|
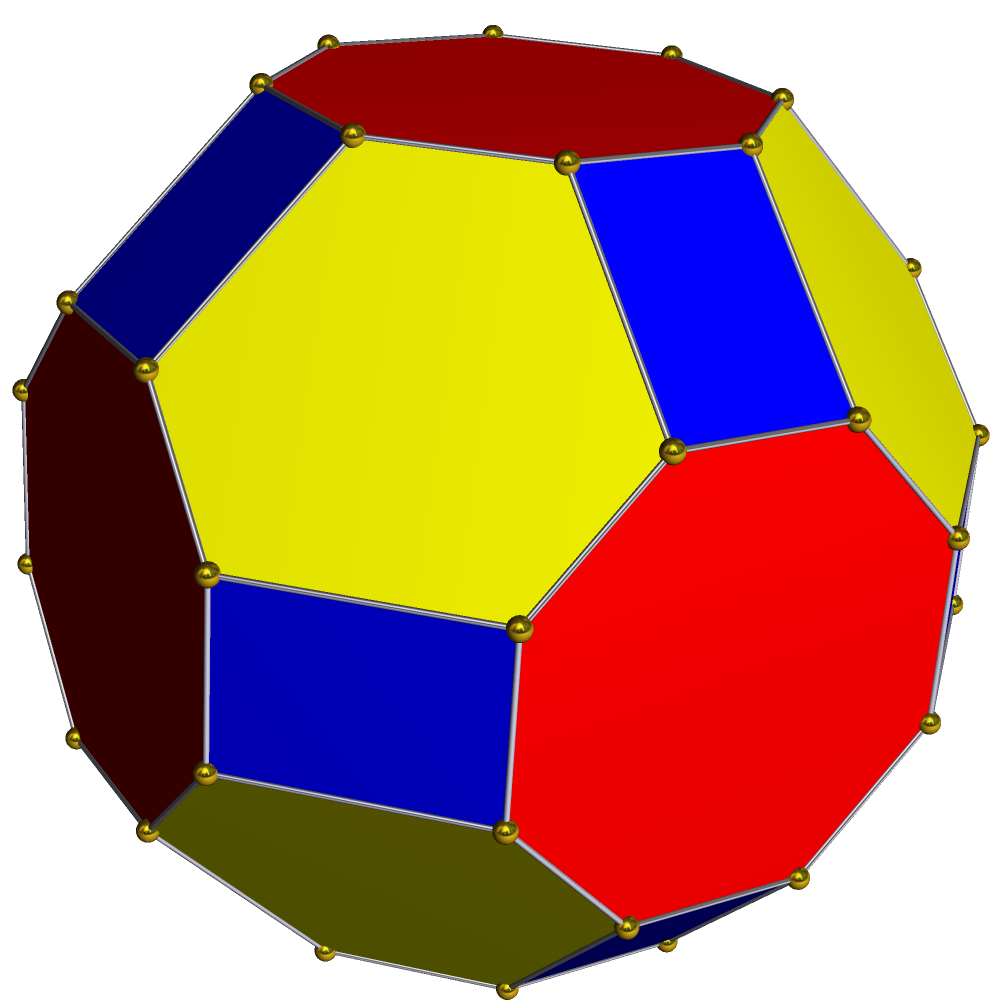
Great Truncated Cuboctahedron
In geometry, the great truncated cuboctahedron (or quasitruncated cuboctahedron or stellatruncated cuboctahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U20. It has 26 faces (12 squares, 8 hexagons and 6 octagrams), 72 edges, and 48 vertices. It is represented by the Schläfli symbol tr, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . It is sometimes called the quasitruncated cuboctahedron because it is related to the truncated cuboctahedron, , except that the octagonal faces are replaced by octagrams. Convex hull Its convex hull is a nonuniform truncated cuboctahedron. The truncated cuboctahedron and the great truncated cuboctahedron form isomorphic graphs despite their different geometric structure. Orthographic projections Cartesian coordinates Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a great truncated cuboctahedron centered at the origin are all permutations of \Bigl( \pm 1, \ \pm\left -\sqrt 2 \right \ \pm\left -2\sqrt 2\rightBigr). See also * List of uniform polyhedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Truncated Cuboctahedron
In geometry, the great truncated cuboctahedron (or quasitruncated cuboctahedron or stellatruncated cuboctahedron) is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron, indexed as U20. It has 26 faces (12 squares, 8 hexagons and 6 octagrams), 72 edges, and 48 vertices. It is represented by the Schläfli symbol tr, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram . It is sometimes called the quasitruncated cuboctahedron because it is related to the truncated cuboctahedron, , except that the octagonal faces are replaced by octagrams. Convex hull Its convex hull is a nonuniform truncated cuboctahedron. The truncated cuboctahedron and the great truncated cuboctahedron form isomorphic graphs despite their different geometric structure. Orthographic projections Cartesian coordinates Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a great truncated cuboctahedron centered at the origin are all permutations of \Bigl( \pm 1, \ \pm\left -\sqrt 2 \right \ \pm\left -2\sqrt 2\rightBigr). See also * List of uniform polyhedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geometries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonconvex Uniform Polyhedron
In geometry, a uniform star polyhedron is a self-intersecting uniform polyhedron. They are also sometimes called nonconvex polyhedra to imply self-intersecting. Each polyhedron can contain either star polygon faces, star polygon vertex figures, or both. The complete set of 57 nonprismatic uniform star polyhedra includes the 4 regular ones, called the Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, 5 quasiregular ones, and 48 semiregular ones. There are also two infinite sets of ''uniform star prisms'' and ''uniform star antiprisms''. Just as (nondegenerate) star polygons (which have polygon density greater than 1) correspond to circular polygons with overlapping tiles, star polyhedra that do not pass through the center have polytope density greater than 1, and correspond to spherical polyhedra with overlapping tiles; there are 47 nonprismatic such uniform star polyhedra. The remaining 10 nonprismatic uniform star polyhedra, those that pass through the center, are the hemipolyhedra as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adjacent sides. It is the only regular polygon whose internal angle, central angle, and external angle are all equal (90°), and whose diagonals are all equal in length. A square with vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted . Characterizations A convex quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is any one of the following: * A rectangle with two adjacent equal sides * A rhombus with a right vertex angle * A rhombus with all angles equal * A parallelogram with one right vertex angle and two adjacent equal sides * A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles * A quadrilateral where the diagonals are equal, and are the perpendicular bisectors of each other (i.e., a rhombus with equal diagonals) * A convex quadrilateral with successiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A ''regular polygon, regular hexagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a Truncation (geometry), truncated equilateral triangle, t, which alternates two types of edges. A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral polygon, equilateral and equiangular polygon, equiangular. It is bicentric polygon, bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic polygon, cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential polygon, tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals \tfrac times the apothem (radius of the inscribed figure, inscribed circle). All internal angles are 120 degree (angle), degrees. A regular hexago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octagram
In geometry, an octagram is an eight-angled star polygon. The name ''octagram'' combine a Greek numeral prefix, '' octa-'', with the Greek suffix '' -gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from γραμμή (''grammḗ'') meaning "line". Detail In general, an octagram is any self-intersecting octagon (8-sided polygon). The regular octagram is labeled by the Schläfli symbol , which means an 8-sided star, connected by every third point. Variations These variations have a lower dihedral, Dih4, symmetry: The symbol Rub el Hizb is a Unicode glyph ۞ at U+06DE. As a quasitruncated square Deeper truncations of the square can produce isogonal (vertex-transitive) intermediate star polygon forms with equal spaced vertices and two edge lengths. A truncated square is an octagon, t=. A quasitruncated square, inverted as , is an octagram, t=.The Lighter Side of Mathematics: Proceedings of the Eugène Strens Memorial Conference on Recreational Mathematics and its History, (1994), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schläfli Symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations. The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more than three dimensions and discovered all their convex regular polytopes, including the six that occur in four dimensions. Definition The Schläfli symbol is a recursive description, starting with for a ''p''-sided regular polygon that is convex. For example, is an equilateral triangle, is a square, a convex regular pentagon, etc. Regular star polygons are not convex, and their Schläfli symbols contain irreducible fractions ''p''/''q'', where ''p'' is the number of vertices, and ''q'' is their turning number. Equivalently, is created from the vertices of , connected every ''q''. For example, is a pentagram; is a pentagon. A regular polyhedron that has ''q'' regular ''p''-sided Face (geometry), polygon faces around each Verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncated Cuboctahedron
In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid, named by Kepler as a truncation of a cuboctahedron. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices, and 72 edges. Since each of its faces has point symmetry (equivalently, 180° rotational symmetry), the truncated cuboctahedron is a 9-zonohedron. The truncated cuboctahedron can tessellate with the octagonal prism. Names There is a nonconvex uniform polyhedron with a similar name: the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron. Cartesian coordinates The Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a truncated cuboctahedron having edge length 2 and centered at the origin are all the permutations of: :(±1, ±(1 + ), ±(1 + 2)). Area and volume The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of the truncated cuboctahedron of edge length ''a'' are: :\begin A &= 12\left(2+\sqrt+\sqrt\right) a^2 &&\approx 61.755\,1724~a^2, \\ V &= \left(22+14\sqrt\right) a^3 &&\approx 41. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Hull
In geometry, the convex hull or convex envelope or convex closure of a shape is the smallest convex set that contains it. The convex hull may be defined either as the intersection of all convex sets containing a given subset of a Euclidean space, or equivalently as the set of all convex combinations of points in the subset. For a bounded subset of the plane, the convex hull may be visualized as the shape enclosed by a rubber band stretched around the subset. Convex hulls of open sets are open, and convex hulls of compact sets are compact. Every compact convex set is the convex hull of its extreme points. The convex hull operator is an example of a closure operator, and every antimatroid can be represented by applying this closure operator to finite sets of points. The algorithmic problems of finding the convex hull of a finite set of points in the plane or other low-dimensional Euclidean spaces, and its dual problem of intersecting half-spaces, are fundamental problems of com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Isomorphism
In graph theory, an isomorphism of graphs ''G'' and ''H'' is a bijection between the vertex sets of ''G'' and ''H'' : f \colon V(G) \to V(H) such that any two vertices ''u'' and ''v'' of ''G'' are adjacent in ''G'' if and only if f(u) and f(v) are adjacent in ''H''. This kind of bijection is commonly described as "edge-preserving bijection", in accordance with the general notion of isomorphism being a structure-preserving bijection. If an isomorphism exists between two graphs, then the graphs are called isomorphic and denoted as G\simeq H. In the case when the bijection is a mapping of a graph onto itself, i.e., when ''G'' and ''H'' are one and the same graph, the bijection is called an automorphism of ''G''. If a graph is finite, we can prove it to be bijective by showing it is one-one/onto; no need to show both. Graph isomorphism is an equivalence relation on graphs and as such it partitions the class of all graphs into equivalence classes. A set of graphs isomorphic to each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Truncated Cuboctahedron Convex Hull
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" *Artel Great (born 1981), American actor Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training Gang Resistance Education And Training, abbreviated G.R.E.A.T., provides a school-based, police officer instructed program that includes classroom instruction and various learning activities. Their intention is to teach the students to avoid gang ..., or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'', a 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |