|
Gland Seal
A stuffing box or gland package is an assembly which is used to house a gland seal. It is used to prevent leakage of fluid, such as water or steam, between sliding or turning parts of machine elements. Components A stuffing box of a sailing boat will have a stern tube that is slightly bigger than the prop shaft. It will also have packing nut threads or a gland nut. The packing is inside the gland nut and creates the seal. The shaft is wrapped by the packing and put in the gland nut. Through tightening it onto the stern tube, the packing is compressed, creating a seal against the shaft. , WindCheck Magazine, Retrieved April 27, 2016. Creating a proper plunger alignment is critical for correct flow and a long wear life. Stuffing box components are of stainless steel, brass or other application-specific m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Element
Machine element or hardware refers to an elementary component of a machine. These elements consist of three basic types: # '' structural components'' such as frame members, bearings, axles, splines, fasteners, seals, and lubricants, # '' mechanisms'' that control movement in various ways such as gear trains, belt or chain drives, linkages, cam and follower systems, including brakes and clutches, and # '' control components'' such as buttons, switches, indicators, sensors, actuators and computer controllers. While generally not considered to be a machine element, the shape, texture and color of covers are an important part of a machine that provide a styling and operational interface between the mechanical components of a machine and its users. ''Machine elements'' are basic mechanical parts and features used as the building blocks of most machines. Most are standardized to common sizes, but customs are also common for specialized applications. Machine elements may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off from DuPont, which originally discovered the compound in 1938. Polytetrafluoroethylene is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high-molecular-weight polymer consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. PTFE is hydrophobic: neither water nor water-containing substances wet PTFE, as fluorocarbons exhibit only small London dispersion forces due to the low electric polarizability of fluorine. PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. Polytetrafluoroethylene is used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. It is non-reactive, partly because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds, so it is often used in containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals. Where used as a lubricant, PTFE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seals (mechanical)
Seals may refer to: * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, or "true seal" ** Fur seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join In military: * United States Navy SEALs, the U.S. Navy's principal special operations force * Royal Thai Navy SEALs, part of the Royal Thai Navy In sport: * Florida Seals, a minor league ice hockey team from 2002 and 2007 * California Golden Seals, originally ''California Seals'', a former NHL ice hockey team * San Francisco Seals (baseball), a minor league baseball team in the Pacific Coast League from 1903 until 1957 * San Francisco Seals (ice hockey), a minor league hockey team in the Western Hockey League from 1961 unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Propulsion
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems. Human-powered paddles and oars, and later, sails were the first forms of marine propulsion. Rowed galleys, some equipped with sail, played an important early role in early human seafaring and warfares. The first advanced mechanical means of marine propulsion was the marine steam engine, introduced in the early 19th century. During the 20th century it was replaced by two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines, outboard motors, and gas turbine engines on faster ships. Marine nuclear reactors, which appeared in the 1950s, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistons
{{DEFAULTSORT:Piston ...
A piston is an engineering component of engines and pumps. Piston(s) may also refer to: Science and technology * Piston (optics) * Piston (subcellular structure) * Piston valve * Fire piston, an ancient device for kindling fire * Gas-operated reloading, sometimes referred to as a gas piston. * Piston, the working name for the Steam Machine gaming platform People and groups * Pist.On, an American heavy metal band * Detroit Pistons, an American basketball team * Steinbach Pistons, a Canadian ice hockey team * Walter Piston, an American composer * Web Piston, a software and web hosting company Other * Piston (music), a type of oboe * Piston controls the combination action on a pipe organ The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurized air (called ''wind'') through the organ pipes selected from a keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single pitch, the pipes are provided in sets called ''ranks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinth Seal
A labyrinth seal is a type of mechanical seal that provides a tortuous path to help prevent leakage. An example of such a seal is sometimes found within an axle's bearing to help prevent the leakage of the oil lubricating the bearing. A labyrinth seal may be composed of many grooves that press tightly inside another axle, or inside a hole, so that the fluid has to pass through a long and difficult path to escape. Sometimes screw threads exist on the outer and inner portion. These interlock, to produce the long characteristic path which slows leakage. For labyrinth seals on a rotating shaft, a very small clearance must exist between the tips of the labyrinth threads and the running surface. The "teeth" of the labyrinth seal may be on the rotating shaft (Teeth On Rotor - TOR) or on the stator (TOS), or both, in an interlocking configuration. Labyrinth seals on rotating shafts provide non-contact sealing action by controlling the passage of fluid through a variety of chambers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
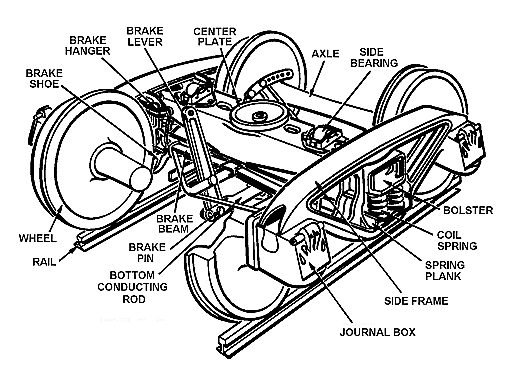
Journal Box
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Bearing
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding contact bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing, journal bearing, or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe. Plain bearings, in general, are the least expensive type of bearing. They are also compact and lightweight, and they have a high load-carrying capacity. Design The design of a plain bearing depends on the type of motion the bearing must provide. The three types of motions possible are: * ''Journal'' (''friction'', ''radial'' or ''rotary'') ''bearing'': This is the most common type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Seal Fitting
A compression seal fitting, also known as a sealing gland, is intended to seal some type of element ( probe, wire, conductor, pipe, tube, fiber optic cable, etc.) when the element must pass through a pressure or environmental boundary. A compression seal fitting may serve several purposes: *It restrains the element from moving as a result of a pressure difference. *It prohibits the leakage of gas or liquid media along the element. *In some cases, it electrically isolates the element from the mounting device. A compression seal fitting, unlike an epoxy seal or gasket, uses mechanical components and an axial force to compress a soft sealant inside a body which then creates a seal. An epoxy seal differs in that it is composed of some type of compound which is poured into a mold in an attempt to create a seal. Applications Typical applications include pressure vessels, autoclaves, holding tanks, pipelines, furnaces, or anywhere wires or sensors need to pass from inside to outside a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilge
The bilge of a ship or boat is the part of the hull that would rest on the ground if the vessel were unsupported by water. The "turn of the bilge" is the transition from the bottom of a hull to the sides of a hull. Internally, the bilges (usually used in the plural in this context) is the lowest compartment on a ship or seaplane, on either side of the keel and (in a traditional wooden vessel) between the floors. The first known use of the word is from 1513. Bilge water The word is sometimes also used to describe the water that collects in this area. Water that does not drain off the side of the deck or through a hole in the hull, typically via a scupper, drains down into the ship into the bilge. This water may be from rough seas, rain, leaks in the hull or stuffing box, or other interior spillage. The collected water must be pumped out to prevent the bilge from becoming too full and threatening to sink the ship. Bilge water can be found aboard almost every vessel. Depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axlebox
A bogie or railroad truck holds the wheel sets of a rail vehicle. Axlebox An ''axle box'', also known as a ''journal box'' in North America, is the mechanical subassembly on each end of the axles under a railway wagon, coach or locomotive; it contains bearings and thus transfers the wagon, coach or locomotive weight to the wheels and rails; the bearing design is typically oil-bathed plain bearings on older rolling stock, or roller bearings on newer rolling stock. Plain bearings are now illegal for interchange service in North America. As early as 1908 axle boxes contained a set of long cylindrical rollers allowing the axle to rotate. It was also used on steam locomotives such as the Victorian Railways A2 class, the LMS Garratt, the LSWR 415 class, and the GCR Class 1. Center pin A large steel pin—or rod—which passes through the center plates on the body bolster and truck bolster. The truck turns about the pin, and stress is taken by the center plates. Center pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)