|
Greek Constitution Of 1911
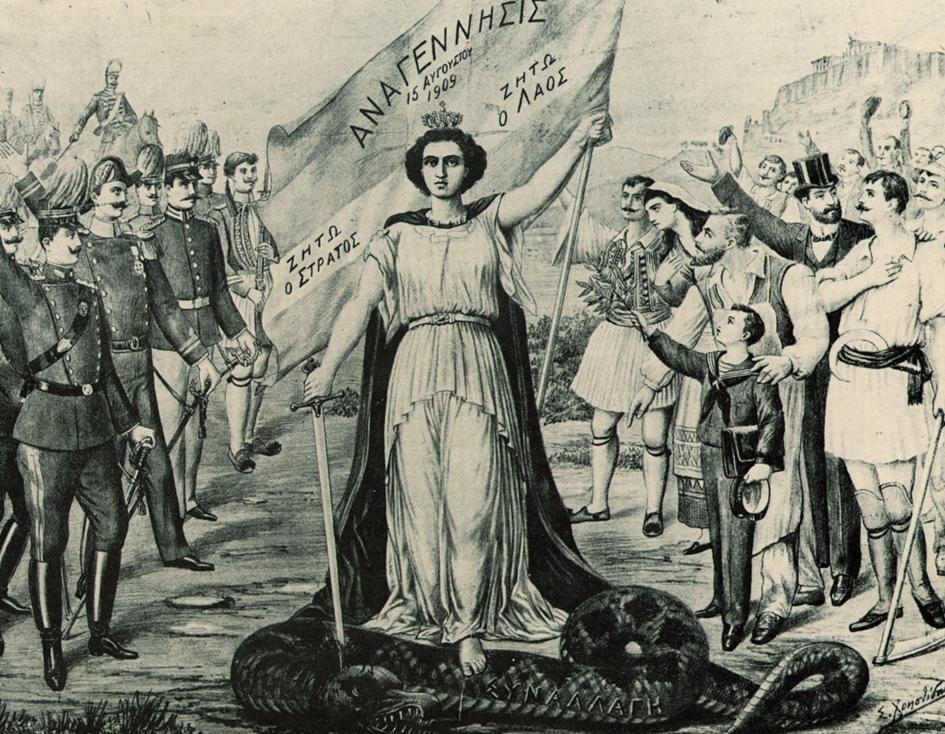
The Greek Constitution of 1911 was a major step forward in the constitutional history of Greece. Following the rise to power of Eleftherios Venizelos after the Goudi revolt in 1909, Venizelos set about attempting to reform the state. The main outcome of this was a major revision to the Greek Constitution of 1864. The most noteworthy amendments to the Constitution of 1864 concerning the protection of human rights, were the more effective protection of personal security, equality in tax burdens, of the right to assemble and of the inviolability of the domicile. Furthermore, the Constitution facilitated expropriation to allocate property to landless farmers, while simultaneously judicially protecting property rights. Other important changes included the institution of an Electoral Court for the settlement of election disputes stemming from the parliamentary elections, the addition of new conflicts for MPs, the re-establishment of the State Council as the highest administrative c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Constitution Of 1911
The Greek Constitution of 1911 was a major step forward in the constitutional history of Greece. Following the rise to power of Eleftherios Venizelos after the Goudi revolt in 1909, Venizelos set about attempting to reform the state. The main outcome of this was a major revision to the Greek Constitution of 1864. The most noteworthy amendments to the Constitution of 1864 concerning the protection of human rights, were the more effective protection of personal security, equality in tax burdens, of the right to assemble and of the inviolability of the domicile. Furthermore, the Constitution facilitated expropriation to allocate property to landless farmers, while simultaneously judicially protecting property rights. Other important changes included the institution of an Electoral Court for the settlement of election disputes stemming from the parliamentary elections, the addition of new conflicts for MPs, the re-establishment of the State Council as the highest administrative c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional History Of Greece
In the modern history of Greece, starting from the Greek War of Independence, the Constitution of 1975/1986/2001 is the last in a series of democratically adopted Constitutions (with the exception of the Constitutions of 1968 and 1973 imposed by a dictatorship). Greek War of Independence During the Greek War of Independence, three constitutional texts (Constitutions of 1822, 1823 and 1827) were adopted by the Greek National Assemblies, the national representative political gatherings of the Greek revolutionaries. These constitutions were influenced by: *the French Constitutions of 1793 and 1795, *the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, *the Draft Constitution of Rigas Velestinlis, *the three Constitutions of the Ionian Islands. A year before the adoption of the Greek Constitution of 1822, local Assemblies had ratified the so-called Greek local statutes, such as the Senate Organization of Western Greece, the Legal Order of Eastern Greece and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos ( el, Ελευθέριος Κυριάκου Βενιζέλος, translit=Elefthérios Kyriákou Venizélos, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Greek statesman and a prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. He is noted for his contribution to the expansion of Greece and promotion of liberal-democratic policies.Kitromilides, 2006, p. 178"Liberty Still Rules" '''', 18 February 1924. As leader of the , he held office as |
Goudi Revolt
The Goudi coup ( el, κίνημα στο Γουδί) was a military coup d'état that took place in Greece on the night of , starting at the barracks in Goudi, a neighborhood on the eastern outskirts of Athens. The coup was a pivotal event in modern Greek history, as it led to the arrival of Eleftherios Venizelos in Greece and his eventual appointment as Prime Minister. At one stroke, this put an end to the old political system, and ushered in a new period. Henceforth and for several decades, Greek political life would be dominated by two opposing forces: liberal, republican Venizelism and conservative, monarchist anti-Venizelism. The coup itself was the result of simmering tensions in Greek society, which reeled under the effects of the disastrous Greco-Turkish War of 1897, financial troubles, a lack of necessary reforms and disillusionment with the established political system. Emulating the Young Turks, several junior Army officers founded a secret society, the Military Leagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Constitution Of 1864
The Second National Assembly of the Hellenes took place in Athens (1863–1864) and dealt both with the election of a new sovereign as well as with the drafting of a new Constitution, thereby implementing the transition from constitutional monarchy to a crowned republic. Following the refusal of Prince Alfred of Great Britain (who was elected by an overwhelming majority in the first referendum of the country in November 1862) to accept the crown of the Kingdom of Greece, the government offered the crown to the Danish prince George Christian Willem of the House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, who was crowned constitutional King of Greece under the name "George I, King of the Hellenes". The Constitution of 1864 was drafted following the models of the Constitutions of Belgium of 1831 and of Denmark of 1849, and established in clear terms the principle of popular sovereignty, since the only legislative body with reversionary powers was now the Parliament. Furthermore, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
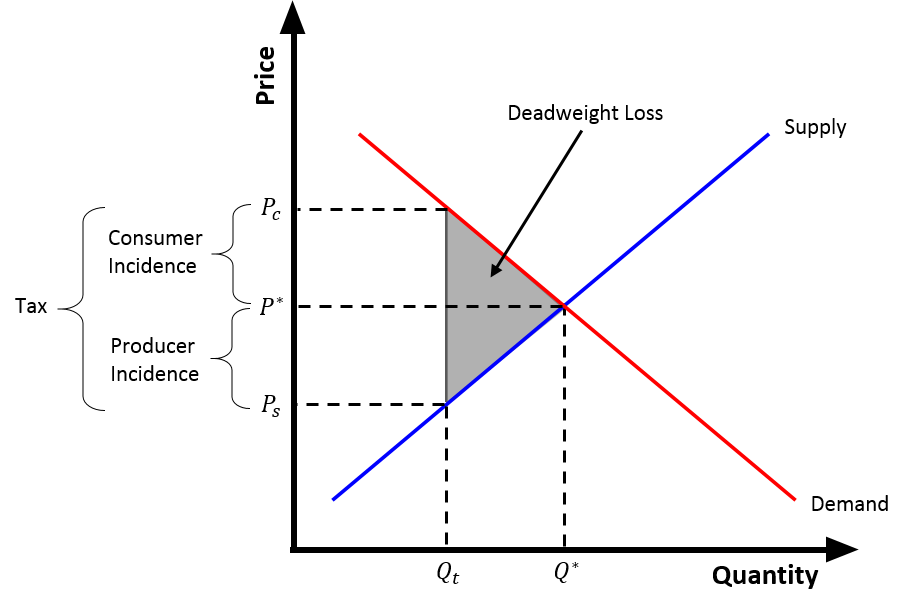
Tax Burden
In economics, tax incidence or tax burden is the effect of a particular tax on the distribution of economic welfare. Economists distinguish between the entities who ultimately bear the tax burden and those on whom tax is initially imposed. The tax burden measures the true economic weight of the tax, measured by the difference between real incomes or utilities before and after imposing the tax, taking into account how the tax leads prices to change. If a 10% tax is imposed on sellers of butter, for example, but the market price rises 8% as a result, most of the burden is on buyers, not sellers. The concept of tax incidence was initially brought to economists' attention by the French Physiocrats, in particular François Quesnay, who argued that the incidence of all taxation falls ultimately on landowners and is at the expense of land rent. Tax incidence is said to "fall" upon the group that ultimately bears the burden of, or ultimately suffers a loss from, the tax. The key concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
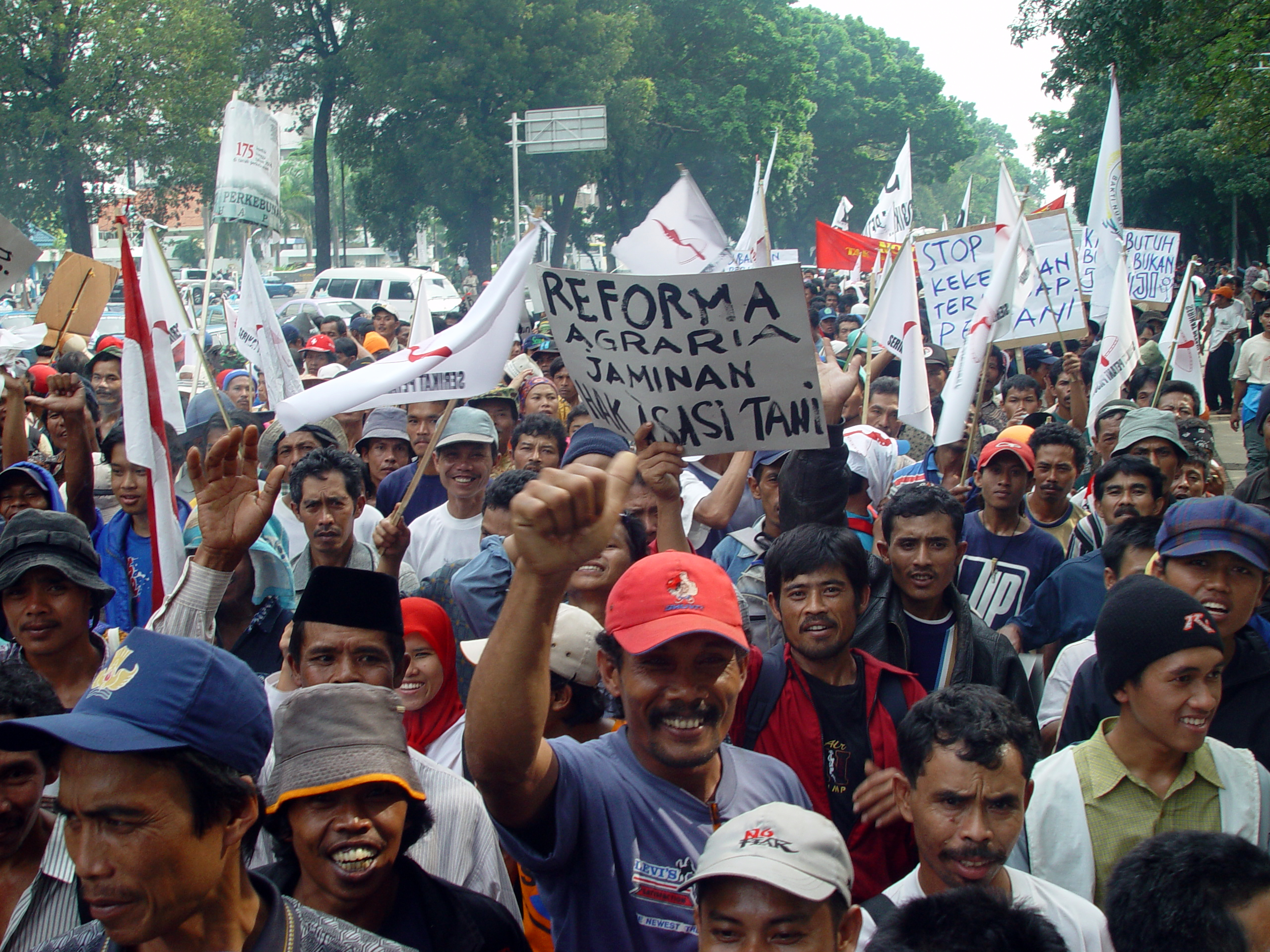
Land Reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural land. Land reform can, therefore, refer to transfer of ownership from the more powerful to the less powerful, such as from a relatively small number of wealthy or noble owners with extensive land holdings (e.g., plantations, large ranches, or agribusiness plots) to individual ownership by those who work the land. Such transfers of ownership may be with or without compensation; compensation may vary from token amounts to the full value of the land. Land reform may also entail the transfer of land from individual ownership—even peasant ownership in smallholdings—to government-owned collective farms; it has also, in other times and places, referred to the exact opposite: division of government-owned collective farms into smallholdings. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Constitution Of 1927
The Greek Constitution of 1927 was the constitution in force during most of the Second Hellenic Republic (1924–1935). The Republic had been declared in 1924, but the proposed 1925 constitution was never put into practice due to the dictatorship of Theodoros Pangalos in 1925–26. After Pangalos was overthrown, a new constitution was drawn up, which relied on, but heavily amended the previous 1911 constitution in several places. The new 1927 constitution had 127 articles. Any reference to the Greek monarchy was removed, and a parliamentary republic, with a bicameral legislature and an elected president as ceremonial head of state were introduced. Most notably, for the first time the hitherto unwritten principle of parliamentary majority ('' dedilomeni'') was formalized. The constitution of 1927 was suspended in October 1935, when a military coup under Georgios Kondylis overthrew the Republic and restored the monarchy, bringing back the 1911 constitution into force. Elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katharevousa
Katharevousa ( el, Καθαρεύουσα, , literally "purifying anguage) is a conservative form of the Modern Greek language conceived in the late 18th century as both a literary language and a compromise between Ancient Greek and the contemporary vernacular, Demotic Greek. Originally, it was widely used for both literary and official purposes, though sparingly in daily language. In the 20th century, it was increasingly adopted for official and formal purposes, until minister of education Georgios Rallis made Demotic Greek the official language of Greece in 1976, and in 1982 Prime Minister Andreas Papandreou abolished the polytonic system of writing for both Demotic and Katharevousa. Katharevousa was conceived by the intellectual and revolutionary leader Adamantios Korais (1748–1833). A graduate of the University of Montpellier, Korais spent most of his life as an expatriate in Paris. As a classical scholar credited with both laying the foundations of Modern Greek literature a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 Documents
A notable ongoing event was the Comparison of the Amundsen and Scott Expeditions, race for the South Pole. Events January * January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are added to the Commonwealth of Australia. * January 3 ** 1911 Kebin earthquake: An earthquake of 7.7 Moment magnitude scale, moment magnitude strikes near Almaty in Russian Turkestan, killing 450 or more people. ** Siege of Sidney Street in London: Two Latvian people, Latvian anarchists die, after a seven-hour siege against a combined police and military force. Home Secretary Winston Churchill arrives to oversee events. * January 5 – Egypt's Zamalek SC is founded as a general sports and Association football club by Belgian lawyer George Merzbach as Qasr El Nile Club. * January 14 – Roald Amundsen's South Pole expedition makes landfall, on the eastern edge of the Ross Ice Shelf. * January 18 – Eugene B. El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Greece
The Constitution of Greece ( el, Σύνταγμα της Ελλάδας, Syntagma tis Elladas) was created by the Fifth Revisionary Parliament of the Hellenes in 1974, after the fall of the Greek military junta and the start of the Third Hellenic Republic. It came into force on 11 June 1975 (adopted two days prior) and has been amended in 1986, 2001, 2008 and 2019. The constitutional history of Greece goes back to the Greek War of Independence (1821–1832), during which the first three Greek constitutions were adopted by the revolutionary national assemblies. Syntagma Square (''Plateia Syntagmatos'') in Athens is named after the first constitution adopted in the modern Greek State. Context The Constitution consists of 120 articles, in four parts: *The first part (articles 1-3), ''Basic Provisions'', establishes Greece as a ''presidential parliamentary democracy'' (or ''republic'' – the Greek δημοκρατία can be translated both ways), and confirms the preva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |