|
Gorals
The Gorals ( pl, Górale; Goral dialect: ''Górole''; sk, Gorali; Cieszyn Silesian: ''Gorole''), also known as the Highlanders (in Poland as the Polish Highlanders) are an indigenous ethnographic or ethnic group primarily found in their traditional area of southern Poland, northern Slovakia and in the region of Cieszyn Silesia in the Czech Republic, where they are known as the Silesian Gorals. There is also a significant Goral diaspora in the area of Bukovina in western Ukraine and in northern Romania, as well as in Chicago, the seat of the Polish Highlanders Alliance of North America. History In the 13th century, Vlach shepherds migrated to the Western Carpathian mountains, gradually moving northwest from the Balkans and settling on Polish lands there. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Gorals settled the upper Kysuca and Orava rivers and part of northern Spiš in Slovakia, which at the time were part of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the 19th century, between 1803–1819, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Gorals
Silesian Gorals ( pl, Górale śląscy, cs, Slezští Goralé, Cieszyn Silesian: ''Gorole''; literally "highlanders") are an ethnographic group (subgroup of Gorals) living in Silesian Beskids and Moravian-Silesian Beskids within historical region of Cieszyn Silesia. They are one of the four major ethnographic groups of Cieszyn Silesia. Vlach colonization of Silesian Beskids began in the late 15th century roughly at the time when Brenna was first mentioned in 1490. It peaked in two following centuries. The group now shares a lot of cultural traits with other Gorals of Western Carpathians stemming from a common way of living from shepherding in mountainous pastures, but they are also characterised by various different cultural and spiritual elements like dialect, beliefs, customs, costume, etc. Wincenty Pol in his survey of Gorals in the middle of the 19th century subdivided Silesian Gorals into 4 groups: * Breniacy – in Brenna. * Wiślanie – in Wisła. * Jabłonkow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
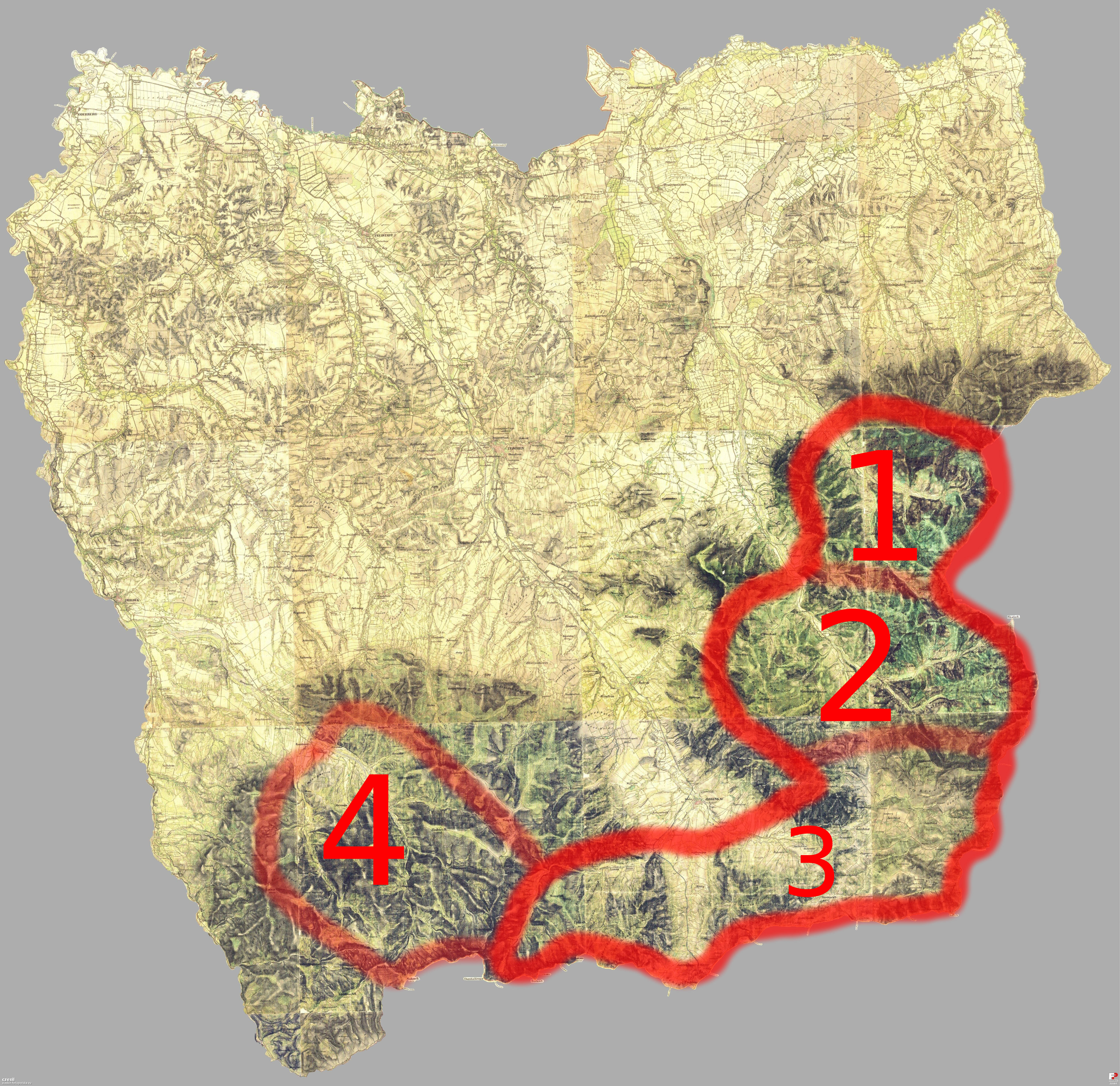
Podhale
Podhale (literally "below the mountain pastures") is Poland's southernmost region, sometimes referred to as the "Polish Highlands". The Podhale is located in the foothills of the Tatra mountains , Tatra range of the Carpathian mountains. It is the most famous region of the Gorals#Population, Goral Lands which are a network of historical regions inhabited by Gorals. Local folklore The region is characterized by its unique folklore, which is distinct from other folk cultures in Poland. Its folklore was brought there mainly by settlers from the Lesser Poland region further north and partly by Wallachia, Wallachian (Vlach) settlers in the centuries during their migrations. The name Podhale literally translates as "below the mountains" in English. The various Dialects of Polish, Goral dialects as well as Polish language, Polish are spoken in the region. Regional attractions Among the region's attractions are the popular mountain resort of Zakopane and the lake known as Morskie O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasant Rebellion In Podhale
The Peasant rebellion in Podhale (1669-1670) was a rebellion of rural Goral residents of the region of Podhale in present day southern Poland and a few villages in present day northern Slovakia against the high taxes imposed on them by the government of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It resulted in the defeat of the rebels and end of the Podhale Republic. In the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Gorals of Podhale frequently opposed local authorities, high taxes and the rule of the nobility: the best known of these revolts was the Kostka-Napierski Uprising, which took place in 1651. In late September 1669, a heavy cavalry unit of Jan Wielopolski (see Towarzysz pancerny, Choragiew (military unit)) came to Podhale to winter in the region. By December, the cavalrymen had found their lodgings in the area of Nowy Targ: according to the legal regulations, local residents were obliged to provide food to the soldiers and their officers. Jan Wielopolski sent his envoys to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Highlanders Alliance Of North America
The Polish Highlanders Alliance of America (pl. ''Związek Podhalan w Ameryce Północnej'') was founded in 1929 in Chicago as an organization that unites all other Góral organizations in the United States. Most of Chicago's Góral community is concentrated on Chicago's Southwest Side along Archer Avenue where the headquarters, also known as the "Highlander Home" ("Dom Podhalan" in Polish) is located. The Highlander House is styled as a Carpathian chalet in the traditional Zakopane Style of Architecture. Located at 4808 S. Archer Avenue in Chicago, the structure underwent renovation under the eye of famed artist Jerzy Kenar in 2005. In 2012 the Highlander House was upgraded with state of the art audio and video equipment. The Polish Highlanders Alliance of North America is a nonprofit organization run by an executive board. The members of the current (2011-2014) board are: ::Andrzej Gedlek - president ::Karolina Walkosz-Strzelec - vice president ::Michal Ploskonka- vice p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiš
Spiš (Latin: ''Cips/Zepus/Scepus/Scepusia'', german: Zips, hu, Szepesség/Szepes, pl, Spisz) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (14 villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one of the 21 official tourism regions of Slovakia. The region is not an administrative division in its own right, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary, (see separate article Szepes county). Etymology The name is probably related to the appellative ''spiška'', ''špiška'' known from Slovak (Eastern Slovakia and Orava) and Moravian dialects ( Haná) - a (cut) stick, a piece of wood or sugar, etc. Old Slavic ''pьchjati'', ''pichjati'' - to stab, to cut → prefixed form sъ-pich-jь → after palatalization and extinction of yers ''spiš''. Spiš probably means "a cut forest". The theory is supported also by the fact that almost all early Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( pl, Śląsk Cieszyński ; cs, Těšínské Slezsko or ; german: Teschener Schlesien or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český Těšín and bisected by the Olza River. Since 1920 it has been divided between Poland and Czechoslovakia, and later the Czech Republic. It covers an area of about and has about 810,000 inhabitants, of which (44%) is in Poland, while (56%) is in the Czech Republic. The historical boundaries of the region are roughly the same as those of the former independent Duchy of Teschen/Cieszyn. Currently, over half of Cieszyn Silesia forms one of the euroregions, the Cieszyn Silesia Euroregion, with the rest of it belonging to Euroregion Beskydy. Administrative division From an administrative point of view, the Polish part of Cieszyn Silesia lies within the Silesian Voivodeship and comprises Cieszyn County, the western part of Bielsko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksander Kostka Napierski
Aleksander Leon Kostka-Napierski (1620–1651), Polish captain during the Thirty Years' War in Swedish service, participant of battle in Germany and organizer of the Kostka-Napierski Uprising. According to the historian prof. Paweł Wieczorkiewicz, Napierski was in service to Khmelnytsky. Professor of History Janusz Tazbir was of a similar opinion. However, other historians, such as Adam Kersten, cautiously connect Kostka-Napierski with the Swedish king, with Khmelnytsky, or with the court of Rákóczi. Life and service Kostka-Napierski served in the Swedish army as a mercenary during the Thirty Years' War. He returned to Poland after the death of Władysław IV Vasa. He contacted Bohdan Khmelnytsky, attempting to expand the his revolt onto Tatra Polish lands and became the leader of the Tatra highlands peasants ('' Górale''), In 1651, he organized recruitment to the rebel army in the Tatra mountains in Podhale (with M. Radocki and S. Łętowski). Napierski called on every peas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kostka-Napierski Uprising
The Kostka Napierski uprising () was a peasant revolt in Poland in 1651. It took place at the same time as the more important Khmelnytsky Uprising, in the south-east part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and during the Swedish preparations to invade the Commonwealth. Aleksander Kostka Napierski was an adventurer and officer in the Polish army. During the revolt, he acted most likely as a spy for Bohdan Khmelnytsky or the Prince of Transylvania. He recruited his forces from among some rebellious gorals in Podhale, a mountainous region in Lesser Poland. They attacked and captured the castle of Czorsztyn in Pieniny. Napierski called on every peasant in Poland to rise and overthrow the nobles and remove them from their positions of power. His attempts to spread the revolt were totally unsuccessful. Napierski and his rebel group remained isolated in the castle, which was soon recaptured by the forces of Piotr Gembicki, the bishop of Kraków. Napierski and the other leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cieszyn Silesia Dialect
The Cieszyn Silesian dialect or Teschen Silesian dialect (Cieszyn Silesian: ''cieszyńsko rzecz''; pl, gwara cieszyńska or '; cs, těšínské nářečí; Silesian: ''ćeszyński djalekt'') is one of the Silesian dialects. It has its roots mainly in Old Polish and also has strong influences from Czech and German and, to a lesser extent, from Vlach and Slovak. It is spoken in Cieszyn Silesia, a region on both sides of the Polish- Czech border. It remains mostly a spoken language. The dialect is better preserved today than traditional dialects of many other West Slavic regions.Hannan 1996, p. 191 On the Czech side of the border (in Zaolzie) it is spoken mainly by the Polish minority, where it was and still is strongly influenced mainly by Czech (mainly lexicon and syntax). It is used to reinforce a feeling of regional solidarity. Polish and Czech linguists differ in their views on the classification of the dialect. Most Czech linguists make a distinction between the dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed during the Cold War (1947–1991). These states followed the ideology of Marxism–Leninism, in opposition to the capitalist Western Bloc. The Eastern Bloc was often called the Second World, whereas the term " First World" referred to the Western Bloc and "Third World" referred to the non-aligned countries that were mainly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America but notably also included former pre-1948 Soviet ally SFR Yugoslavia, which was located in Europe. In Western Europe, the term Eastern Bloc generally referred to the USSR and Central and Eastern European countries in the Comecon (East Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania). In Asia, the Soviet Bloc comprised Mongolia, Vietnam, Laos, Kampuchea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podhale W Ogniu
''Podhale w ogniu'' () is a Polish historical film about the Kostka-Napierski uprising. It was released in 1956 Events January * January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan. * January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim Elliot and Pete Fleming, are kille .... References External links * 1956 films Polish historical films 1950s Polish-language films 1950s historical films {{Poland-film-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orava (river)
, , pl, Orawa , name_etymology = , image = OravaRiver.jpg , image_size = , image_caption = Orava at Dolný Kubín, showing houses of Záskalie neighbourhood , map = , map_size = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = , pushpin_map_size = , pushpin_map_caption= , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Slovakia , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , subdivision_type3 = , subdivision_name3 = , subdivision_type4 = , subdivision_name4 = , subdivision_type5 = , subdivision_name5 = , length = , width_min = , width_avg = , width_max = , depth_min = , depth_avg = , depth_max = , discharge1_location= mouth , discharge1_min = , discharge1_avg = , discharge1_max = , source1 = Orava reservoir, taking water from ''White Orava'' in Slovakia and from ''Black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |