September 18, 1779 – September 10, 1845) was an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, serving from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin v. Hunter's Lessee'' and ''United States v. The Amistad'', and especially for his ''Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States'', first published in 1833. Dominating the field in the 19th century, this work is a cornerstone of early American jurisprudence. It is the second comprehensive treatise on the provisions of the U.S. Constitution and remains a critical source of historical information about the forming of the American republic and the early struggles to define its law. Story opposed Jacksonian democracy, saying it was "oppression" of property rights by republican governments when popular majorities began in the 1830s to restrict and erode the property rights of the minority of rich men. R. Kent Newmyer presents Story as a "Statesman of the Old Republic" who tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associate Justice Of The United States Supreme Court
An associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States is any member of the Supreme Court of the United States other than the chief justice of the United States. The number of associate justices is eight, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1869. Article II, Section 2, Clause 2 of the Constitution of the United States grants plenary power to the president to nominate, and with the advice and consent (confirmation) of the Senate, appoint justices to the Supreme Court. Article III, Section 1 of the Constitution effectively grants life tenure to associate justices, and all other federal judges, which ends only when a justice dies, retires, resigns, or is removed from office by impeachment. Each Supreme Court justice has a single vote in deciding the cases argued before it, and the chief justice's vote counts no more than that of any other justice; however, the chief justice leads the discussion of the case among the justices. Furthermore, the chief justice—when in the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Biddle
Richard Biddle (March 25, 1796 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania – July 6, 1847 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) was an American author and politician. Richard Biddle received a classical education, graduated from the University of Pennsylvania in 1811, and was admitted to the bar, practicing law in Pittsburgh. He went to England in 1827, and remained three years, publishing while there a critical ''Review of Captain Basil Hall's Travels in North America.'' He also published ''A Memoir of Sebastian Cabot, with a Review of the History of Maritime Discovery'' (London, 1831). Biddle was twice elected to Congress, as an Anti-Mason, serving from March 4, 1837, until his resignation on July 21, 1840. Richard Biddle was the brother of American financier Nicholas Biddle, nephew of Congressman Edward Biddle and uncle of Congressman Charles John Biddle. References Bibliography * External links *The Political Graveyard {{DEFAULTSORT:Biddle, Richard 1796 births 1847 deaths Polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesne Profits
Mesne (pronounced "mean") profits are sums of money paid for the occupation of land to a person with right of immediate occupation, where no permission has been given for that occupation.Farran, Sue and Paterson, Donald. ''South Pacific Property Law.'' Florence, Ky.: Routledge, 2004, p. 90. The concept is feudal in origin, and common in countries which rely on the English legal system (including many former British colonies). The word is derived from the root word demesne. Mesne profits commonly occur where a landlord has obtained an order from a court to evict a tenant, or where an individual sues to eject a ''bona fide'' landowner to whom title to land was improperly conveyed. The mesne profit represents the value (living rent-free, profits earned from the land, etc.) the ejected tenant received from the property between the time the court ordered the eviction and the time when the tenant actually left the property. Mesne profits must be drawn from the land itself, rather than i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conveyancing
In law, conveyancing is the transfer of legal title of real property from one person to another, or the granting of an encumbrance such as a mortgage or a lien. A typical conveyancing transaction has two major phases: the exchange of contracts (when equitable interests are created) and completion (also called settlement, when legal title passes and equitable rights merge with the legal title). The sale of land is governed by the laws and practices of the jurisdiction in which the land is located. It is a legal requirement in all jurisdictions that contracts for the sale of land be in writing. An exchange of contracts involves two copies of a contract of sale being signed, one copy of which is retained by each party. When the parties are together, both would usually sign both copies, one copy of which being retained by each party, sometimes with a formal handing over of a copy from one party to the other. However, it is usually sufficient that only the copy retained by each part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
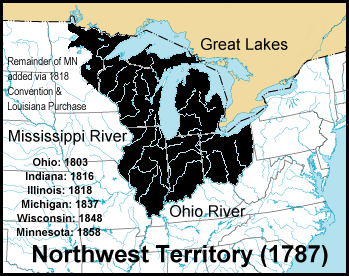
Northwest Ordinance
The Northwest Ordinance (formally An Ordinance for the Government of the Territory of the United States, North-West of the River Ohio and also known as the Ordinance of 1787), enacted July 13, 1787, was an organic act of the Congress of the Confederation of the United States. It created the Northwest Territory, the new nation's first organized incorporated territory, from lands beyond the Appalachian Mountains, between British North America and the Great Lakes to the north and the Ohio River to the south. The upper Mississippi River formed the territory's western boundary. Pennsylvania was the eastern boundary. In the 1783 Treaty of Paris, which formally ended the American Revolutionary War, Great Britain yielded the region to the United States. However, the Confederation Congress faced numerous problems gaining control of the land such as the unsanctioned movement of American settlers into the Ohio Valley; violent confrontations with the region's indigenous peoples; the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Ordinance Of 1785
The Land Ordinance of 1785 was adopted by the United States Congress of the Confederation on May 20, 1785. It set up a standardized system whereby settlers could purchase title to farmland in the undeveloped west. Congress at the time did not have the power to raise revenue by direct taxation, so land sales provided an important revenue stream. The Ordinance set up a survey system that eventually covered over three-quarters of the area of the continental United States. The earlier Land Ordinance of 1784 was a resolution written by Thomas Jefferson calling for Congress to take action. The land west of the Appalachian Mountains, north of the Ohio River and east of the Mississippi River was to be divided into ten separate states. However, the 1784 resolution did not define the mechanism by which the land would become states, or how the territories would be governed or settled before they became states. The Ordinance of 1785 put the 1784 resolution in operation by providing a mechanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)