|
GLIC
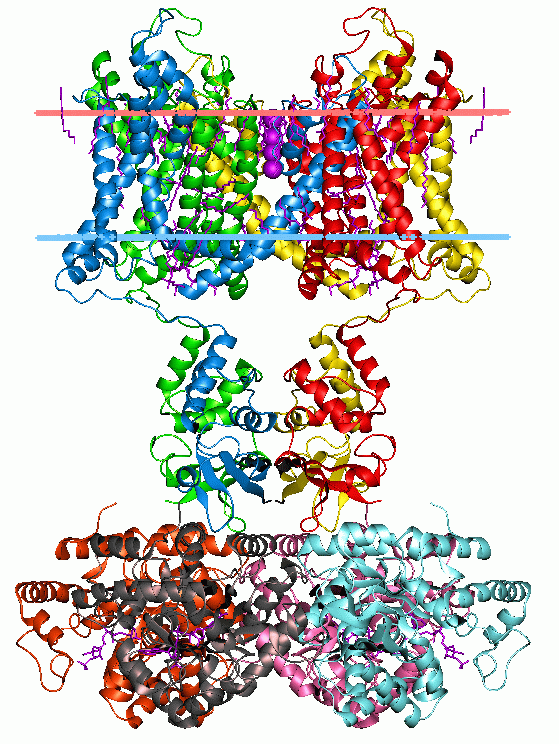
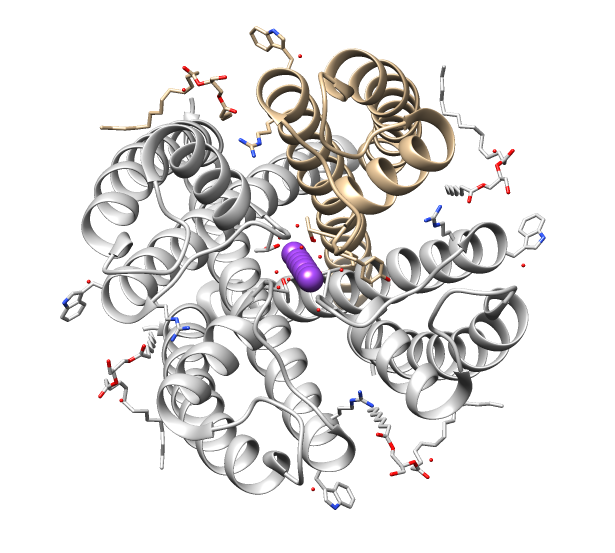
The GLIC receptor is a bacterial ( Gloeobacter) Ligand-gated Ion Channel, homolog to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is a proton-gated (the channel opens when it binds a proton, ion), cation-selective channel (it selectively lets the positive ions through). Like the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is a functional pentameric oligomer (the channel normally works as an assembly of five subunits). However while its eukaryotic homologues are hetero-oligomeric (assembled from different subunits), all until now known bacteria known to express LICs encode a single monomeric unit, indicating the GLIC to be functionally homo-oligomeric (assembled from identical subunits). The similarity of amino-acid sequence to the eukaryotic LGICs is not localized to any single or particular tertiary domain, indicating the similar function of the GLIC to its eukaryotic equivalents. Regardless, the purpose of regulating the threshold for action potential excitation in the nerve signal transmiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cys-loop Receptors
The Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel superfamily is composed of nicotinic acetylcholine, GABAA, GABAA-ρ, glycine, 5-HT3, and zinc-activated (ZAC) receptors. These receptors are composed of five protein subunits which form a pentameric arrangement around a central pore. There are usually 2 alpha subunits and 3 other beta, gamma, or delta subunits (some consist of 5 alpha subunits). The name of the family refers to a characteristic loop formed by 13 highly conserved amino acids between two cysteine (Cys) residues, which form a disulfide bond near the N-terminal extracellular domain. Cys-loop receptors are known only in eukaryotes, but are part of a larger family of pentameric ligand-gated ion channels. Only the Cys-loop clade includes the pair of bridging cysteine residues. The larger superfamily includes bacterial (e.g. GLIC) as well as non-Cys-loop eukaryotic receptors, and is referred to as "pentameric ligand-gated ion channels", or "Pro-loop receptors". All subunits consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand-gated Ion Channel
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter. When a presynaptic neuron is excited, it releases a neurotransmitter from vesicles into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter then binds to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. If these receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, a resulting conformational change opens the ion channels, which leads to a flow of ions across the cell membrane. This, in turn, results in either a depolarization, for an excitatory receptor response, or a hyperpolarization, for an inhibitory response. These receptor proteins are typically composed of at least two different domains: a transmembrane domain which includes the ion pore, and an extracellular domain wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionotropic Receptors
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter. When a presynaptic neuron is excited, it releases a neurotransmitter from vesicles into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter then binds to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. If these receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, a resulting conformational change opens the ion channels, which leads to a flow of ions across the cell membrane. This, in turn, results in either a depolarization, for an excitatory receptor response, or a hyperpolarization, for an inhibitory response. These receptor proteins are typically composed of at least two different domains: a transmembrane domain which includes the ion pore, and an extracellular domain wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGIC
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter. When a presynaptic neuron is excited, it releases a neurotransmitter from vesicles into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter then binds to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. If these receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, a resulting conformational change opens the ion channels, which leads to a flow of ions across the cell membrane. This, in turn, results in either a depolarization, for an excitatory receptor response, or a hyperpolarization, for an inhibitory response. These receptor proteins are typically composed of at least two different domains: a transmembrane domain which includes the ion pore, and an extracellular domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Neuroscience
Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject covers topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics and epigenetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic. Locating neurotransmitters In molecular biology, communication between neurons typically occurs by chemical transmission across gaps between the cells called synapses. The transmitted chemicals, known as neurotransmitters, regulate a significant fraction of vital body functions. It is possible to anatomically locate neurotransmitters by labeling techniques. It is possible to chemically identify certain neurotransmitters such as catecholamines by fixing neural tissue sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek , ''ēlektron'', "amber" etymology of "electron"">Electron#Etymology">etymology of "electron" , ''physis'', "nature, origin"; and , '' -logia'') is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring. Definition and scope Classical electrophysiological techniques Principle and mechanisms Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that pertains broadly to the flow of ions (ion current) in biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure.Branden C. and Tooze J. "Introduction to Protein Structure" Garland Publishing, New York. 1990 and 1991. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.Kyte, J. "Structure in Protein Chemistry." Garland Publishing, New York. 1995. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |