|
Government Of Wallis And Futuna
Politics of Wallis and Futuna takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas collectivity, whereby the President of the Territorial Assembly is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Overview The territory of Wallis and Futuna is divided into three traditional chiefdoms ('' royaumes coutumiers''): Uvea, on the island of Wallis, Sigave, on the western part of the island of Futuna, and Alo, on the eastern part of the island of Futuna and the island of Alofi. Uvea is further subdivided into three districts: Hihifo, Hahake and Mu'a. The capital of the collectivity is Matâ'Utu on the island of Wallis, the most populated island. As an overseas collectivity of France, it is governed under the French constitution of September 28, 1958, uses both the French legal system and customary local laws (''"coutume"''), and suffrage is universal for those over 18 years of age. The Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallis And Futuna
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands (; french: Wallis-et-Futuna or ', Fakauvea and Fakafutuna: '), is a French island collectivity in the South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east, and Tokelau to the northeast. Mata Utu is its capital and largest city. Its land area is . It had a population of 11,558 at the 2018 census (down from 14,944 at the 2003 census). The territory is made up of three main volcanic tropical islands and a number of tiny islets. It is divided into two island groups that lie about apart: the Wallis Islands (also known as Uvea) in the northeast; and the Hoorn Islands (also known as the Futuna Islands) in the southwest, including Futuna Island proper and the mostly uninhabited Alofi Island. Since 28 March 2003, Wallis and Futuna has been a French overseas collectivity (''collectivité d'outre-mer'', or ''COM''). Between 1961 and 2003, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ministry Of The Interior
Minister of the Interior (french: Ministre de l'Intérieur; ) is a prominent position in the Government of France. The position is equivalent to the interior minister in other countries, like the Home Secretary in the United Kingdom, the Minister of Public Safety in Canada, or similar to a combination of the Attorney General and the Secretary of Homeland Security in the United States. Responsibilities The Minister of the Interior is responsible for the following: * The general interior security of the country, with respect to criminal acts or natural catastrophes ** including the major law-enforcement forces *** the National Police *** the National Gendarmerie for its police operations since 2009; as a part of the French Armed Forces, the Gendarmerie is administratively under the purview of the Ministry of Armed Forces ** General directorate for civil defence and crisis management (Sécurité Civile) *** the directorate of Firefighters (Sapeurs-Pompiers) * the granting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFP Franc
The CFP franc ( French: , called the ''franc'' in everyday use) is the currency used in the French overseas collectivities (, or COM) of French Polynesia, New Caledonia, and Wallis and Futuna. The initials ''CFP'' originally stood for ('French colonies of the Pacific'). This was later changed to ('Pacific Financial Community') and then to its present term, ('Pacific Franc Exchange'). Its ISO 4217 currency code is ''XPF''. The CFP franc is subdivided into 100 centimes. History 1945–1949 The CFP franc was created in December 1945, together with the CFA franc, used in Africa. The reason for the creation of these francs was the weakness of the French franc immediately after the Second World War. When France ratified the Bretton Woods Agreement in December 1945, the French franc was devalued in order to set a fixed exchange rate with the US dollar. New currencies were created in the French colonies to spare them the strong devaluation of December 1945. René Pleven, the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouméa
Nouméa () is the capital and largest city of the French special collectivity of New Caledonia and is also the largest francophone city in Oceania. It is situated on a peninsula in the south of New Caledonia's main island, Grande Terre, and is home to the majority of the island's European, Polynesian ( Wallisians, Futunians, Tahitians), Indonesian, and Vietnamese populations, as well as many Melanesians, Ni-Vanuatu and Kanaks who work in one of the South Pacific's most industrialised cities. The city lies on a protected deepwater harbour that serves as the chief port for New Caledonia. At the September 2019 census, there were 182,341 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Greater Nouméa (), 94,285 of whom lived in the city (commune) of Nouméa proper. 67.2% of the population of New Caledonia live in Greater Nouméa, which covers the communes of Nouméa, Le Mont-Dore, Dumbéa and Païta. History The first European to establish a settlement in the vicinity was British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customary Law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior that can be objectively verified within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law". Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists where: #a certain legal practice is observed and #the relevant actors consider it to be an opinion of law or necessity (''opinio juris''). Most customary laws deal with ''standards of the community'' that have been long-established in a given locale. However, the term can also apply to areas of international law where certain standards have been nearly universal in their acceptance as correct bases of action – for example, laws against piracy or slavery (see ''hostis humani generis''). In many, though not all instances, customary laws will have supportive court rulings and case law that have evolved over time to give additional weight to their rule as law and also to demonstrate the trajectory of evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
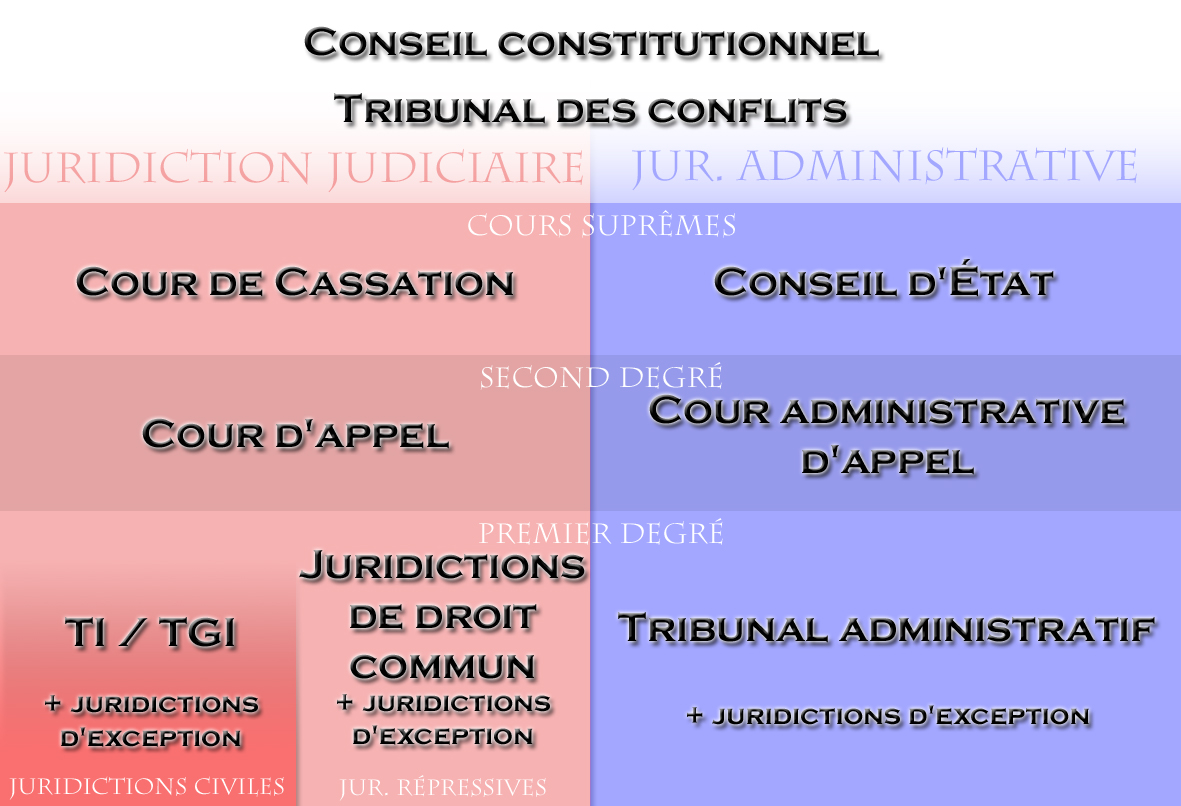
French Law
The Law of France refers to the legal system in the French Republic, which is a civil law legal system primarily based on legal codes and statutes, with case law also playing an important role. The most influential of the French legal codes is the Napoleonic Civil Code, which inspired the civil codes of Europe and later across the world. The Constitution of France adopted in 1958 is the supreme law in France. European Union law is becoming increasingly important in France, as in other EU member states. In academic terms, French law can be divided into two main categories: private law (''Droit privé'') and public law (''droit public''). This differs from the traditional common law concepts in which the main distinction is between criminal law and civil law. Private law governs relationships between individuals. It includes, in particular: * Civil law ('). This branch refers to the field of private law in common law systems. This branch encompasses the fields of inheritance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2022 Wallis And Futuna Territorial Assembly Election
Elections for the Territorial Assembly of Wallis and Futuna were held on 20 March 2022 where all 20 seats were up for election. Background The 2017 Wallis and Futuna Territorial Assembly election saw 19 electoral lists sharing the 20 seats of the Territorial Assembly. The only list able to gain two seats was Fakatahi kihe kaha'u e lelei / Ensemble pour un avenir meilleur (Together for a Better Future). There were nine newly elected members in the 20-seat Assembly. Among the elected members, six were women. The 2017 elections were noted for their very high participation, one of the highest in the recent history of Wallis and Futuna. Slightly more than 88% of the electorate voted, with voter turnout at 87% on Wallis (island), Wallis and 93% on Futuna (Wallis and Futuna), Futuna. Results Half the seats were won by new members. Turnout was over 84 percent. Elected members References Elections in Wallis and Futuna 2022 in Wallis and Futuna, Assembly election 2022 elections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French National Assembly
The National Assembly (french: link=no, italics=set, Assemblée nationale; ) is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate (). The National Assembly's legislators are known as (), meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word ''deputy'', which is the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems). There are 577 , each elected by a single-member constituency (at least one per department) through a two-round system; thus, 289 seats are required for a majority. The president of the National Assembly, Yaël Braun-Pivet, presides over the body. The officeholder is usually a member of the largest party represented, assisted by vice presidents from across the represented political spectrum. The National Assembly's term is five years; however, the President of France may dissolve the Assembly, thereby calling for new elections, unless it has been dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallis And Futuna's 1st Constituency
The constituency of Wallis and Futuna is a French legislative constituency covering the whole of the overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. It is represented in the XVIth legislature by Mikaele Seo of Renaissance who defeated fellow centrist Etuato Mulikihaamea in the 2022 election. Deputies Election results 2022 2018 by-election Napole Polutele's 2017 election was invalidated and a by-election held in 2018. Only the first round of the election was required. 2017 Napole Polutele obtained sufficient votes to be elected in the first round. Note, this election was later invalidated, leading to the 2018 by-election 2013 by-election David Vergé's 2012 election was annulled due to financial irregularities, causing a by-election on 17 and 24 March 2013. Two candidates stood for the left, including Laurianne Vergé for the Socialists. She was the first woman ever to stand as a candidate for Parliament to represent the constitue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Senate
The Senate (french: Sénat, ) is the upper house of the French Parliament, with the lower house being the National Assembly (France), National Assembly, the two houses constituting the legislature of France. The French Senate is made up of 348 senators (''sénateurs'' and ''sénatrices'') elected by part of the country's Territorial collectivity, local councillors (in indirect elections), as well as by representatives of French citizens living abroad. Senators have six-year terms, with half of the seats up for election every three years. The Senate enjoys less prominence than the first, or lower house, the National Assembly (France), National Assembly, which is elected on Direct election, direct universal ballot and upon the majority of which the Government of France, Government has to rely: in case of disagreement, the Assembly can in many cases have the last word, although the Senate keeps a role in some key procedures, such as Constitution of France, constitutional amendmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assemblée Territoriale
The Territorial Assembly of Wallis and Futuna (French: ''Assemblée Territoriale''; Wallisian and Futunan: ''Fono fakatelituale'') is the legislature of Wallis and Futuna. It consists of 20 members, elected for a five-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies. The Assembly sits in Mata Utu, the capital of the territory. History The Assembly was established by article 11 of the 1961 statute which established Wallis and Futuna as an overseas territory. Elections The territorial assembly consists of 20 members, elected for a five-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies. ʻUvea has 13 seats — 6 for the Mua District, 4 for the Hahake District, and 3 for the Hihifo District. Futuna has 7 seats, 4 for the Alo District and 3 for Sigave. The electoral system uses a closed list, with voters voting for a single party. The seats are distributed in each constituency using the highest averages method. Latest election Powers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)