|
Gers (other)
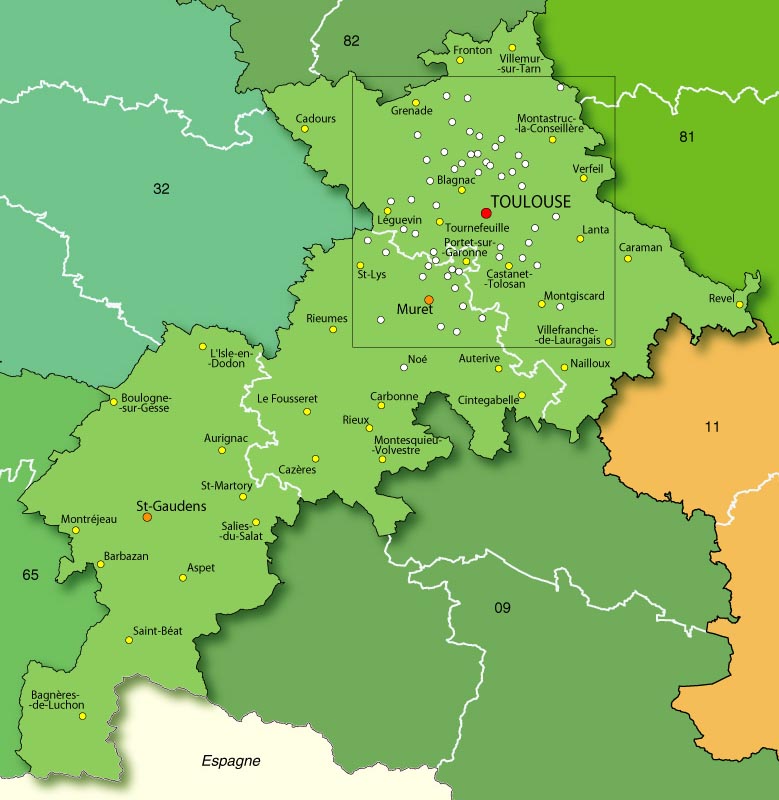
Gers (; oc, Gers or , ) is a department in the region of Occitania, Southwestern France. Gers becoming the largest producer of foie gras in France, known for its rural scene and bastides. Gers is bordered by the departments of Hautes-Pyrénées and Pyrénées-Atlantiques to the south, Haute-Garonne and Tarn-et-Garonne to the east, Lot-et-Garonne to the north and Landes to the west. Named after the Gers River, its inhabitants are called the ''Gersois'' and ''Gersoises'' in French. In 2019, it had a population of 191,377.Populations légales 2019: 32 Gers INSEE History In the , the |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of The Gers Department
The following is a list of the 17 cantons of the Gers department, in France, following the French canton reorganisation which came into effect in March 2015: * Adour-Gersoise * Armagnac-Ténarèze Armagnac-Ténarèze is one of the three ''terroirs'' (plantation areas) in the Armagnac region of France where grapes for the distillation of the Armagnac eau-de-vie can be cultivated. This area lies between Bas-Armagnac and Haut-Armagnac, coveri ... * Astarac-Gimone * Auch-1 * Auch-2 * Auch-3 * Baïse-Armagnac * Fezensac * Fleurance-Lomagne * Gascogne-Auscitaine * Gimone-Arrats * Grand-Bas-Armagnac * L'Isle-Jourdain * Lectoure-Lomagne * Mirande-Astarac * Pardiac-Rivière-Basse * Val de Save References {{Cantons of France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarn-et-Garonne
Tarn-et-Garonne (; oc, Tarn e Garona ) is a department in the Occitania region in Southern France. It is traversed by the rivers Tarn and Garonne, from which it takes its name. The area was originally part of the former provinces of Quercy and Languedoc. The department was created in 1808 under Napoleon, with territory taken from the neighbouring Lot, Haute-Garonne, Lot-et-Garonne, Gers and Aveyron departments. The department is mostly rural with fertile agricultural land in the broad river valley, but there are hilly areas to the south, east and north. The departmental prefecture is Montauban; the sole subprefecture is Castelsarrasin. In 2019, it had a population of 260,669.Populations légales 2019: 82 Tarn-et-Garonne INSEE History History of the regi ...
|
Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; oc, Nauta Garona, ; en, Upper Garonne) is a department in the Occitanie region of Southwestern France. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's fourth-largest. In 2019, it had a population of 1,400,039.Populations légales 2019: 31 Haute-Garonne INSEE History Haute-Garonne is one of the original 83 departments created during the on 4 March 1790. It was created from part of the former provinces of an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrénées-Atlantiques
Pyrénées-Atlantiques (; Gascon Occitan: ''Pirenèus Atlantics''; eu, Pirinio Atlantiarrak or ) is a department in the southwest corner of France and of the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Named after the Pyrenees mountain range and the Atlantic Ocean, it covers the French Basque Country and the Béarn. Its prefecture is Pau. In 2019, it had a population of 682,621.Populations légales 2019: 64 Pyrénées-Atlantiques INSEE History Originally named Basses-Pyrénées, it is one of the first 83 created during the |
Hautes-Pyrénées
Hautes-Pyrénées (; Gascon/Occitan: ''Nauts Pirenèus / Hauts Pirenèus'' awts piɾeˈnɛʊs es, Altos Pirineos; ca, Alts Pirineus alts piɾiˈneʊs English: Upper Pyrenees) is a department in the region of Occitania, southwestern France. In 2019, its population was 229,567;Populations légales 2019: 65 Hautes-Pyrénées INSEE its is . It is named after the mountain range. History [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastide
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the first bastides.Bastide in the French Wikipedia, retrieved March 8, 2007. Some of the first bastides were built under Raymond VII of Toulouse to replace villages destroyed in the Albigensian Crusade. He encouraged the construction of others to colonize the wilderness, especially of southwest France. Almost 700 bastides were built between 1222 (Cordes-sur-Ciel, Tarn) and 1372 (La Bastide d'Anjou, Tarn). History were developed in number under the terms of the Treaty of Paris (1229), which permitted Raymond VII of Toulouse to build new towns in his shattered domains but not to fortify them. When the Capetian Alphonse of Poitiers inherited, under a marriage stipulated by the treaty, this " founder of unparalleled energy" consolidated his regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foie Gras
Foie gras (, ; ) is a specialty food product made of the liver of a duck or goose. According to French law, foie gras is defined as the liver of a duck or goose fattened by gavage (force feeding). Foie gras is a popular and well-known delicacy in French cuisine. Its flavour is rich, buttery, and delicate, unlike an ordinary duck or goose liver. Foie gras is sold whole or is prepared into mousse, parfait, or pâté, and may also be served as an accompaniment to another food item, such as steak. French law states, "Foie gras belongs to the protected cultural and gastronomical heritage of France." The technique of gavage dates as far back as 2500 BC, when the ancient Egyptians began keeping birds for food and deliberately fattened the birds through force-feeding. Today, France is by far the largest producer and consumer of foie gras, though there are producers and markets worldwide, particularly in other European nations, the United States, and China. Gavage-based foie gras pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of France
France is divided into eighteen administrative regions (french: régions, singular ), of which thirteen are located in metropolitan France (in Europe), while the other five are overseas regions (not to be confused with the overseas collectivities, which have a semi-autonomous status). All of the thirteen metropolitan administrative regions (including Corsica ) are further subdivided into two to thirteen administrative departments, with the prefect of each region's administrative centre's department also acting as the regional prefect. The overseas regions administratively consist of only one department each and hence also have the status of overseas departments. Most administrative regions also have the status of regional territorial collectivities, which comes with a local government, with departmental and communal collectivities below the region level. The exceptions are Corsica, French Guiana, Mayotte and Martinique, where region and department functions are managed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as bays, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Summer Time
Central European Summer Time (CEST), sometimes referred to as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+02:00, which makes it the same as Eastern European Time, Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia. Names Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST), Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT), and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet). Period of observation Since 1996, European Summer Time has been observed between 01:00 UTC (02:00 CET and 03:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March, and 01:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union. There were proposals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |