|
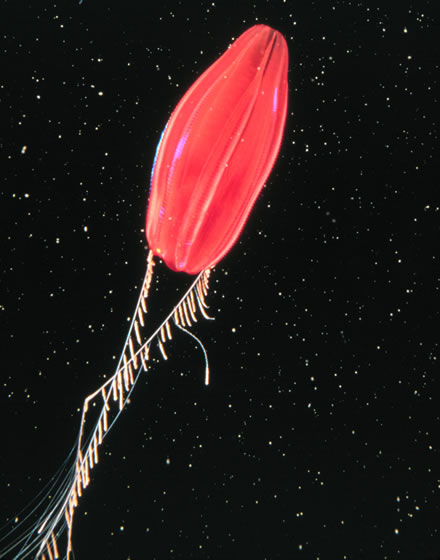
Gonionemus Agilis
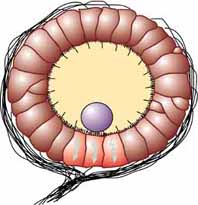
''Gonionemus'' is a genus of hydrozoans that uses adhesive discs near the middle of each tentacle to attach to eelgrass, sea lettuce, or various types of algae instead of swimming. They are small (bell diameter to 25 mm) and hard to see when hanging onto swaying seaweed. Nevertheless, they are capable of swimming when necessary. The bell is transparent, revealing the four orange to yellowish-tan gonads that lie along most of the length of the four radial canals. The pale yellow manubrium has four short, frilly lips. Up to 80 tentacles line the bell margin, with about an equal number of statocysts. Copepods are a favored prey. This marine hydrozoan is common in warmer waters. The conspicuous stage in the dimorphic lifecycle is the small medusa. The polypoid stage is present as a tiny, solitary polyp which feeds on protozoans and other small plants and animals. The polyp stage closely resembles ''Hydra''. The medusae are active swimmers that propel themselves upward in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonionemus Vertens
''Gonionemus vertens'', the clinging jellyfish, is a small species of hydrozoan in the family Olindiidae found in coastal regions throughout large parts of the Northern Hemisphere. Description and behavior The appearance of ''Gonionemus vertens'' is usually described as having a transparent bell lined with 60–80 (exceptionally up to 100–110) tentacles. The gonads are distinctly colored orange, red or violet if the specimen is female, or yellow-brown if it is male. The gonads are arranged hanging from four radial canals so that when viewed from above, the gonads are lined perpendicularly. The manubrium, colored tan, hangs down in the middle. The bell of the jellyfish (medusae) is only in diameter, exceptionally up to , and when fully extended a tentacle can be twice the length of the bell diameter. The medusae reproduce sexually and the tens of thousands of eggs and sperm are released into the sea. They become planula larvae that eventually attach themselves to the seabed on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Emanuel Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer. Biography Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland and immigrated to the United States with his parents, Louis and Cecile (Braun) Agassiz, in 1846. He graduated from Harvard University in 1855, subsequently studying engineering and chemistry, and taking the degree of Bachelor of Science at the Lawrence Scientific School of the same institution in 1857; in 1859 became an assistant in the United States Coast Survey. Thenceforward he became a specialist in marine ichthyology. Agassiz was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1862. Up until the summer of 1866, Agassiz worked as assistant curator in the museum of natural history that his father founded at Harvard. E. J. Hulbert, a friend of Agassiz's brother-in-law, Quincy Adams Shaw, had discovered a rich copper lode known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrozoan
Hydrozoa (hydrozoans; ) are a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria. Some examples of hydrozoans are the freshwater jelly (''Craspedacusta sowerbyi''), freshwater polyps ('' Hydra''), ''Obelia'', Portuguese man o' war (''Physalia physalis''), chondrophores (Porpitidae), "air fern" (''Sertularia argentea''), and pink-hearted hydroids (''Tubularia''). Anatomy Most hydrozoan species include both a polypoid and a medusoid stage in their lifecycles, although a number of them have only one or the other. For example, ''Hydra'' has no medusoid stage, while '' Liriope'' lacks the polypoid stage. Polyps The hydroid fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostera
''Zostera'' is a small genus of widely distributed seagrasses, commonly called marine eelgrass, or simply seagrass or eelgrass, and also known as seaweed by some fishermen and recreational boaters including yachtsmen. The genus ''Zostera'' contains 15 species. Ecology ''Zostera marina'' is found on sandy substrates or in estuaries, usually submerged or partially floating. Most ''Zostera'' are perennial. They have long, bright green, ribbon-like leaves, the width of which are about . Short stems grow up from extensive, white branching rhizomes. The flowers are enclosed in the sheaths of the leaf bases; the fruits are bladdery and can float. ''Zostera'' beds are important for sediment deposition, substrate stabilization, as substrate for epiphytic algae and micro-invertebrates, and as nursery grounds for many species of economically important fish and shellfish. ''Zostera'' often forms beds in bay mud in the estuarine setting. It is an important food for brant geese and wigeon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Lettuce
The sea lettuces comprise the genus ''Ulva'', a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus ''Ulva'' is ''Ulva lactuca'', wikt:lactuca, ''lactuca'' being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus ''Enteromorpha'', the former members of which are known under the common name green nori. Description Individual blades of ''Ulva'' can grow to be more than 400 mm (16 in) in size, but this occurs only when the plants are growing in sheltered areas. A macroscopic alga which is light to dark green in colour, it is attached by disc holdfast. Their structure is a leaflike flattened thallus. Nutrition and contamination Sea lettuce is eaten by a number of different sea animals, including manatees and the sea slugs known as sea hares. Many species of sea lettuce are a food source for humans in Scandinavia, Great Britain, Ireland, China, and Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm in the form of spermatozoa. The female gonad, the ovary, produces egg cells. Both of these gametes are haploid cells. Some hermaphroditic animals have a type of gonad called an ovotestis. Evolution It is hard to find a common origin for gonads, but gonads most likely evolved independently several times. Regulation The gonads are controlled by luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, produced and secreted by gonadotropes or gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland. This secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced in the hypothalamus. Development Gonads start developing as a common primordium (an organ in the earliest stage of development), in the form of genital ridges, which are only l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manubrium
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, statocysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthos, benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonionemus Agilis
''Gonionemus'' is a genus of hydrozoans that uses adhesive discs near the middle of each tentacle to attach to eelgrass, sea lettuce, or various types of algae instead of swimming. They are small (bell diameter to 25 mm) and hard to see when hanging onto swaying seaweed. Nevertheless, they are capable of swimming when necessary. The bell is transparent, revealing the four orange to yellowish-tan gonads that lie along most of the length of the four radial canals. The pale yellow manubrium has four short, frilly lips. Up to 80 tentacles line the bell margin, with about an equal number of statocysts. Copepods are a favored prey. This marine hydrozoan is common in warmer waters. The conspicuous stage in the dimorphic lifecycle is the small medusa. The polypoid stage is present as a tiny, solitary polyp which feeds on protozoans and other small plants and animals. The polyp stage closely resembles ''Hydra''. The medusae are active swimmers that propel themselves upward in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |