|
Giraffa Jumae
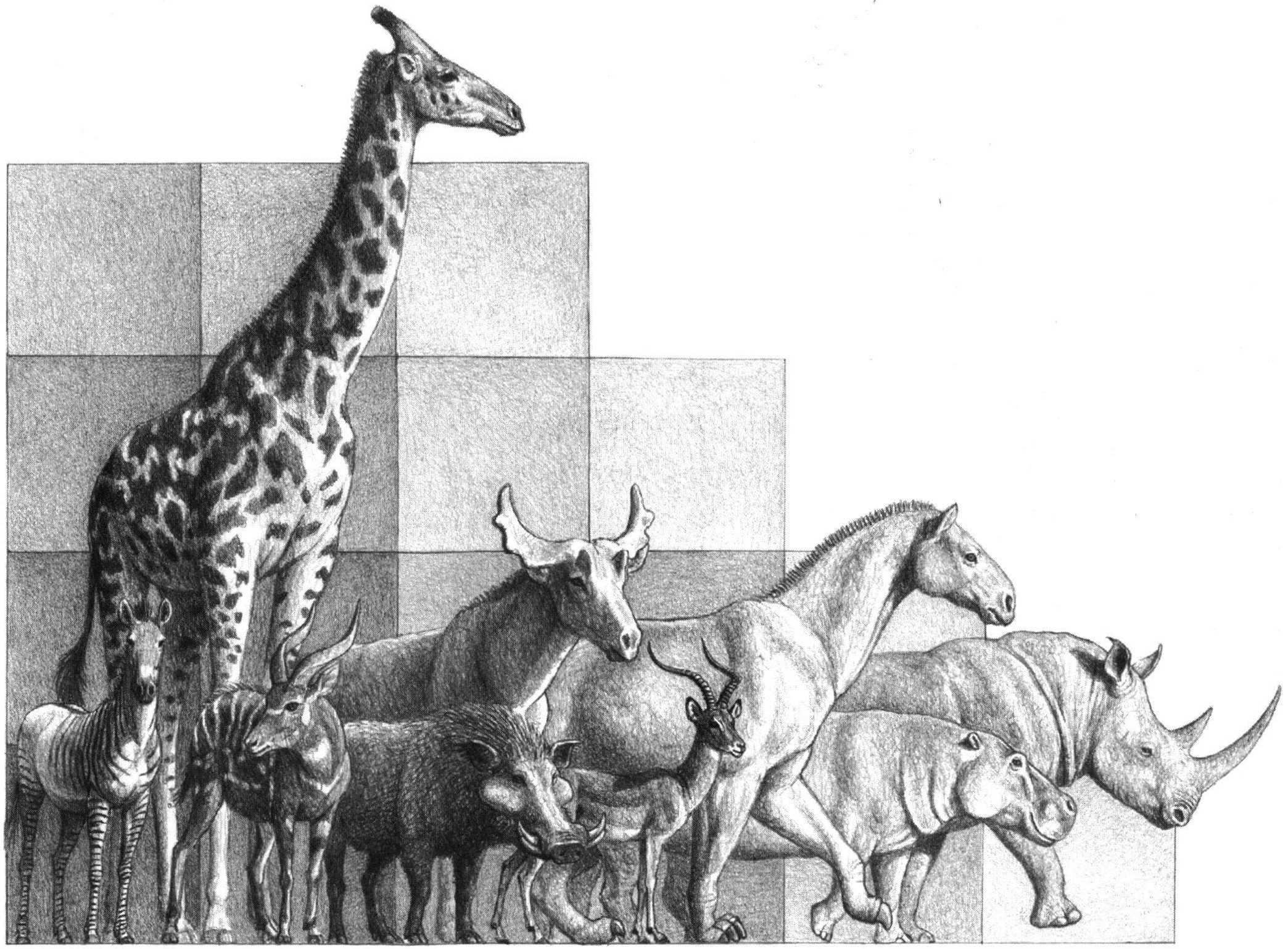
''Giraffa jumae'' is an extinct species of even-toed ungulate in the Giraffidae family. The species ranged from Malawi to Chad with a possible occurrence of the species or a closely related species found in Turkey. The type specimen was discovered during trenching excavations on the upper member of the Rawi Formation by Louis Leakey in the 1930s. The specimen was found with '' Ceratotherium simum'', Suidae such as '' Metridiochoerus andrewsi'', a ''Hippopotamus gorgops'', and a nearly complete pygmy hippopotamus mandible. The species is considered a possible ancestor to the modern giraffe The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, ''Giraffa camelopardalis ...s. References Pliocene mammals of Africa Pleistocene mammals of Africa Prehistoric giraffes Pleistocene even-toed ungulates P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suidae
Suidae is a family of artiodactyl mammals which are commonly called pigs, hogs or swine. In addition to numerous fossil species, 18 extant species are currently recognized (or 19 counting domestic pigs and wild boars separately), classified into between four and eight genera. Within this family, the genus ''Sus'' includes the domestic pig, ''Sus scrofa domesticus'' or ''Sus domesticus'', and many species of wild pig from Europe to the Pacific. Other genera include babirusas and warthogs. All suids, or swine, are native to the Old World, ranging from Asia to Europe and Africa. The earliest fossil suids date from the Oligocene epoch in Asia, and their descendants reached Europe during the Miocene. Several fossil species are known and show adaptations to a wide range of different diets, from strict herbivory to possible carrion-eating (in Tetraconodontinae). Physical characteristics Suids belong to the order Artiodactyla, and are generally regarded as the living members of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Giraffes
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Mammals Of Africa
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós ( latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Mammals Of Africa
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraffe
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa''. It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. Traditionally, giraffes were thought to be one species, '' Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into up to eight extant species due to new research into their mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, as well as morphological measurements. Seven other extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's chief distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, its horn-like ossicones, and its spotted coat patterns. It is classified under the family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south, and from Niger in the west to Somalia in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and woodlands. Their food source is leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulates From The Pliocene Of Eastern Africa
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as Whale, whales, Dolphin, dolphins, and Porpoise, porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized Gut microbiota, gut bacteria to allow them to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygmy Hippopotamus
The pygmy hippopotamus or pygmy hippo (''Choeropsis liberiensis'') is a small hippopotamid which is native to the forests and swamps of West Africa, primarily in Liberia, with small populations in Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ivory Coast. It has been extirpated from Nigeria. The pygmy hippo is reclusive and nocturnal. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being its much larger relative, the common hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius'') or Nile hippopotamus. The pygmy hippopotamus displays many terrestrial adaptations, but like the hippo, it is semiaquatic and relies on water to keep its skin moist and its body temperature cool. Behaviors such as mating and giving birth may occur in water or on land. The pygmy hippo is herbivorous, feeding on ferns, broad-leaved plants, grasses, and fruits it finds in the forests. A rare nocturnal forest creature, the pygmy hippopotamus is a difficult animal to study in the wild. Pygmy hippos were unkno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus Gorgops
''Hippopotamus gorgops'' is an extinct species of hippopotamus. It first appeared in Africa during the late Pliocene, and eventually migrated into Europe (where its fossils were first discovered) during the early Pleistocene. It became extinct during the Middle Pleistocene. Fossil records found at Ubeidiya, Israel suggested that they migrated out of Africa around 1.6 million years ago. Some have speculated that ''H. gorgops'' and '' H. behemoth'' are actually the same species given their similar sizes and where they have been found. Taxonomy With an estimated length of , a shoulder height of , and a weight of 3,900-4,500 kg (8,600-9,900 lb), ''H. gorgops'' was larger than its living relative, ''H. amphibius''. Another feature setting it apart from ''H. amphibius'' was the placement of its eyes. Modern hippos have eyes placed high on the skull, but ''H. gorgops'' had eyestalk In anatomy, an eyestalk (sometimes spelled eye stalk and also known as an ommatophore) is a protrusio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metridiochoerus
''Metridiochoerus'' is an extinct genus in the pig family indigenous to the Pliocene and Pleistocene of Africa. It is also known as the giant warthog. Description ''Metridiochoerus'' was a large animal, in length, resembling a giant warthog. It had two large pairs of tusks which were pointed sideways and curved upwards. Based on the complicated, knobbly pattern of the creature's molars, ''Metridiochoerus'' is considered to have been an omnivore. References *Barry Cox, Colin Harrison, R.J.G. Savage, and Brian Gardiner. (1999): The Simon & Schuster Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Creatures: A Visual Who's Who of Prehistoric Life. Simon & Schuster Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest pub .... *David Norman . (2001): The Big Book Of Dinosaurs. pg. 226, Walcome b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratotherium
''Ceratotherium'' (Greek: "horn" (keratos), "beast" (therion)) is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the white rhinoceros, and its extinct relatives, ''Ceratotherium neumayri'' and ''Ceratotherium mauritanicum'', of which ''Ceratotherium efficax'' is considered a synonym. Another species known as ''Ceratotherium praecox'' is now considered a member of the related ''Diceros ''Diceros'' (Greek: "two" (dio), "horn" (keratos)) is a genus of rhinoceros containing the living black rhinoceros ''(Diceros bicornis)'' and at least one extinct species. Taxonomy ''Diceros'' is generally believed to have branched off from an ...''. References Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by John Edward Gray Rhinoceroses Mammal genera Extant Tortonian first appearances {{oddtoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
