|
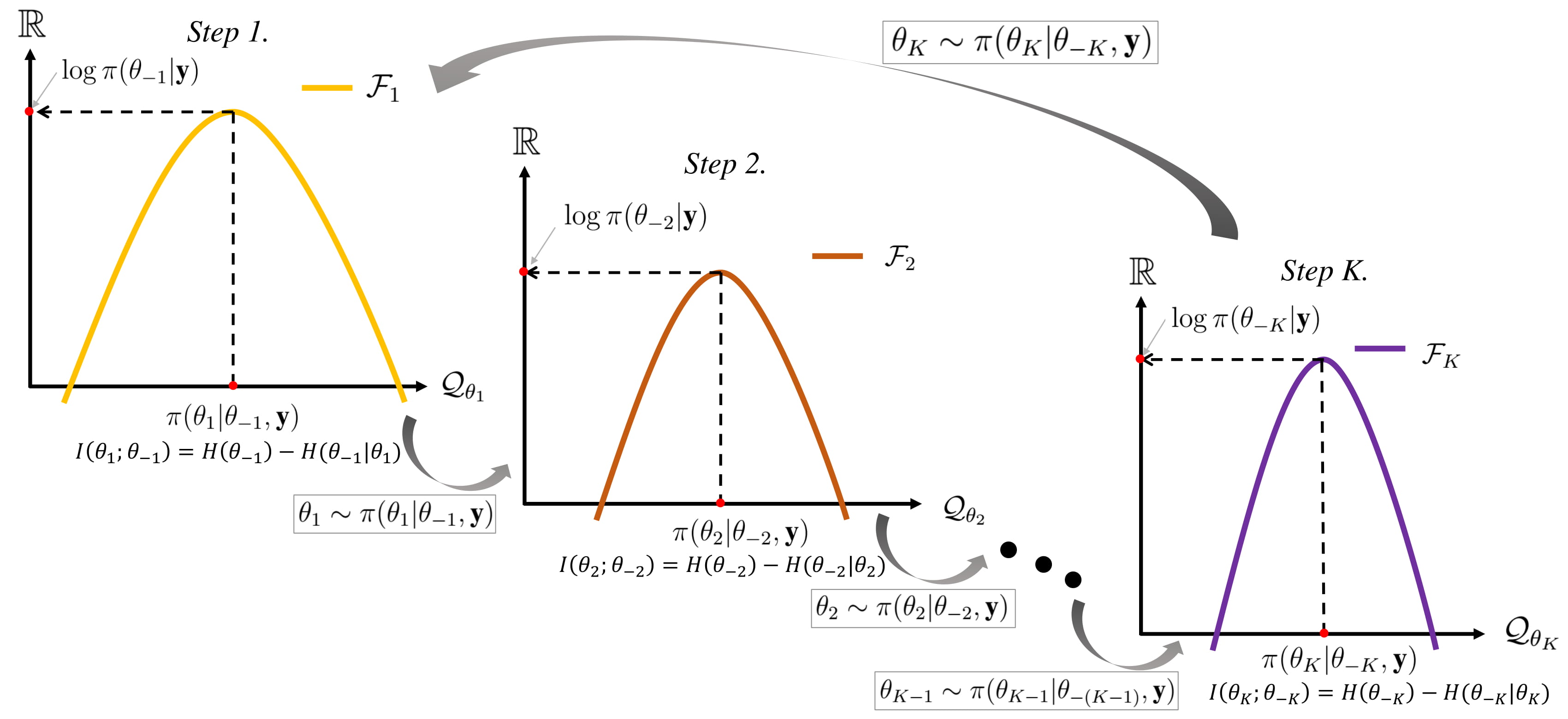
Gibbs Sampling
In statistics, Gibbs sampling or a Gibbs sampler is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm for sampling from a specified multivariate distribution, multivariate probability distribution when direct sampling from the joint distribution is difficult, but sampling from the Conditional probability distribution, conditional distribution is more practical. This sequence can be used to approximate the joint distribution (e.g., to generate a histogram of the distribution); to approximate the marginal distribution of one of the variables, or some subset of the variables (for example, the unknown parameters or latent variables); or to compute an integral (such as the expected value of one of the variables). Typically, some of the variables correspond to observations whose values are known, and hence do not need to be sampled. Gibbs sampling is commonly used as a means of statistical inference, especially Bayesian inference. It is a randomized algorithm (i.e. an algorithm that makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Chain
In probability theory and statistics, a Markov chain or Markov process is a stochastic process describing a sequence of possible events in which the probability of each event depends only on the state attained in the previous event. Informally, this may be thought of as, "What happens next depends only on the state of affairs ''now''." A countably infinite sequence, in which the chain moves state at discrete time steps, gives a discrete-time Markov chain (DTMC). A continuous-time process is called a continuous-time Markov chain (CTMC). Markov processes are named in honor of the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov. Markov chains have many applications as statistical models of real-world processes. They provide the basis for general stochastic simulation methods known as Markov chain Monte Carlo, which are used for simulating sampling from complex probability distributions, and have found application in areas including Bayesian statistics, biology, chemistry, economics, fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). While it is one of several forms of causal notation, causal networks are special cases of Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Probability
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior probability contains everything there is to know about an uncertain proposition (such as a scientific hypothesis, or parameter values), given prior knowledge and a mathematical model describing the observations available at a particular time. After the arrival of new information, the current posterior probability may serve as the prior in another round of Bayesian updating. In the context of Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability distribution usually describes the epistemic uncertainty about statistical parameters conditional on a collection of observed data. From a given posterior distribution, various point and interval estimates can be derived, such as the maximum a posteriori (MAP) or the highest posterior density int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Distribution
Conditional (if then) may refer to: * Causal conditional, if X then Y, where X is a cause of Y *Conditional probability, the probability of an event A given that another event B * Conditional proof, in logic: a proof that asserts a conditional, and proves that the antecedent leads to the consequent *Material conditional, in propositional calculus, or logical calculus in mathematics * Relevance conditional, in relevance logic * Conditional (computer programming), a statement or expression in computer programming languages *A conditional expression in computer programming languages such as ?: *Conditions in a contract A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of thos ... Grammar and linguistics * Conditional mood (or conditional tense), a verb form in many languages * Conditional se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slice Sampling
Slice sampling is a type of Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm for pseudo-random number sampling, i.e. for drawing random samples from a statistical distribution. The method is based on the observation that to sample a random variable one can sample uniformly from the region under the graph of its density function. Motivation Suppose you want to sample some random variable ''X'' with distribution ''f''(''x''). Suppose that the following is the graph of ''f''(''x''). The height of ''f''(''x'') corresponds to the likelihood at that point. If you were to uniformly sample ''X'', each value would have the same likelihood of being sampled, and your distribution would be of the form ''f''(''x'') = ''y'' for some ''y'' value instead of some non-uniform function ''f''(''x''). Instead of the original black line, your new distribution would look more like the blue line. In order to sample ''X'' in a manner which will retain the distribution ''f''(''x''), some sampling technique must be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variations And Extensions
Variation or Variations may refer to: Science and mathematics * Variation (astronomy), any perturbation of the mean motion or orbit of a planet or satellite, particularly of the moon * Genetic variation, the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations ** Human genetic variation, genetic differences in and among populations of humans * Magnetic variation, difference between magnetic north and true north, measured as an angle * ''p''-variation in mathematical analysis, a family of seminorms of functions * Coefficient of variation in probability theory and statistics, a standardized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution or frequency distribution * Total variation in mathematical analysis, a way of quantifying the change in a function over a subset of \mathbb^n or a measure space * Calculus of variations in mathematical analysis, a method of finding maxima and minima of functionals Arts * Variation (ballet) or pas seul, solo dance or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis–Hastings Algorithm
In statistics and statistical physics, the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for obtaining a sequence of random samples from a probability distribution from which direct sampling is difficult. New samples are added to the sequence in two steps: first a new sample is proposed based on the previous sample, then the proposed sample is either added to the sequence or rejected depending on the value of the probability distribution at that point. The resulting sequence can be used to approximate the distribution (e.g. to generate a histogram) or to compute an integral (e.g. an expected value). Metropolis–Hastings and other MCMC algorithms are generally used for sampling from multi-dimensional distributions, especially when the number of dimensions is high. For single-dimensional distributions, there are usually other methods (e.g. adaptive rejection sampling) that can directly return independent samples from the distribution, and these are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence
''IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence'' (sometimes abbreviated as ''IEEE PAMI'' or simply ''PAMI'') is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the IEEE Computer Society. Background The journal covers research in computer vision and image understanding, pattern analysis and recognition, machine intelligence, machine learning, search techniques, document and handwriting analysis, medical image analysis, video and image sequence analysis, content-based retrieval of image and video, and face and gesture recognition. The editor-in-chief is Kyoung Mu Lee (Seoul National University). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 20.8. References Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Geman
Donald Jay Geman (born September 20, 1943) is an American applied mathematician and a leading researcher in the field of machine learning and pattern recognition. He and his brother, Stuart Geman, are very well known for proposing the Gibbs sampler and for the first proof of the convergence of the simulated annealing algorithm, in an article that became a highly cited reference in engineering (over 21K citations according to Google Scholar, as of January 2018). He is a professor at the Johns Hopkins University and simultaneously a visiting professor at École Normale Supérieure de Cachan. Biography Geman was born in Chicago in 1943. He graduated from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in 1965 with a B.A. degree in English Literature and from Northwestern University in 1970 with a Ph.D. in mathematics. His dissertation was entitled as "Horizontal-window conditioning and the zeros of stationary processes." He joined University of Massachusetts - Amherst in 1970, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Geman
Stuart Alan Geman (born March 23, 1949) is an American mathematician, known for influential contributions to computer vision, statistics, probability theory, machine learning, and the neurosciences. ikipediaList of important publications in computer science. He and his brother, Donald Geman, are well known for proposing the Gibbs sampler, and for the first proof of convergence of the simulated annealing algorithm. Biography Geman was born and raised in Chicago. He was educated at the University of Michigan (B.S., Physics, 1971), Dartmouth Medical College (MS, Neurophysiology, 1973), and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Ph.D, Applied Mathematics, 1977). Since 1977, he has been a member of the faculty at Brown University, where he has worked in the Pattern Theory group, and is currently the James Manning Professor of Applied Mathematics. He has received many honors and awards, including selection as a Presidential Young Investigator and as an ISI Highly Cited researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Physics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applications include many problems in a wide variety of fields such as biology, neuroscience, computer science, information theory and sociology. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion. Statistical mechanics arose out of the development of classical thermodynamics, a field for which it was successful in explaining macroscopic physical properties—such as temperature, pressure, and heat capacity—in terms of microscopic parameters that fluctuate about average values and are characterized by probability distributions. While classical thermodynamics is primarily concerned with thermodynamic equilibrium, statistical mechanics has been applied in non-equilibrium stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |