|
Greater Koa-finch
The greater koa finch (''Rhodacanthis palmeri'') was a species of finch in the family Fringillidae. It was found only in the Hawaiian Islands. It has been extinct since the late 19th century. Description The bird was about 7–8 in (18–20 cm) long when fully grown. It was the largest known honey-creeper, although its typical weight is unknown. The bird was sexually dimorphic; the male was brilliant scarlet-orange on head, neck, and breast, with lighter orange on its bottom, and olive brown with orange touches on back, wings, and tail; however, the female was brownish olive, and somewhat lighter below. It had a thick black bill which allowed it to break open seed pods that were found in the trees. In historical times, its range was largely confined to the Kona District of the island of Hawaii, although it was observed in the Kīlauea area in 1895. It was much more widespread prior to the arrival of humans in Hawaii, and related species lived on other islands. In Kona, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild
Lionel Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild, (8 February 1868 – 27 August 1937) was a British banker, politician, zoologist and soldier, who was a member of the Rothschild family. As a Zionist leader, he was presented with the Balfour Declaration, which pledged British support for a Jewish national home in Palestine. Rothschild was the president of the Board of Deputies of British Jews from 1925 to 1926. Early life Walter Rothschild was born in London as the eldest son and heir of Emma Louise von Rothschild and Nathan Rothschild, 1st Baron Rothschild, an immensely wealthy financier of the international Rothschild financial dynasty and the first Jewish peer in England. The eldest of three children, Walter was deemed to have delicate health and was educated at home. As a young man, he travelled in Europe, attending the University of Bonn for a year before entering Magdalene College, Cambridge. In 1889, leaving Cambridge after two years, he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodonaea Viscosa
''Dodonaea viscosa'', also known as the broadleaf hopbush, is a species of flowering plant in the ''Dodonaea'' (hopbush) genus that has a cosmopolitan distribution in Tropics, tropical, Subtropics, subtropical and warm temperate regions of Africa, the Americas, southern Asia and Australasia. ''Dodonaea'' is part of Sapindaceae, the soapberry family. This species is notable for its extremely wide distribution, which it achieved only over the last 2 million years (from its region of origin in Australia) via oceanic dispersal. Harrington and Gadek (2009) referred to ''D. viscosa'' as having "a distribution equal to some world’s greatest transoceanic dispersers". Common names The common name hopbush is used for ''D. viscosa'' specifically and also for the genus as a whole. In the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu, this plant is called ''virāli'' (விராலி). Australian common names include: broad leaf hopbush, candlewood, giant hopbush, narrow leaf hopbush, sticky hopbus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Extinctions Since 1500
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Birds Of Hawaii
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the Endling, last individual of the species, although the Functional extinction, capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever Life, lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of Hawaii
There are 71 known taxa of birds endemic to the Hawaiian Islands, of which 30 are extinct, 6 possibly extinct and 30 of the remaining 48 species and subspecies are listed as endangered or threatened by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Habitat loss and avian disease are thought to have had the greatest effect on endemic bird species in Hawaii. List of species The following is a list of bird species and subspecies endemic to the Hawaiian Islands: Procellariidae * Hawaiian petrel or uau, ''Pterodroma sandwichensis'' * Newell's shearwater or ao, ''Puffinus newelli'' * Bryan's shearwater, ''Puffinus bryani'' ('' P. assimilis'': ) * Bonin petrel, ''Pterodroma hypoleuca'' 99% of the total population breeds on the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands Anatidae * Hawaiian goose or nēnē, ''Branta sandvicensis'' * Hawaiian duck or koloa maoli, ''Anas wyvilliana'' * Laysan duck, ''Anas laysanensis'' Diomedeidae * Laysan albatross, ''Phoebastria immutabilis'' 99.7% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
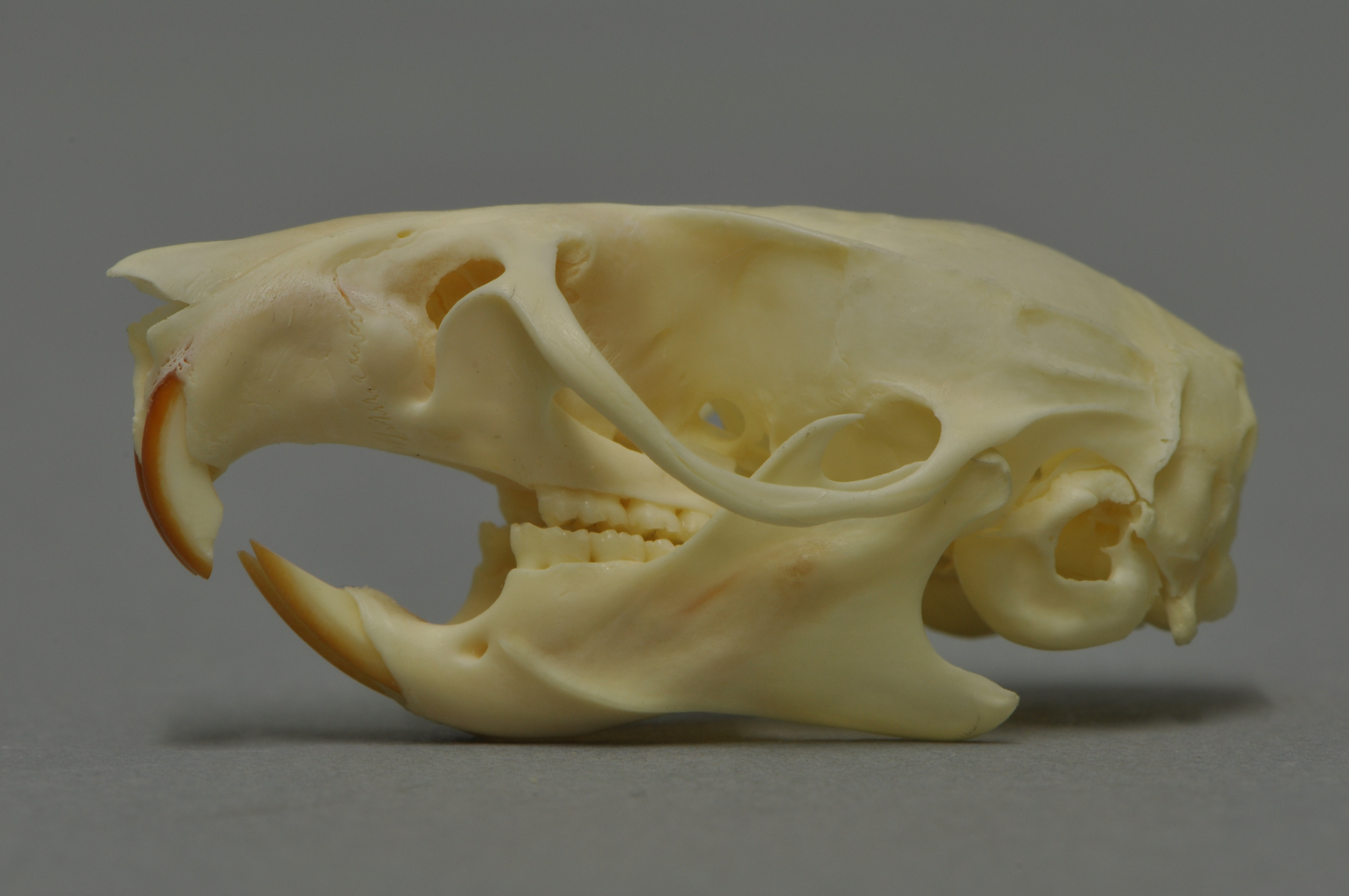
Rhodacanthis
''Rhodacanthis'' is an extinct genus of Hawaiian honeycreepers commonly known as koa finches. All four species were endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. Members of this genus were granivores, with bills adapted to the seeds and pods of legumes. The two species that became extinct in the 1890s, '' R. flaviceps'' and '' R. palmeri'', inhabited upper elevation mesic forests dominated by koa ''(Acacia koa'') on the island of Hawaii. Both were large birds; ''R. flaviceps'' measured , while ''R. palmeri'' was in length. The combination of a giant bill with brightly colored plumage (yellow for ''R. flaviceps'', orange for ''R. palmeri'') gave the males a very striking appearance. Koa seeds were the preferred food for the two species, but caterpillars were taken if necessary. The two prehistoric species, '' R. forfex'' and '' R. litotes'', were denizens of more lowland tropical dry forests and shrublands on Kauai, Maui, and Oahu. It is speculated that koaia (''Acacia koaia'') was an im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts. The mosquito life cycle consists of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Eggs are laid on the water surface; they hatch into motile larvae that feed on aquatic algae and organic material. These larvae are important food sources for many freshwater animals, such as dragonfly nymphs, many fish, and some birds such as ducks. The adult females of most species have tube-like mouthparts (called a proboscis) that can pierce the skin of a host and feed on blood, which contains protein and iron needed to produce eggs. Thousands of mosquito species feed on the blood of various hosts � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian Malaria
Avian malaria is a parasitic disease of birds, caused by parasite species belonging to the genera ''Plasmodium'' and '' Hemoproteus'' (phylum Apicomplexa, class Haemosporidia, family Plasmoiidae). The disease is transmitted by a dipteran vector including mosquitoes in the case of ''Plasmodium'' parasites and biting midges for ''Hemoproteus.'' The range of symptoms and effects of the parasite on its bird hosts is very wide, from asymptomatic cases to drastic population declines due to the disease, as is the case of the Hawaiian honeycreepers. The diversity of parasites is large, as it is estimated that there are approximately as many parasites as there are species of hosts. Co-speciation and host switching events have contributed to the broad range of hosts that these parasites can infect, causing avian malaria to be a widespread global disease, found everywhere except Antarctica. Cause Avian malaria is most notably caused by ''Plasmodium relictum'', a protist that infects birds i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian Pox
''Avipoxvirus'' (avian pox) is a genus of viruses within the family ''Poxviridae''. ''Poxviridae'' is the family of viruses which cause the afflicted organism to have poxes as a symptom. Poxviruses have generally large genomes, and other such examples include smallpox and monkeypox. Members of the genus ''Avipoxvirus'' infect specifically birds. Avipoxviruses are unable to complete their replication cycle in non-avian species. Although it is comparably slow-spreading, ''Avipoxvirus'' is known to cause symptoms like pustules full of pus lining the skin and diphtheria-like symptoms. These diphtheria-like symptoms might include diphtheric necrotic membranes lining the mouth and the upper respiratory tract. Like other avian viruses, it can be transmitted through vectors mechanically such as through mosquitoes. There is no evidence that this virus can infect humans. ''Avipoxvirus'' is a virus that is brick-shaped and is usually 200 nanometres in diameter. This is much larger tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rat
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed rodent of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent, but is now found worldwide. The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple in Deshnoke. Taxonomy ''Mus rattus'' was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the black rat. Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs: *''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat *''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat *''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat Characteristics A typical adult black rat is long, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesic Habitat
In ecology, a mesic habitat is a type of habitat with a moderate or well-balanced supply of moisture, e.g., a mesic forest, a temperate hardwood forest, or dry-mesic prairie. Mesic habitats transition to xeric shrublands in a non-linear fashion, which is evidence of a threshold. Mesic is one of a triad of terms used to describe the amount of water in a habitat. The others are xeric and hydric. Further examples of mesic habitats include streamsides, wet meadows, springs, seeps, irrigated fields, and high elevation habitats. These habitats effectively provide drought insurance as land at higher elevations warms due to seasonal or other change. Healthy mesic habitats act like sponges in that they store water in such a way that it can be deposited to neighboring habitats as needed. They are common in dryer regions of the western United States, and can be a good water source to neighboring desert habitats. Healthy mesic habitats also provide forb and insects for organisms belonging t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)