|
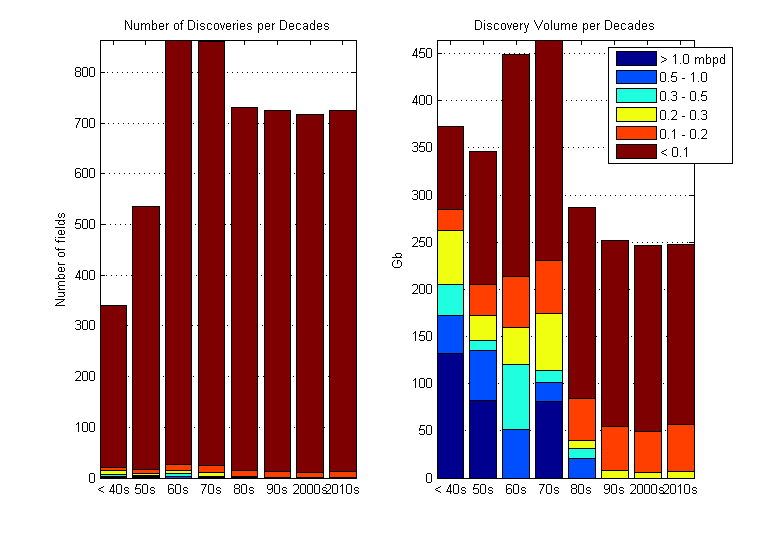
Giant Oil And Gas Fields
The world's 932 giant oil and gas fields are considered those with of ultimately recoverable oil or gas equivalent. Geoscientists believe these giants account for 40 percent of the world's petroleum reserves. They are clustered in 27 regions of the world, with the largest clusters in the Persian Gulf and Western Siberian basin. The past three decades reflect declines in discoveries of giant fields. The years 2000–11 reflect an upturn in discoveries and appears on track to be the third best decade for discovery of giant oil and gas fields in the 150-year history of modern oil and gas exploration. Recent work in tracking giant oil and gas fields follows the earlier efforts of the late exploration geologist Michel T. Halbouty, who tracked trends in giant discoveries from the 1960s to 2004. Tectonic settings Geophysicists and exploration geologists who look for oil and gas fields classify the subsurface characteristics, or tectonic setting, of geological structures that contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Oil
Peak oil is the hypothetical point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production is reached, after which it is argued that production will begin an irreversible decline. It is related to the distinct concept of oil depletion; while global petroleum reserves are finite, the limiting factor is not whether the oil exists but whether it can be extracted economically at a given price. A secular decline in oil extraction could be caused both by depletion of accessible reserves and by reductions in demand that reduce the price relative to the cost of extraction, as might be induced to reduce carbon emissions. Numerous predictions of the timing of peak oil have been made over the past century before being falsified by subsequent growth in the rate of petroleum extraction.David White, "The unmined supply of petroleum in the United States," ''Transactions of the Society of Automotive Engineers'', 1919, v.14, part 1, p.227.Daniel Yergin“There will be oil,”Wall Street Jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Megaprojects
Oil megaprojects are large oil field projects. Summary of megaprojects Megaprojects predicted for individual years Application to oil supply forecasting A series of project tabulations and analyses by Chris Skrebowski, editor of ''Petroleum Review'', have presented a more pessimistic picture of future oil supply. In a 2004 report, based on an analysis of new projects over , he argued that although ample supply might be available in the near-term, after 2007 "the volumes of new production for this period are well below likely requirements." By 2006, although "the outlook for future supply appears somewhat brighter than even six months ago", nonetheless, if "all the factors reducing new capacity come into play, markets will remain tight and prices high. Only if new capacity flows into the system rather more rapidly than of late, will there be any chance of rebuilding spare capacity and softening prices." The smallest fields, even in aggregate, do not contribute a large fractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Oil Fields
This list of oil fields includes some major oil fields of the past and present. The list is incomplete; there are more than 25,000 oil and gas fields of all sizes in the world. However, 94% of known oil is concentrated in fewer than 1500 giant and major fields. Most of the world's largest oilfields are located in the Middle East, but there are also supergiant (>10 billion bbls) oilfields in Brazil, Mexico, Venezuela, Kazakhstan, and Russia. Amounts listed below, in billions of barrels, are the estimated ultimate recoverable petroleum resources (proved reserves plus cumulative production), given historical production and current extraction technology. Oil shale reserves (perhaps ) and coal reserves, both of which can be converted to liquid petroleum, are not included in this chart. Other non-conventional liquid fuel sources are similarly excluded from this list. Oil fields greater than {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Field !! Location !! Discovered !! Started production !! ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Natural Gas Fields
This list of natural gas fields includes major fields of the past and present. N.B. Some of the items listed are basins or projects that comprise many fields (e.g. Sakhalin has three fields: Chayvo, Odoptu, and Arkutun-Dagi). 25 Largest conventional non-associated gas fields ''Table sources: Data was retrieved from, depletion levels from or calculated from open source production data. Notes: *Gasfields are non-associated gas and condensate fields. *Size refers to ultimate recoverable reserves (including past production) expressed in trillion cubic feet. By location ; Algeria * Hassi R'mel () ; Australia * Bass Strait * Jansz () * Greater Gorgon () * Browse Venture ( * North West Shelf Venture () * Yolla gas field * Fairview, Scotia, Spring Gully, Bowen Basin ; Azerbaijan * Shah Deniz gas field () ; Bahrain * Awali () ; Bolivia (~1.5×1012 m³) * Margarita * Sabalo * San Alberto * Itau ; Brazil * Albacora-Leste oil field () * Jupiter gas field (17 x 10¹²) cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Countries By Oil Proven Reserves
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon Exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for deposits of hydrocarbons, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth using petroleum geology. Exploration methods Visible surface features such as oil seeps, natural gas seeps, pockmarks (underwater craters caused by escaping gas) provide basic evidence of hydrocarbon generation (be it shallow or deep in the Earth). However, most exploration depends on highly sophisticated technology to detect and determine the extent of these deposits using exploration geophysics. Areas thought to contain hydrocarbons are initially subjected to a gravity survey, magnetic survey, passive seismic or regional seismic reflection surveys to detect large-scale features of the sub-surface geology. Features of interest (known as ''leads'') are subjected to more detailed seismic surveys which work on the principle of the time it takes for reflected sound waves to travel throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantarell Field
Cantarell Field or Cantarell Complex is an supergiant offshore oil field in Mexico. It was discovered in 1976 after oil stains were noticed by a fisherman, Rudesindo Cantarell Jimenez, in 1972. It was placed on nitrogen injection in 2000, and production peaked at in 2004. In terms of cumulative production to date, it was the largest oil field in Mexico, and one of the largest in the world. However, production has declined since 2004, falling to in 2019. In 2009 it was superseded by Ku-Maloob-Zaap as Mexico's largest oil field. Location Cantarell is located offshore in the Bay of Campeche. This complex comprises four major fields: Akal (by far the largest), Nohoch, Chac and Kutz. The reservoirs are formed from carbonate breccia of Late Cretaceous age, the rubble from the asteroid impact that created the Chicxulub Crater. The recently discovered Sihil field (1-15,000 million barrels) contains light oil in Jurassic strata below the other reservoirs and is generally referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and sea ice, ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
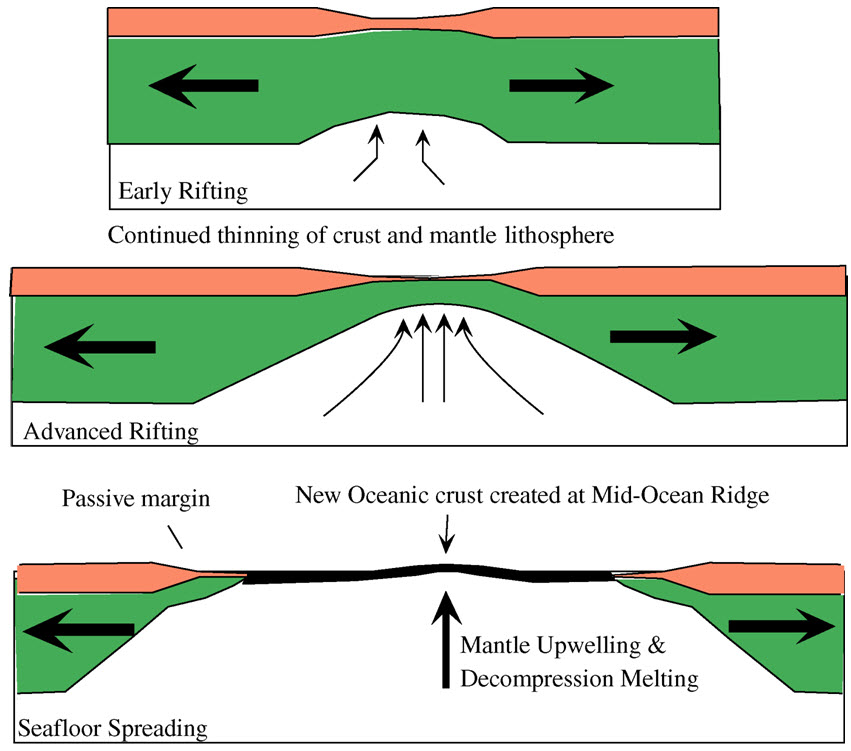
Passive Margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting creates new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally created by rifting is known as a passive margin. Global distribution Passive margins are found at every ocean and continent boundary that is not marked by a strike-slip fault or a subduction zone. Passive margins define the region around the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and western Indian Ocean, and define the entire coasts of Africa, Australia, Greenland, and the Indian Subcontinent. They are also found on the east coast of North America and South America, in Western Europe and most of Antarctica. Northeas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Reservoir
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as ''conventional'' and '' unconventional'' reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods. Oil field An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |