|
Graphical Timeline Of The Stelliferous Era
This is the timeline of the stelliferous era but also partly charts the primordial era, and charts more of the degenerate era of the heat death scenario. The scale is 10 \times \log_\ where \ is the time since the Big Bang expressed in years. Example: one million years is \ = 1000000;\ \ 10 \times \log_\ = 10\times 6 = 60. Timeline ImageSize = width:720 height:2000 PlotArea = left:40 right:235 bottom:75 top:75 Colors = id:period1 value:rgb(1,1,0.7) # light yellow id:period2 value:rgb(0.7,0.7,1) # light blue id:events value:rgb(1,0.7,1) # light purple id:era2 value:lightorange id:era1 Value:yellowgreen DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:56 till:200 TimeAxis = format:yyyy orientation:vertical ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:60 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:56 AlignBars = justify BarData = bar:Era bar:Dummy2 bar:Dummy3 bar:Periods bar:Dummy4 bar:Events TextData = fontsize:M pos:(250,75) text:"Photon epoch" po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Of An Expanding Universe
Observations suggest that the expansion of the universe will continue forever. The prevailing theory is that the universe will cool as it expands, eventually becoming too cold to sustain life. For this reason, this future scenario once popularly called "Heat Death" is now known as the "Big Chill" or "Big Freeze". If dark energy—represented by the cosmological constant, a ''constant'' energy density filling space homogeneously, or scalar fields, such as quintessence or moduli, ''dynamic'' quantities whose energy density can vary in time and space—accelerates the expansion of the universe, then the space between clusters of galaxies will grow at an increasing rate. Redshift will stretch ancient, incoming photons (even gamma rays) to undetectably long wavelengths and low energies. Stars are expected to form normally for 1012 to 1014 (1–100 trillion) years, but eventually the supply of gas needed for star formation will be exhausted. As existing stars run out of fuel and cease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or lower. The appearance of the red giant is from yellow-white to reddish-orange, including the spectral types K and M, sometimes G, but also class S stars and most carbon stars. Red giants vary in the way by which they generate energy: * most common red giants are stars on the red-giant branch (RGB) that are still fusing hydrogen into helium in a shell surrounding an inert helium core * red-clump stars in the cool half of the horizontal branch, fusing helium into carbon in their cores via the triple-alpha process * asymptotic-giant-branch (AGB) stars with a helium burning shell outside a degenerate carbon–oxygen core, and a hydrogen-burning shell just beyond that. Many of the well-known bright stars are red giants because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Timelines
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of data, as in design and manufacture, in typesetting and the graphic arts, and in educational and recreational software. Images that are generated by a computer are called computer graphics. Examples are photographs, drawings, line art, mathematical graphs, line graphs, charts, diagrams, typography, numbers, symbols, geometric designs, maps, engineering drawings, or other images. Graphics often combine text, illustration, and color. Graphic design may consist of the deliberate selection, creation, or arrangement of typography alone, as in a brochure, flyer, poster, web site, or book without any other element. The objective can be clarity or effective communication, association with other cultural elements, or merely the creation of a distinctive style. Graphics can be func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Asimov
yi, יצחק אזימאװ , birth_date = , birth_place = Petrovichi, Russian SFSR , spouse = , relatives = , children = 2 , death_date = , death_place = Manhattan, New York City, U.S. , nationality = Russian (1920–1922)Soviet (1922–1928)American (1928–1992) , occupation = Writer, professor of biochemistry , years_active = 1939–1992 , genre = Science fiction (hard SF, social SF), mystery, popular science , subject = Popular science, science textbooks, essays, history, literary criticism , education = Columbia University ( BA, MA, PhD) , movement = Golden Age of Science Fiction , module = , signature = Isaac Asimov signature.svg Isaac Asimov ( ; 1920 – April 6, 1992) was an American writer and professor of biochemistry at Boston University. During his lifetime, Asimov was considered one of the "Big Three" science fiction writers, along with Robert A. Heinlein and Arthur C. Clarke. A prolific writer, he wrote or edited more than 500 books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Last Question
"The Last Question" is a science fiction short story by American writer Isaac Asimov. It first appeared in the November 1956 issue of Science Fiction Quarterly and was anthologized in the collections Nine Tomorrows (1959), The Best of Isaac Asimov (1973), Robot Dreams (1986), The Best Science Fiction of Isaac Asimov (1986), the retrospective Opus 100 (1969), and in Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 1 (1990). While he also considered it one of his best works, “The Last Question” was Asimov's favorite short story of his own authorship, and is one of a loosely connected series of stories concerning a fictional computer called Multivac. Through successive generations, humanity questions Multivac on the subject of entropy. The story overlaps science fiction, theology, and philosophy. History In conceiving Multivac, Asimov was extrapolating the trend towards centralization that characterized computation technology planning in the 1950s to an ultimate centrally-managed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
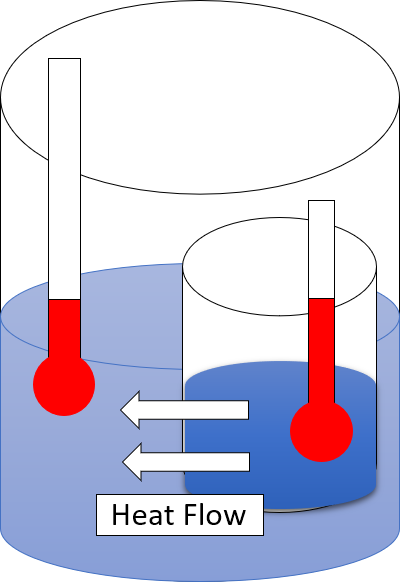
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 E19 S And More
An order of magnitude of time is usually a decimal prefix or decimal order-of-magnitude quantity together with a base unit of time, like a microsecond or a million years. In some cases, the order of magnitude may be implied (usually 1), like a "second" or "year". In other cases, the quantity name implies the base unit, like "century". In most cases, the base unit is seconds or years. Prefixes are not usually used with a base unit of years. Therefore, it is said "a million years" instead of "a mega year". Clock time and calendar time have duodecimal or sexagesimal orders of magnitude rather than decimal, e.g., a year is 12 months, and a minute is 60 seconds. The smallest meaningful increment of time is the Planck time―the time light takes to traverse the Planck distance, many decimal orders of magnitude smaller than a second. The largest realized amount of time, based on known scientific data, is the age of the universe, about 13.8 billion years—the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultimate Fate Of The Universe
The ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology, whose theoretical restrictions allow possible scenarios for the evolution and ultimate fate of the universe to be described and evaluated. Based on available observational evidence, deciding the fate and evolution of the universe has become a valid cosmological question, being beyond the mostly untestable constraints of mythological or theological beliefs. Several possible futures have been predicted by different scientific hypotheses, including that the universe might have existed for a finite and infinite duration, or towards explaining the manner and circumstances of its beginning. Observations made by Edwin Hubble during the 1930s–1950s found that galaxies appeared to be moving away from each other, leading to the currently accepted Big Bang theory. This suggests that the universe began very dense about 13.787 billion years ago, and it has expanded and (on average) become less dense ever since. Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Final Anthropic Principle
Frank Jennings Tipler (born February 1, 1947) is an American mathematical physicist and cosmologist, holding a joint appointment in the Departments of Mathematics and Physics at Tulane University. Tipler has written books and papers on the Omega Point based on Pierre Teilhard de Chardin's religious ideas, which he claims is a mechanism for the resurrection of the dead. He is also known for his theories on the Tipler cylinder time machine. His work has attracted criticism, most notably from Quaker and systems theorist George Ellis who has argued that his theories are largely pseudoscience. Biography Tipler was born in Andalusia, Alabama, to Frank Jennings Tipler Jr., a lawyer, and Anne Tipler, a homemaker. Tipler attended the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from 1965 to 1969, where he completed a Bachelor of Science degree in physics. In 1976 he completed his PhD with the University of Maryland. Tipler was hired in a series of postdoctoral research positions at three u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyson's Eternal Intelligence
Dyson's eternal intelligence concept (the Dyson Scenario), proposed by Freeman Dyson in 1979, proposes a means by which an immortal society of intelligent beings in an open universe may escape the prospect of the heat death of the universe by extending subjective time to infinity even though expending only a finite amount of energy. Bremermann's limit can be invoked to deduce that the amount of time to perform a computation on 1 bit is inversely proportional to the change in energy in the system. As a result, the amount of computations that can be performed grows over time. The increase in energy available slows logarithmically, but never stops. Therefore, for any specific computation rate that requires a specific amount of energy, there will come a time when that energy is available to be used. The intelligent beings would begin by storing a finite amount of energy. They then use half (or any fraction) of this energy to power their thought. When the energy gradient created by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Model
A cyclic model (or oscillating model) is any of several cosmological models in which the universe follows infinite, or indefinite, self-sustaining cycles. For example, the oscillating universe theory briefly considered by Albert Einstein in 1930 theorized a universe following an eternal series of oscillations, each beginning with a Big Bang and ending with a Big Crunch; in the interim, the universe would expand for a period of time before the gravitational attraction of matter causes it to collapse back in and undergo a bounce. Overview In the 1920s, theoretical physicists, most notably Albert Einstein, considered the possibility of a cyclic model for the universe as an (everlasting) alternative to the model of an expanding universe. However, work by Richard C. Tolman in 1934 showed that these early attempts failed because of the cyclic problem: according to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, entropy can only increase. This implies that successive cycles grow longer and larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale form. These models offer a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The overall uniformity of the Universe, known as the flatness problem, is explained through cosmic inflation: a sudden and very rapid expansion of space during the earliest moments. However, physics currently lacks a widely accepted theory of quantum gravity that can successfully model the earliest conditions of the Big Bang. Crucially, these models are compatible with the Hubble–Lemaître law—the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)