|
Giant-cell Glioblastoma
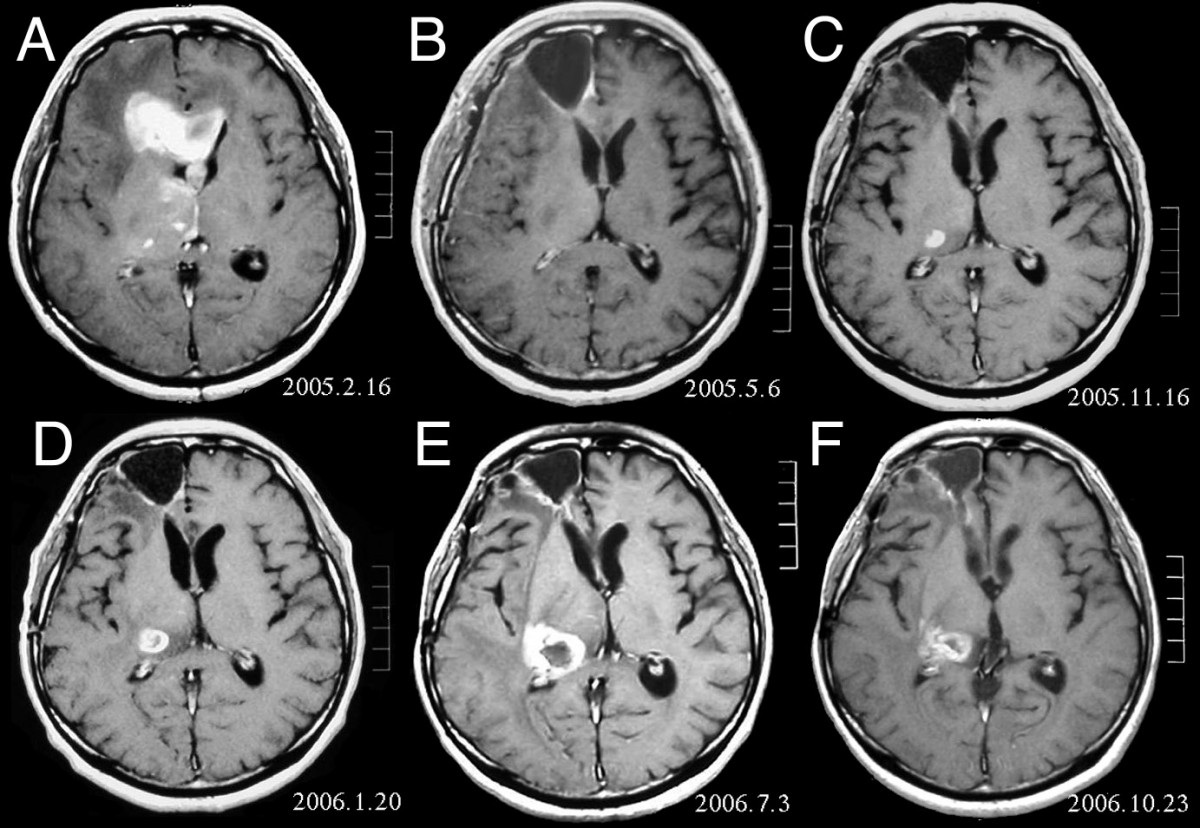
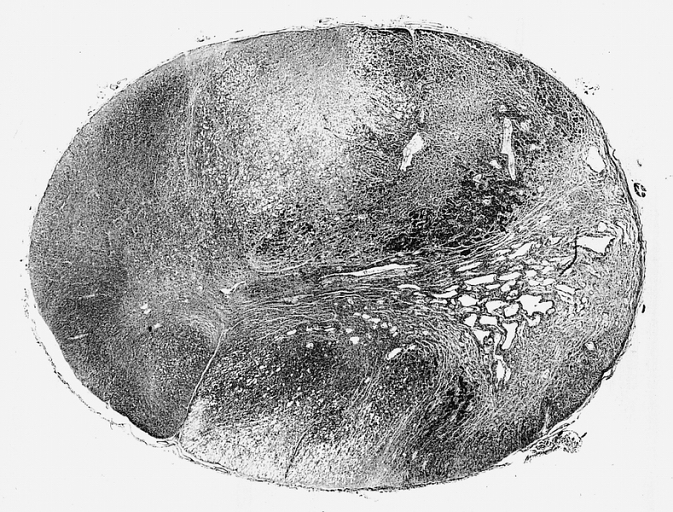
The giant-cell glioblastoma is a histological variant of glioblastoma, presenting a prevalence of bizarre, multinucleated (more than 20 nuclei) giant (up to 400 μm diameter) cells. It occasionally shows an abundant stromal reticulin network and presents a high frequency of ''TP53'' gene mutations. Symptoms and signs are similar to those of the ordinary glioblastoma. Methodology of diagnosis and treatment are the same. Prognosis is similar to the ordinary glioblastoma (about 12 months). Some authors (see later) refer cases with a slightly better outcome. Historical annotation The giant-cell glioblastoma was originally termed "monstrocellular sarcoma", because of its stromal reticulin network, but the astrocytic nature of the tumor was firmly established through the consistent GFAP expression analysis. Epidemiology Incidence The giant-cell glioblastoma is a rare neoplasia: its incidence is less than 1% of all brain tumors. It represents up to 5% of glioblastomas. Age and sex d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Classification Of The Tumors Of The Central Nervous System
The following is a simplified (deprecated) version of the 2021 WHO classification of the tumours of the central nervous system. Currently, as of 2021, clinicians are using the WHO grade 5th edition, which incorporates recent advances in molecular pathology. Listed for each tumour are the WHO official name, the ICD-O code (with Arabic numeral, where /0 indicates "benign" tumour, /3 malignant tumour and /1 borderline tumour), and the WHO Grade (a parameter connected with the "aggressiveness" of the tumour), also in Arabic numerals as per the updated 2021 guidelines.See the article Grading of the tumors of the central nervous system. 1. Gliomas, glioneuronal tumors, and neuronal tumours :1.1 Adult-type diffuse gliomas ::1.1.1 Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant ::1.1.2 Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant, and 1p/19q-codeleted ::1.1.3 Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype :1.2 Pediatric-type diffuse low-grade gliomas ::1.2.1 Diffuse astrocytoma, MYB- or MYBL1-altered ::1.2.2 Angiocentric glioma ::1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Classification Of Diseases For Oncology
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries. It is currently in its third revision (ICD-O-3). ICD-10 includes a list of morphology codes. They stem from ICD-O second edition (ICD-O-2) that was valid at the time of publication. Axes The classification has two axes: topography and morphology. Morphology The morphology axis addresses the microscopic structure (histology) of the tumor. This axis has particular importance because the Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine ("SNOMED") has adopted the ICD-O classification of morphology. SNOMED has been changing continuously, and several different versions of SNOMED are in use. Accordingly, mapping of ICD-O codes to SNOMED requires careful assessment of whether entities are indeed true matches. Topography The topogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grading Of The Tumors Of The Central Nervous System
The concept of grading of the tumors of the central nervous system, agreeing for such the regulation of the "progressiveness" of these neoplasias (from benign and localized tumors to malignant and infiltrating tumors), dates back to 1926 and was introduced by P. Bailey and H. Cushing, in the elaboration of what turned out the first systematic classification of gliomas. In the following, the grading systems present in the current literature are introduced. Then, through a table, the more relevant are compared. ICD-O scale The first edition of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) dates back to 1893. The current review (ICD-10) dates back to 1994, came into use in the U.S. in 2015, and is revised yearly, being very comprehensive. In 1976 the World Health Organization (WHO) published the first edition of the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O), which is now at the third edition (ICD-O-3, 2000). In this last edition, the Arabic numeral after t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Medicine/Neurology Task Force
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They can either start from normal brain cells or develop from an existing low-grade astrocytoma. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is frequently used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They can either start from normal brain cells or develop from an existing low-grade astrocytoma. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is frequently used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |